Earth Science - Green Local Schools
... Average atomic mass energy levels Metal Valence electron Nonmetal Period Semiconductor Group Alkali metal Ion Alkaline-earth metal Atomic number Transition metal Mass number Noble gases Electron Cloud Model / Bohr Model Be able to find the number of neutrons, protons, and electrons in an atom Be ...
... Average atomic mass energy levels Metal Valence electron Nonmetal Period Semiconductor Group Alkali metal Ion Alkaline-earth metal Atomic number Transition metal Mass number Noble gases Electron Cloud Model / Bohr Model Be able to find the number of neutrons, protons, and electrons in an atom Be ...
Molecular Models Lab - Valley Catholic School
... The short grey links are used to represent single covalent bonds. Two flexible grey links are used to represent a double bond, and three flexible grey links are needed for a triple bond. Prelab Assignment: 1. Describe resonance. 2. Describe how formal charge can be used to determine which resonance ...
... The short grey links are used to represent single covalent bonds. Two flexible grey links are used to represent a double bond, and three flexible grey links are needed for a triple bond. Prelab Assignment: 1. Describe resonance. 2. Describe how formal charge can be used to determine which resonance ...
Equilibrium 4 Noteform - IndustrialProcesses
... (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
... (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
Chapter 4: Life is based on molecules with carbon (organic
... Much of the chemistry of life is based on organic compounds A. organic compounds have at least one carbon atom covalently bound to another carbon atom or to hydrogen; the chemistry of organic molecules is organized around the carbon atom B. carbon atoms have six electrons - 2 in level 1, and 4 in th ...
... Much of the chemistry of life is based on organic compounds A. organic compounds have at least one carbon atom covalently bound to another carbon atom or to hydrogen; the chemistry of organic molecules is organized around the carbon atom B. carbon atoms have six electrons - 2 in level 1, and 4 in th ...
Mass spectrometry-led catalyst discovery
... Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) is a fast, sensitive tool capable of studying complex mixtures in solution, capabilities that make it, at first glance, the ideal technique for the direct analysis of homogeneous catalytic reactions. However, a variety of challenges have prevented E ...
... Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) is a fast, sensitive tool capable of studying complex mixtures in solution, capabilities that make it, at first glance, the ideal technique for the direct analysis of homogeneous catalytic reactions. However, a variety of challenges have prevented E ...
chem 464l survival guide
... v. Nomenclature - Just as though you were in a foreign language class, a firm understanding of the functional group terminology from your pre-requisite organic chemistry classes is KEY to being able to follow your instructor during lectures in CHEM 464 and to understand what you read in the textbook ...
... v. Nomenclature - Just as though you were in a foreign language class, a firm understanding of the functional group terminology from your pre-requisite organic chemistry classes is KEY to being able to follow your instructor during lectures in CHEM 464 and to understand what you read in the textbook ...
In organic chemistry, we studied a lot about the essential elements
... up all living organism. They are: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur. And these elements play a very essential in living organism. HYDROGEN: It’s a very universal knowledge that hydrogen and oxygen forms water, an essential substance for life on Earth. However this element is ver ...
... up all living organism. They are: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur. And these elements play a very essential in living organism. HYDROGEN: It’s a very universal knowledge that hydrogen and oxygen forms water, an essential substance for life on Earth. However this element is ver ...
32 . R $ [ ~ % % + l
... (a) decreases, increases, decreases, decreases (b) increases, increases, decreases, increases (c) increases, decreases, increases, decreases (d) decreases, decreases, increases, increases (e) decreases, increases, decreases, increases ...
... (a) decreases, increases, decreases, decreases (b) increases, increases, decreases, increases (c) increases, decreases, increases, decreases (d) decreases, decreases, increases, increases (e) decreases, increases, decreases, increases ...
IB1 Introduction to Ch
... Density is an intensive property. It is constant for most solids and liquids, but it depends on the pressure and temperature for a gas ...
... Density is an intensive property. It is constant for most solids and liquids, but it depends on the pressure and temperature for a gas ...
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... of matter and how it applies to various types of chemical equations (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion). ...
... of matter and how it applies to various types of chemical equations (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion). ...
Chapter 14 - RelyonBiology
... earth could produce organic (carbon containing) molecules. • After a week of performing their experiment, several kinds of amino acids and sugars appeared. ...
... earth could produce organic (carbon containing) molecules. • After a week of performing their experiment, several kinds of amino acids and sugars appeared. ...
New LS-VSEPR Modeling Lab
... Amino acids are a class of biologically important organic molecules. These molecules contain an amine group, NH2, a Bronsted-Lowry base (H+ acceptor) and a carboxylic acid group, COOH, a Bronsted-Lowry acid (H+ donor). The structure of the carboxylic acid unit is similar to the structure and reactiv ...
... Amino acids are a class of biologically important organic molecules. These molecules contain an amine group, NH2, a Bronsted-Lowry base (H+ acceptor) and a carboxylic acid group, COOH, a Bronsted-Lowry acid (H+ donor). The structure of the carboxylic acid unit is similar to the structure and reactiv ...
Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy
... Peak that corresponds to the unfragmented radical cation is parent peak or molecular ion (M+) ...
... Peak that corresponds to the unfragmented radical cation is parent peak or molecular ion (M+) ...
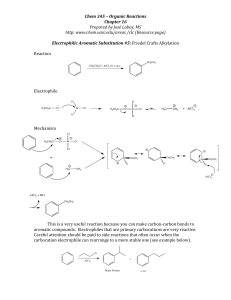
1. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds.
... In the structural formula, O=C=O, each line represents a pair of shared electrons. This arrangement completes the valence shells of all atoms in the molecule. CO2 is the source of carbon for all organic molecules found in organisms. It is usually fixed into organic molecules by the process of photos ...
... In the structural formula, O=C=O, each line represents a pair of shared electrons. This arrangement completes the valence shells of all atoms in the molecule. CO2 is the source of carbon for all organic molecules found in organisms. It is usually fixed into organic molecules by the process of photos ...
PowerPoint - Organic Chemistry
... • All of these have a plant origin • All of these rely on the “fixing” of C from CO2 • Synthetic organic compounds are derived from fossil fuels or plant material ...
... • All of these have a plant origin • All of these rely on the “fixing” of C from CO2 • Synthetic organic compounds are derived from fossil fuels or plant material ...
Slide 1
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...