Industrialization PP - Polk School District
... French Control of Indochina Colonial Impact: • Imposed French culture • All schools, courts, & businesses followed French models • ↓ of local industries • Less food for peasants ...
... French Control of Indochina Colonial Impact: • Imposed French culture • All schools, courts, & businesses followed French models • ↓ of local industries • Less food for peasants ...
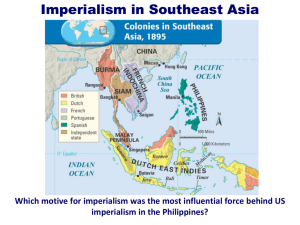
Imperialism in Southeast Asia
... carve up the lands of Southeast Asia. These lands form part of the Pacific Rim, the countries that border the Pacific Ocean. Western nations desired the Pacific Rim lands for their strategic location along the sea route to China. Westerners also recognized the value of the Pacific colonies as source ...
... carve up the lands of Southeast Asia. These lands form part of the Pacific Rim, the countries that border the Pacific Ocean. Western nations desired the Pacific Rim lands for their strategic location along the sea route to China. Westerners also recognized the value of the Pacific colonies as source ...
Imperialism in Asia Cause Event Effect • China was slow to
... Triumphal Arch erected near Seoul, Korea after their victory at Asan. In 1894, Japan went to war with China over control of Korea. Despite being seen as the underdog, Japan won the Sino-Japanese War. ...
... Triumphal Arch erected near Seoul, Korea after their victory at Asan. In 1894, Japan went to war with China over control of Korea. Despite being seen as the underdog, Japan won the Sino-Japanese War. ...
Imperialism -Yea Uen
... - Developed policy called paternalism (Direct control) Europeans governed people in a paternal way by providing for their needs but not giving them rights Europeans brought their own bureaucrats and did not train local people in European methods of governing - The French also supported a policy of ...
... - Developed policy called paternalism (Direct control) Europeans governed people in a paternal way by providing for their needs but not giving them rights Europeans brought their own bureaucrats and did not train local people in European methods of governing - The French also supported a policy of ...
French Indochina
French Indo-China (now commonly known as French Indochina) (French: Indochine française; Khmer: សហភាពឥណ្ឌូចិន; Vietnamese: Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, pronounced [ɗoŋm zɰəŋ tʰuə̀k fǎp], frequently abbreviated to Đông Pháp; Lao: ຝຣັ່ງແຫຼັມອິນດູຈີນ), officially known as the Indo-Chinese Union (French: Union indochinoise) after 1887 and the Indo-Chinese Federation (French: Fédération indochinoise) after 1947, was a grouping of French colonial territories in Southeast Asia.A grouping of the three Vietnamese regions of Tonkin (north), Annam (centre), and Cochinchina (south) with Cambodia was formed in 1887. Laos was added in 1893 and Kwangchow Wan (Kouang-Tchéou-Wan) in 1898. The capital was moved from Saigon (in Cochinchina) to Hanoi (Tonkin) in 1902 and again to Da Lat (Annam) in 1939. In 1945 it was moved back to Hanoi.After the fall of France during World War II, the colony was administered by the Vichy government and was under Japanese occupation until March 1945, when the Japanese overthrew the colonial regime. Beginning in May 1941, the Viet Minh, a communist army led by Ho Chi Minh, began a revolt against the Japanese. In August 1945 they declared Vietnamese independence and extended the war, known as the First Indochina War, against France.In Saigon, the anti-Communist State of Vietnam, led by former Emperor Bảo Đại, was granted independence in 1949. On 9 November 1953, the Kingdom of Laos and the Kingdom of Cambodia became independent. Following the Geneva Accord of 1954, the French evacuated Vietnam and French Indochina came to an end.