Newton*s Laws - MTHS - Kelly
... ->w is weight, m is mass in (kg) g the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 (m/s2) at sea level on earth. ...
... ->w is weight, m is mass in (kg) g the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 (m/s2) at sea level on earth. ...
Unit 4 Review - Clayton School District
... 1. Newton’s Third Law says that if object 1 pushes on object 2 and object 2 accelerates, then the push on object 1 by object 2 is (greather than, less than, equal to) the push on object 2 by object 1. 2. If object 1 pushes on object 2 and object 2 moves at constant speed, then the push on object 1 b ...
... 1. Newton’s Third Law says that if object 1 pushes on object 2 and object 2 accelerates, then the push on object 1 by object 2 is (greather than, less than, equal to) the push on object 2 by object 1. 2. If object 1 pushes on object 2 and object 2 moves at constant speed, then the push on object 1 b ...
MOTION and FORCES
... What is the force of a 250 kg linebacker that hits a dummy at an acceleration of 5 m/s² ? To solve: F=? F=ma = (250kg)(5m/s²) M=250kg = 1250N A=5m/s² ...
... What is the force of a 250 kg linebacker that hits a dummy at an acceleration of 5 m/s² ? To solve: F=? F=ma = (250kg)(5m/s²) M=250kg = 1250N A=5m/s² ...
Newton`S Laws Guided Notes
... An object at rest will ________ ____ _______ and an object in motion will ________ ____ ___________ at a constant _____________, unless acted upon by an _____________________ force. ______________ is the tendency of an object to ____________ ____________ in its velocity: whether in motion or motionl ...
... An object at rest will ________ ____ _______ and an object in motion will ________ ____ ___________ at a constant _____________, unless acted upon by an _____________________ force. ______________ is the tendency of an object to ____________ ____________ in its velocity: whether in motion or motionl ...
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
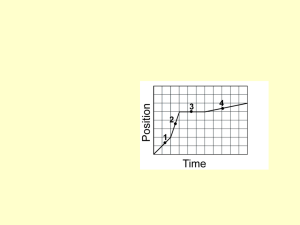
... The only thing you can count on in life, the world, and the universe is that things will change – often, things won’t change just one way, but will oscillate back and forth. Objects in motion that return to the same position after a certain period of time are in harmonic motion or periodic motion. A ...
... The only thing you can count on in life, the world, and the universe is that things will change – often, things won’t change just one way, but will oscillate back and forth. Objects in motion that return to the same position after a certain period of time are in harmonic motion or periodic motion. A ...
Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
... contiue in the same direction at the same speed unless the object is acted upon by a ______________. ...
... contiue in the same direction at the same speed unless the object is acted upon by a ______________. ...
Lecture-21-11
... The same force applied over a smaller area results in greater pressure – think of poking a balloon with your finger and then with a needle. Pressure is a useful concept for discussing fluids, because fluids distribute their force over an area ...
... The same force applied over a smaller area results in greater pressure – think of poking a balloon with your finger and then with a needle. Pressure is a useful concept for discussing fluids, because fluids distribute their force over an area ...
Acceleration and Momentum
... WHAT IS NEWTON’S THIRD LAW OF MOTION? • Newton’s Third of Motion- For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... WHAT IS NEWTON’S THIRD LAW OF MOTION? • Newton’s Third of Motion- For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
ICNS 132 : Rotational Motion and Equilibrium
... Static Equilibrium •Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial reference frame. •Will deal now with the special case in which both of these velocities are equal to zero – This is called static equilibriu ...
... Static Equilibrium •Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial reference frame. •Will deal now with the special case in which both of these velocities are equal to zero – This is called static equilibriu ...
Blank Jeopardy - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... It’s how much speed a free falling object on earth gains each second it falls. ...
... It’s how much speed a free falling object on earth gains each second it falls. ...
Motion and Forces Jeopardy
... 31. Math Daily Triple: Include units, what is the acceleration of a train that goes from rest to 30 m/s in 5 s? 6 m/s2 32. Which Newton’s Law that states for every action there is an opposite and equal reaction. third law 33. Describe Daily Double: Describe the difference between weight and mass. ma ...
... 31. Math Daily Triple: Include units, what is the acceleration of a train that goes from rest to 30 m/s in 5 s? 6 m/s2 32. Which Newton’s Law that states for every action there is an opposite and equal reaction. third law 33. Describe Daily Double: Describe the difference between weight and mass. ma ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Friction acts on materials that are in contact with each other It depends on the types of material in contact and how much of the surfaces are pressed together Friction also occurs in liquids and gases (fluid friction) Air Resistance – friction acting on something moving through air ...
... Friction acts on materials that are in contact with each other It depends on the types of material in contact and how much of the surfaces are pressed together Friction also occurs in liquids and gases (fluid friction) Air Resistance – friction acting on something moving through air ...
Unit 2 Worksheet – Motion and Forces Do Not Write on this Paper
... 28. If you are running and you stub your toe, you fall forward. Explain. 29. Why is it necessary to wear a seat belt to hold you in place if you are riding in a car that stops suddenly? 30. The ___ velocity is the highest velocity that will be reached by a falling object 31. The upward force on an o ...
... 28. If you are running and you stub your toe, you fall forward. Explain. 29. Why is it necessary to wear a seat belt to hold you in place if you are riding in a car that stops suddenly? 30. The ___ velocity is the highest velocity that will be reached by a falling object 31. The upward force on an o ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.