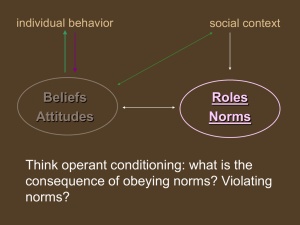
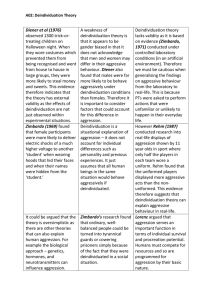
This test includes chapters on Development, States of
... a. the social responsibility norm. b. the just-world phenomenon. c. the two-factor theory. d. deindividuation. e. ingroup bias. 80. When visiting the Bergin-Belsen concentration camp shortly after World War II, one German civilian was said to have remarked, "What terrible criminals these prisoners m ...
... a. the social responsibility norm. b. the just-world phenomenon. c. the two-factor theory. d. deindividuation. e. ingroup bias. 80. When visiting the Bergin-Belsen concentration camp shortly after World War II, one German civilian was said to have remarked, "What terrible criminals these prisoners m ...
Social Psychology
... b. deindividuation on the bystander effect. c. team membership on social loafing. d. role-playing on attitude change. 4. In making wedding preparations, Jason conforms to the expectations of his future bride’s family simply to win their favor. His behavior illustrates the importance of: a. social fa ...
... b. deindividuation on the bystander effect. c. team membership on social loafing. d. role-playing on attitude change. 4. In making wedding preparations, Jason conforms to the expectations of his future bride’s family simply to win their favor. His behavior illustrates the importance of: a. social fa ...
AP Psych 14 - cloudfront.net
... a. the “learner” complained of a slight heart condition just before the experiment began. b. the “learner” screamed as the shocks became more punishing. c. the “teacher” was instructed to administer the learning test and someone else was asked to shock the “learner.” d. the experiment was not associ ...
... a. the “learner” complained of a slight heart condition just before the experiment began. b. the “learner” screamed as the shocks became more punishing. c. the “teacher” was instructed to administer the learning test and someone else was asked to shock the “learner.” d. the experiment was not associ ...
Chapter 16 Test Review 1. Which
... B) complied with the experiment until the “learner” first indicated pain. C) complied with the experiment until the “learner” began screaming in agony. D) complied with all the demands of the experiment. 16. Based on findings from Milgram's obedience studies, participants would be less likely to fol ...
... B) complied with the experiment until the “learner” first indicated pain. C) complied with the experiment until the “learner” began screaming in agony. D) complied with all the demands of the experiment. 16. Based on findings from Milgram's obedience studies, participants would be less likely to fol ...
d. the fundamental attribution error.
... d. they were being paid a lot of money to do the experiment. ...
... d. they were being paid a lot of money to do the experiment. ...
Social Psychology – Practice Test 1. Bart complied with his friends
... D) underestimating situational constraints on another's behavior. E) losing self-restraint in group situations that foster anonymity. ...
... D) underestimating situational constraints on another's behavior. E) losing self-restraint in group situations that foster anonymity. ...
2017 HRQ 14 1
... b. the mere exposure effect. c. the bystander effect. d. social facilitation. e. a situational attribution. ____ 11. Social loafing is MOST likely to occur among a. audience members who are asked to applaud after a speaker is introduced. b. factory workers paid on the basis of individual level of pr ...
... b. the mere exposure effect. c. the bystander effect. d. social facilitation. e. a situational attribution. ____ 11. Social loafing is MOST likely to occur among a. audience members who are asked to applaud after a speaker is introduced. b. factory workers paid on the basis of individual level of pr ...
File
... more consistent e. When our beliefs and behaviors are too similar it causes an unpleasant psychological state of tension. 5. A person who agrees to a small request initially is more likely to comply with a larger demand later. This describes which phenomenon? a. Door-in-face effect b. Foot-in-door e ...
... more consistent e. When our beliefs and behaviors are too similar it causes an unpleasant psychological state of tension. 5. A person who agrees to a small request initially is more likely to comply with a larger demand later. This describes which phenomenon? a. Door-in-face effect b. Foot-in-door e ...
If you were totally invisible for 24 hours and were completely
... crowds/groups act aggressively E.g. Gergen et al (1973) Found that lower levels of individuality didn’t result in aggressive behaviour. ...
... crowds/groups act aggressively E.g. Gergen et al (1973) Found that lower levels of individuality didn’t result in aggressive behaviour. ...
PSY100-socialsum09
... • Deindividuation – loss of self awareness and evaluation apprehension when the situation allows one to feel anonymous • When combined with high states of arousal and a diffusion of responsibility it can create a mob mentality, disinhibiting violent and unacceptable behavior ...
... • Deindividuation – loss of self awareness and evaluation apprehension when the situation allows one to feel anonymous • When combined with high states of arousal and a diffusion of responsibility it can create a mob mentality, disinhibiting violent and unacceptable behavior ...
Deindividuation A02 cut and stick
... Diener et al (1976) observed 1300 trick-ortreating children on Halloween night. When they wore costumes which prevented them from being recognised and went from house to house in large groups, they were more likely to steal money and sweets. This evidence therefore indicates that the theory has exte ...
... Diener et al (1976) observed 1300 trick-ortreating children on Halloween night. When they wore costumes which prevented them from being recognised and went from house to house in large groups, they were more likely to steal money and sweets. This evidence therefore indicates that the theory has exte ...
PSY100-social10
... • Deindividuation – loss of self awareness and evaluation apprehension when the situation allows one to feel anonymous • When combined with high states of arousal and a diffusion of responsibility it can create a mob mentality, disinhibiting violent and unacceptable behavior ...
... • Deindividuation – loss of self awareness and evaluation apprehension when the situation allows one to feel anonymous • When combined with high states of arousal and a diffusion of responsibility it can create a mob mentality, disinhibiting violent and unacceptable behavior ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Deindividuation – loss of self awareness and evaluation apprehension when the situation allows one to feel anonymous • When combined with high states of arousal and a diffusion of responsibility it can create a mob mentality, disinhibiting violent and unacceptable behavior ...
... • Deindividuation – loss of self awareness and evaluation apprehension when the situation allows one to feel anonymous • When combined with high states of arousal and a diffusion of responsibility it can create a mob mentality, disinhibiting violent and unacceptable behavior ...