* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton*s Laws - MTHS - Kelly
Survey
Document related concepts
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
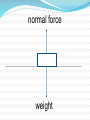
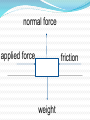
Enduring Understanding: Studying dynamics (causes of motion) has had a profound effect on the way humans view their world. Essential Question: What may be accomplished by understanding dynamics? Essential Question: How may we symbolically represent dynamics information? Essential Question: How are dynamics a predictor of kinematics? 2 Issac Newton’s What do you think? Newton’s Laws -Built on Galileo’s ideas -If I have seen farther it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants Today, we agree with Newton’s Laws of Motion. These laws of motion differ from the views of Aristotle and the Ancient Greeks. Aristotle on Motion -Natural Motion : Vertical Motion. Falling objects or smoke rising. No force recognized. Violent Motion Was motion with a visible force. A push or a pull. It was also believed that an objects natural position was at rest. Newton’s First Law Law of Inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. Inertia: resistance to change A New View of Motion All motion is now seen as caused by Forces. Friction is identified as a cause of slowing and speeding. Falling objects are linked with gravity. Mass – Amount of Inertia More mass means more resistance to change. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Mass is not weight. 1 kg of mass weighs 9.8 Newtons(N) Weight is a downward force due to gravity. ->The unit for weight is the Newton. The Newton is a derived unit. ->To calculate weight, mass and gravity are involved. -> w = m x g ->w is weight, m is mass in (kg) g the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 (m/s2) at sea level on earth. Calculations Involving Weight Unless told otherwise, assume the problems take place at sea level on earth. What is the weight of a 1 kg object? w = mg w = 1(kg) x 9.8(m/s2 ) = 9.8(N) The Newton (N) is derived from the units (kg), (m)eter and (s)econd. What is the weight of a 2 kg object? 19.6 N What is the weight of a 15 kg object? 147 N What is the mass of a 100 N object? 10.2 kg What is the mass of a 250 N object? 25.5 kg Weight, the force due to gravity always acts on an object. The Normal Force is also known as the support force. the weight and the normal force are equal in size and opposite in direction. Net Force At least one force is acting on every object at all times. Net Force is the total of all the forces. All Forces are measured in Newtons. In the tug of war, if the team on the left pulls with a force of 1200 N and the team on the right pulls with 1000 N, what is the net force? Answer 200 N to the left Forces Can Be Added As Vectors. A free body diagram is used to identify the forces acting on an object. More Free Body Diagrams Equilibrium At Equilibrium all forces are balanced. The net force is zero. A number of large forces act on a bridge. What are they? What happens if the forces acting on a bridge are not in equilibrium? Can an object be at equilibrium and still be moving? Yes According to The Law of Inertia, an object in motion will stay in motion at the same speed if all of the forces are in balance. If the forces become out of balance, the object will slow down, speed up or change direction. Free Body Diagram Practice A box is at rest on a table. Draw a free body diagram of the forces acting on it. _____________________________________________________________ normal force _____________________________________________________________ weight The normal force and the weight always act on an object on a surface. A person pushes a box to the right. Draw a free body diagram of the forces acting on it. _________________________________________________________ normal force applied force friction ____________________________________________________________ weight


































![[force and motion]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006065207_1-8bff05158caa0c6fdea67b84566f5781-150x150.png)





