7. Friction - Sakshieducation.com
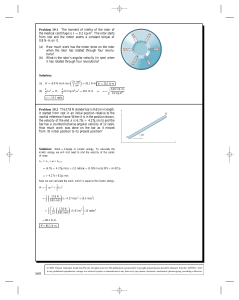
... c) If a < amax frictional force between the two blocks is f = MB a d) If a < amax' then applied force on the upper block is F = (mB + mu) a e) The maximum force for which both blocks move together is Fmax = μs ...
... c) If a < amax frictional force between the two blocks is f = MB a d) If a < amax' then applied force on the upper block is F = (mB + mu) a e) The maximum force for which both blocks move together is Fmax = μs ...
Momentum packet
... remainder of this lesson. To understand the basis of momentum conservation, let's begin with a short logical proof. Consider a collision between two objects - object 1 and object 2. For such a collision, the forces acting between the two objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction (Newt ...
... remainder of this lesson. To understand the basis of momentum conservation, let's begin with a short logical proof. Consider a collision between two objects - object 1 and object 2. For such a collision, the forces acting between the two objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction (Newt ...
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... Although F and a are large for the pin, they vary in time—a complicated situation! One of the main objectives of this chapter is to enable you to understand and analyze such events in a simple way. First, we introduce the concept of momentum, which is useful for describing objects in motion. Imagine ...
... Although F and a are large for the pin, they vary in time—a complicated situation! One of the main objectives of this chapter is to enable you to understand and analyze such events in a simple way. First, we introduce the concept of momentum, which is useful for describing objects in motion. Imagine ...
Vectors in Two Dimensions (cont.)
... Vectors in Two Dimensions • So far in this course, we have only discussed vectors in one dimension but how can you set up a coordinate system for a net force when you are dealing with more than one dimension? And what happens when the forces are not at right angles to each other? • Recall in previou ...
... Vectors in Two Dimensions • So far in this course, we have only discussed vectors in one dimension but how can you set up a coordinate system for a net force when you are dealing with more than one dimension? And what happens when the forces are not at right angles to each other? • Recall in previou ...
Molecular dynamics
... stress its central ideas. The equations of motion are the central equations in MD. The following equations apply to each molecule i: ...
... stress its central ideas. The equations of motion are the central equations in MD. The following equations apply to each molecule i: ...
Form A
... 3. An object in uniform circular motion (constant speed v around a circle with constant R) is acted upon by a centripetal force. Which statement below is FALSE? The centripetal force: A) Is directed inward toward the center of the circle. B) Changes direction continuously. C) Depends on the mass of ...
... 3. An object in uniform circular motion (constant speed v around a circle with constant R) is acted upon by a centripetal force. Which statement below is FALSE? The centripetal force: A) Is directed inward toward the center of the circle. B) Changes direction continuously. C) Depends on the mass of ...
CHAPTER 4 FORCES AND NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... Newton's second law, we can find the net force ∑ F that acts on the boat. Since two of the three forces are known, we can solve for the unknown force FW once the net force ∑ F is known. SOLUTION Let the direction due east be the positive x direction and the direction due north be the positive y dire ...
... Newton's second law, we can find the net force ∑ F that acts on the boat. Since two of the three forces are known, we can solve for the unknown force FW once the net force ∑ F is known. SOLUTION Let the direction due east be the positive x direction and the direction due north be the positive y dire ...
Slides for Motion and Forces
... called a reference point. Reference points are places or objects used to determine the motion of an object. It is extremely important to choose reference points carefully. ...
... called a reference point. Reference points are places or objects used to determine the motion of an object. It is extremely important to choose reference points carefully. ...
The Pendulum Introduction
... remain periodic but the actual period may change. In the pendulum period doubling of the base period occurs many times before aperiodic, chaotic motion is observed Evidently the motion of the damped, driven nonlinear pendulum is much more complex than even the damped pendulum. A convenient way of r ...
... remain periodic but the actual period may change. In the pendulum period doubling of the base period occurs many times before aperiodic, chaotic motion is observed Evidently the motion of the damped, driven nonlinear pendulum is much more complex than even the damped pendulum. A convenient way of r ...
- Lake Fenton Community School District
... (in any instant) you can find your speed by looking at a speedometer. A police officer can find your speed at any instant if he uses his radar gun. The speed on the speedometer or the speed that the police officer finds using a radar gun is called instantaneous speed because it is the speed at an in ...
... (in any instant) you can find your speed by looking at a speedometer. A police officer can find your speed at any instant if he uses his radar gun. The speed on the speedometer or the speed that the police officer finds using a radar gun is called instantaneous speed because it is the speed at an in ...