Lecture-X
... from its equilibrium position. Expand U(r) about r0, the position of the potential minimum. ...
... from its equilibrium position. Expand U(r) about r0, the position of the potential minimum. ...
Document
... learn about in the next two weeks, experiments that look at the cosmic microwave background (CMB) were obtaining data that was consistent with there being just enough energy density in the universe so that the universe is “flat” (too much and the universe would be “closed,” too little and it would b ...
... learn about in the next two weeks, experiments that look at the cosmic microwave background (CMB) were obtaining data that was consistent with there being just enough energy density in the universe so that the universe is “flat” (too much and the universe would be “closed,” too little and it would b ...
Exam 4-2005 - asg.sc.edu
... Ignore the sign of the answer. Answer ‘e’ is to be used as ‘none of the above’, ‘cannot be answered’, etc. You may not have a cell phone or any electronic device and you are not allowed any form of communication with other persons or information systems in any form. You are allowed ONLY a calculator ...
... Ignore the sign of the answer. Answer ‘e’ is to be used as ‘none of the above’, ‘cannot be answered’, etc. You may not have a cell phone or any electronic device and you are not allowed any form of communication with other persons or information systems in any form. You are allowed ONLY a calculator ...
Atomic Physics
... By classical theories, all accelerating charged particles will emit radiation ( energy ). If Rutherford’s model is correct, the accelerating electrons will lose energy continuously, then they will be adhered to the nucleus and all atoms will finally be collapsed! ...
... By classical theories, all accelerating charged particles will emit radiation ( energy ). If Rutherford’s model is correct, the accelerating electrons will lose energy continuously, then they will be adhered to the nucleus and all atoms will finally be collapsed! ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
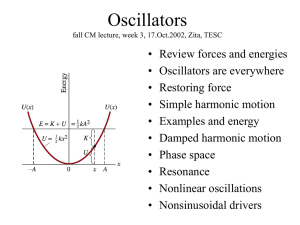
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various m,k. Then: S F = ma - k x = m x” Guess a solution: x = A cost wt? x = B sin wt? x = C e wt? Second-order diffeq needs two linearly independent solutions: x = x1 + x2. Unknown coefficients to be determined by BC. Sub in your solution and solve ...
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various m,k. Then: S F = ma - k x = m x” Guess a solution: x = A cost wt? x = B sin wt? x = C e wt? Second-order diffeq needs two linearly independent solutions: x = x1 + x2. Unknown coefficients to be determined by BC. Sub in your solution and solve ...
Were Bohr and Einstein both right
... in terms of a energy function / Hamiltonian as in quantum theory, and in the urs arising from the fact that (E2 – p2 – m2) = 0 where E is the energy, p the momentum, m the mass; a relativistic equation which leads to Einstein's famous E = mc2 . • for any measurement, there must exist a measurement s ...
... in terms of a energy function / Hamiltonian as in quantum theory, and in the urs arising from the fact that (E2 – p2 – m2) = 0 where E is the energy, p the momentum, m the mass; a relativistic equation which leads to Einstein's famous E = mc2 . • for any measurement, there must exist a measurement s ...
Formula Sheet - Blank File
... Pendulum motion/rollercoaster motion: (If not at top or bottom of circle, you might have to find components of Fg (if FT is toward center) or find components of FT (If FT is NOT toward center)) ...
... Pendulum motion/rollercoaster motion: (If not at top or bottom of circle, you might have to find components of Fg (if FT is toward center) or find components of FT (If FT is NOT toward center)) ...
Standard Model of Physics
... • Baryons are made up of three quarks e.g. Protons (uud) • Mesons are made up of one quark and one anti-quark e.g. Pion + (ud*) • Quarks are never observed alone (in isolation), but exist always in combinations. The rule which is followed here is documented by ‘color confinement’. ...
... • Baryons are made up of three quarks e.g. Protons (uud) • Mesons are made up of one quark and one anti-quark e.g. Pion + (ud*) • Quarks are never observed alone (in isolation), but exist always in combinations. The rule which is followed here is documented by ‘color confinement’. ...
An Overview of the Field of High Energy Physics
... • A vast array of natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. • One can determine what these rules are by observation and experiment. • This is how science has progressed since the 1700’s. ...
... • A vast array of natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. • One can determine what these rules are by observation and experiment. • This is how science has progressed since the 1700’s. ...
Quantum Confinement in Nanometric Structures
... Abstract: This paper discusses the quantum confinement effects in nanometric structures that form low dimensional systems. In such systems, each surface/interface acts like a potential barrier, i.e. the wall of a quantum well, generating new energy levels. These levels are computed in a model that u ...
... Abstract: This paper discusses the quantum confinement effects in nanometric structures that form low dimensional systems. In such systems, each surface/interface acts like a potential barrier, i.e. the wall of a quantum well, generating new energy levels. These levels are computed in a model that u ...
Microscopic Foundations of Ohm and Joule`s Laws
... Emission spectra of chemical elements had also been known since the nineteenth century and no theoretical explanation was available at that time. It became clear that electrons play a key role in this phenomenon. However, the classical solar system model of the atom failed to explain the emitted or ...
... Emission spectra of chemical elements had also been known since the nineteenth century and no theoretical explanation was available at that time. It became clear that electrons play a key role in this phenomenon. However, the classical solar system model of the atom failed to explain the emitted or ...
Representation Theory, Symmetry, and Quantum
... In the early 20th century, it had become apparent to physicists that many phenomena, from the orbiting of electrons in atoms to the emission and absorption of light waves, did not occur on a continuous spectrum, as classical theories would predict. Einstein’s 1905 discovery of the photoelectic effec ...
... In the early 20th century, it had become apparent to physicists that many phenomena, from the orbiting of electrons in atoms to the emission and absorption of light waves, did not occur on a continuous spectrum, as classical theories would predict. Einstein’s 1905 discovery of the photoelectic effec ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... • The energy of the electron is greater when it is in orbits farther from the nucleus • The atom achieves the ground state when atoms occupy the closest possible positions around the nucleus • Electromagnetic radiation is emitted when electrons move closer to the nucleus. ...
... • The energy of the electron is greater when it is in orbits farther from the nucleus • The atom achieves the ground state when atoms occupy the closest possible positions around the nucleus • Electromagnetic radiation is emitted when electrons move closer to the nucleus. ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... • The energy of the electron is greater when it is in orbits farther from the nucleus • The atom achieves the ground state when atoms occupy the closest possible positions around the nucleus • Electromagnetic radiation is emitted when electrons move closer to the nucleus. ...
... • The energy of the electron is greater when it is in orbits farther from the nucleus • The atom achieves the ground state when atoms occupy the closest possible positions around the nucleus • Electromagnetic radiation is emitted when electrons move closer to the nucleus. ...
January 2001
... (taken to be centered on the origin in the x-y plane) by a magnetic field Bz (r, t) while their energy is increased via a changing magnetic flux dΦ/dt = πR2 dBz,ave /dt through the circle. Motion of the electrons perpendicular to the circle is prevented by means that need not be considered here. Ded ...
... (taken to be centered on the origin in the x-y plane) by a magnetic field Bz (r, t) while their energy is increased via a changing magnetic flux dΦ/dt = πR2 dBz,ave /dt through the circle. Motion of the electrons perpendicular to the circle is prevented by means that need not be considered here. Ded ...