Chapter 9 Quantum Mechanics
... classical theory of physics — Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory of light, but the other three cases conflict with any reasonable interpretation of the classical theory of physics. 9.2.2 Problem investigation and Einstein’s solution 1. three trouble cases in the photoelectric effect (a) The existence ...
... classical theory of physics — Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory of light, but the other three cases conflict with any reasonable interpretation of the classical theory of physics. 9.2.2 Problem investigation and Einstein’s solution 1. three trouble cases in the photoelectric effect (a) The existence ...
Homework Assignment for CHEM 5591 Professor JM Weber
... state |nℓ>, based on the shape of the potential energy function of an H-atom in an external electric field with strength E0. Compare with the result you obtained in (b) and comment on the validity of Bohr’s correspondence principle at n = 100. ...
... state |nℓ>, based on the shape of the potential energy function of an H-atom in an external electric field with strength E0. Compare with the result you obtained in (b) and comment on the validity of Bohr’s correspondence principle at n = 100. ...
15.06.18_CAP-Edmonton-CWL
... (iii) fully relativistic – obeying the weak principle of equivalence, no violation of causal structure, well-defined metric. (iv) gravity/spacetime is treated as a quantum field as well as matter ...
... (iii) fully relativistic – obeying the weak principle of equivalence, no violation of causal structure, well-defined metric. (iv) gravity/spacetime is treated as a quantum field as well as matter ...
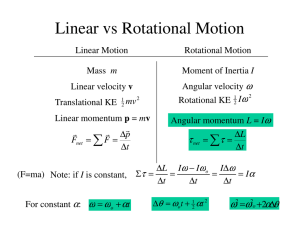
The angular momentum of particle subject to no torque is conserved.
... – Calculate the angular momentum before and after the jump. ...
... – Calculate the angular momentum before and after the jump. ...
String Theory
... String Theory is believed to bridge the gap between General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics This is because Relativistic Quantum Field Theory only works when gravity is ignored (very weak) General Relativity only works when we can assume the universe can be described by classical physics (no quantu ...
... String Theory is believed to bridge the gap between General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics This is because Relativistic Quantum Field Theory only works when gravity is ignored (very weak) General Relativity only works when we can assume the universe can be described by classical physics (no quantu ...
Chapter 7
... The most stable arrangement of electrons in subshells is the one with the greatest number of parallel spins (Hund’s rule). ...
... The most stable arrangement of electrons in subshells is the one with the greatest number of parallel spins (Hund’s rule). ...
May 1999
... A solid ball of radius r and mass m is rolling without slipping inside a long hollow vertical cylinder of radius R > r under the influence of gravity. Initially the velocity v(t = 0) is in the horizontal direction and there is no spin perpendicular to the wall about the point of contact. (Though lat ...
... A solid ball of radius r and mass m is rolling without slipping inside a long hollow vertical cylinder of radius R > r under the influence of gravity. Initially the velocity v(t = 0) is in the horizontal direction and there is no spin perpendicular to the wall about the point of contact. (Though lat ...
May 2000
... A massive particle X with spin 2 decays into a spin 0 particle with no orbital angular momentum and with the simultaneous emission of two alpha particles, each of which is known to be in a p-wave. Given an ensemble of unpolarized X particles at rest, what is the probability distribution in the angle ...
... A massive particle X with spin 2 decays into a spin 0 particle with no orbital angular momentum and with the simultaneous emission of two alpha particles, each of which is known to be in a p-wave. Given an ensemble of unpolarized X particles at rest, what is the probability distribution in the angle ...
Phys202_Final_Exam_Spr2006.doc
... 53. If an object of length 5 m is moving at a velocity of 0.9999c then what is its length as seen by that observer who sees it moving? a. 0.015 b. 0.16 c. ~ 0.07 d. 0.08 ...
... 53. If an object of length 5 m is moving at a velocity of 0.9999c then what is its length as seen by that observer who sees it moving? a. 0.015 b. 0.16 c. ~ 0.07 d. 0.08 ...
slides - Frontiers of Fundamental Physics (FFP14)
... the problem of the individuality of the photon, which is entirely quantic, with the corpuscular properties of the electron, which can be related to an entirely classical description. ...
... the problem of the individuality of the photon, which is entirely quantic, with the corpuscular properties of the electron, which can be related to an entirely classical description. ...
divinity - Particle Theory Group
... interact via all of the forces — except gravity. For gravity, we still use Einstein’s General Relativity, a classical theory that has worked pretty well because gravity effects are so weak. ...
... interact via all of the forces — except gravity. For gravity, we still use Einstein’s General Relativity, a classical theory that has worked pretty well because gravity effects are so weak. ...