Biochem basics POGIL
... 18. In chemistry you learned that covalent bonds are one type of intramolecular bond. They occur between nonmetal atoms in a molecule. You may have also learned about a type of intermolecular bond called a hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds are weak attractive forces between polar molecules containing t ...
... 18. In chemistry you learned that covalent bonds are one type of intramolecular bond. They occur between nonmetal atoms in a molecule. You may have also learned about a type of intermolecular bond called a hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds are weak attractive forces between polar molecules containing t ...
Summer Assignment 2015
... Name ________________________________ Complete this assignment on a separate sheet(s) of paper. To receive full credit you must show all work, report your answers to the proper number of significant figures, and your answers must have the appropriate units. Refer to the links on the last page for he ...
... Name ________________________________ Complete this assignment on a separate sheet(s) of paper. To receive full credit you must show all work, report your answers to the proper number of significant figures, and your answers must have the appropriate units. Refer to the links on the last page for he ...
Chemistry Exam Review Sheet
... Rate of forward reaction = rate of reverse reaction Properties remain constant Does this mean you have equal amounts of product and reactant? Shifts. . . if conditions are changed (the concentration of reactants or products). . . Can you predict the SHIFT? Acid and Base pH related to the hydrogen io ...
... Rate of forward reaction = rate of reverse reaction Properties remain constant Does this mean you have equal amounts of product and reactant? Shifts. . . if conditions are changed (the concentration of reactants or products). . . Can you predict the SHIFT? Acid and Base pH related to the hydrogen io ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... a. Thomson, b. Millikan, c. Chadwick, d. Rutherford, e. Dalton Dalton’s billiard ball model-sphere of uniform density. Thomson’s plum pudding model-negative electrons dispersed in positive atom. Rutherford’s nuclear model-dense, positive nucleus surrounded by negative electrons. Bohr’s planetary mod ...
... a. Thomson, b. Millikan, c. Chadwick, d. Rutherford, e. Dalton Dalton’s billiard ball model-sphere of uniform density. Thomson’s plum pudding model-negative electrons dispersed in positive atom. Rutherford’s nuclear model-dense, positive nucleus surrounded by negative electrons. Bohr’s planetary mod ...
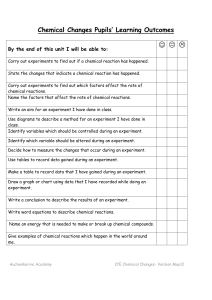
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... Write an aim for an experiment I have done in class. Use diagrams to describe a method for an experiment I have done in class. Identify variables which should be controlled during an experiment. Identify which variable should be altered during an experiment. Decide how to measure the changes that oc ...
... Write an aim for an experiment I have done in class. Use diagrams to describe a method for an experiment I have done in class. Identify variables which should be controlled during an experiment. Identify which variable should be altered during an experiment. Decide how to measure the changes that oc ...
Molar Heat of Reaction
... dissolving one mole of solute in the solvent (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of ...
... dissolving one mole of solute in the solvent (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
A Guide to Organic Molecules
... 11.1.2 Volatility – is the ease with which a substance turns into vapour. It is directly related to the vapour pressure. 11.1.3 Viscosity – a measure of a substance’s resistance to flow – solids and ‘thick’ fluids like oil do not flow so have high viscosity. Gases flow easily hence have low viscosit ...
... 11.1.2 Volatility – is the ease with which a substance turns into vapour. It is directly related to the vapour pressure. 11.1.3 Viscosity – a measure of a substance’s resistance to flow – solids and ‘thick’ fluids like oil do not flow so have high viscosity. Gases flow easily hence have low viscosit ...
AQA Core Science Final Test - Atoms and Chemical equations
... There is one Calcium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms in this reaction. ...
... There is one Calcium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms in this reaction. ...
Ch. 21- Organic Reactions and Biochemistry
... -invention made it clear that macromolecules could be made in an infinite variety of structures by organic chemistry (found an ever-expanding number of uses for these molecules) ...
... -invention made it clear that macromolecules could be made in an infinite variety of structures by organic chemistry (found an ever-expanding number of uses for these molecules) ...
Chemistry 2011-2012
... SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matter is used to determine chemical composition in compounds and chemical reactions. SC2c. Apply concepts of the mole and Avogadro’s number to conceptualize and calculate • Empirical/molecular formulas, • Mass, moles and molecules relationship ...
... SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matter is used to determine chemical composition in compounds and chemical reactions. SC2c. Apply concepts of the mole and Avogadro’s number to conceptualize and calculate • Empirical/molecular formulas, • Mass, moles and molecules relationship ...
Section 16.1 A Model for Reaction Rates
... Collision Theory (cont.) • The minimum amount of energy that reacting particles must have to form the activated complex and lead to a reaction is called the activation energy ”Ea”. •A high Ea means that relatively few collisions have the required energy to produce the activated complex, and the rea ...
... Collision Theory (cont.) • The minimum amount of energy that reacting particles must have to form the activated complex and lead to a reaction is called the activation energy ”Ea”. •A high Ea means that relatively few collisions have the required energy to produce the activated complex, and the rea ...
Introduction to reaction dynamics
... forces acting on an atom determine its motion, the potential energy surface for a reaction determines its course, including what (if any) products will be formed, in what direction(s) they are scattered, what their geometries and energies will be, how fast the reaction will proceed, and so on. Calcu ...
... forces acting on an atom determine its motion, the potential energy surface for a reaction determines its course, including what (if any) products will be formed, in what direction(s) they are scattered, what their geometries and energies will be, how fast the reaction will proceed, and so on. Calcu ...