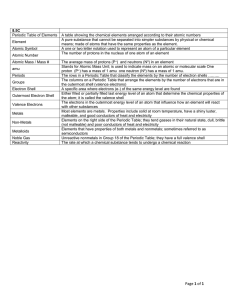
Name - TeacherWeb
... because of van der Waal interactions. 10. What uses do halogenated hydrocarbons have? ...
... because of van der Waal interactions. 10. What uses do halogenated hydrocarbons have? ...
CHAPTER 4: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... Organic Chemistry-branch of chemistry that specializes in the study of carbon compounds Functional Groups-parts of molecules most commonly involved in chemical reactions. You are responsible for knowing the functional groups on pgs. 64-65. CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules -Mac ...
... Organic Chemistry-branch of chemistry that specializes in the study of carbon compounds Functional Groups-parts of molecules most commonly involved in chemical reactions. You are responsible for knowing the functional groups on pgs. 64-65. CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules -Mac ...
Practice Exam 3 - University of Missouri
... Δ H > 0, Δ S = 0 b. Δ H > 0, Δ S < 0 c. Δ H < 0, Δ S > 0 d. Δ H < 0, Δ S < 0 e. Δ H > 0, Δ S > 0 4. In total, how many localized bonds and how many lone pairs respectively are there in H2O? a. 2 and 2 b. 4 and 8 c. 4 and 6 d. 2 and 6 e. 2 and 8 5. Which one of the following molecules is polar becaus ...
... Δ H > 0, Δ S = 0 b. Δ H > 0, Δ S < 0 c. Δ H < 0, Δ S > 0 d. Δ H < 0, Δ S < 0 e. Δ H > 0, Δ S > 0 4. In total, how many localized bonds and how many lone pairs respectively are there in H2O? a. 2 and 2 b. 4 and 8 c. 4 and 6 d. 2 and 6 e. 2 and 8 5. Which one of the following molecules is polar becaus ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Carbon Chemistry)
... Carbon has the ability to form long chains of atoms held together by strong covalent bonds. Molecules with over 700 carbon atoms bonded together are not uncommon! The carbon-carbon single bond is very strong and very stable – it takes strong UV light or lots of heat to crack it. The PROPERTIES OF OR ...
... Carbon has the ability to form long chains of atoms held together by strong covalent bonds. Molecules with over 700 carbon atoms bonded together are not uncommon! The carbon-carbon single bond is very strong and very stable – it takes strong UV light or lots of heat to crack it. The PROPERTIES OF OR ...
chemical bonds - geraldinescience
... • A chemical equation must be balanced to be useful for showing the types and amounts of the products that could from from a particular set of reactants • An equation is balanced when the number of atoms of each element on the right side of the equation is equal to the number of atoms of the same el ...
... • A chemical equation must be balanced to be useful for showing the types and amounts of the products that could from from a particular set of reactants • An equation is balanced when the number of atoms of each element on the right side of the equation is equal to the number of atoms of the same el ...
Slide 1
... In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as follows for O2 with glu ...
... In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as follows for O2 with glu ...
Computers in Chemistry - University of St Andrews
... mechanics needed to simulate a chemical reaction. Nonetheless, molecular dynamics is very important for understanding shape changes, interactions and energetics of large molecules. ...
... mechanics needed to simulate a chemical reaction. Nonetheless, molecular dynamics is very important for understanding shape changes, interactions and energetics of large molecules. ...
word doc (perfect formatting)
... 4) Represents an atom of an alkali earth metal Questions 5-8 refer to the following descriptions of bonding in different types of solids. a) Lattice of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic forces b) Closely packed lattice with delocalized electrons throughout giving ability to c ...
... 4) Represents an atom of an alkali earth metal Questions 5-8 refer to the following descriptions of bonding in different types of solids. a) Lattice of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic forces b) Closely packed lattice with delocalized electrons throughout giving ability to c ...
Organic Chemistry Unit
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) ...
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) ...
Ch 8 Notes: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... III. Energy in chemical reactions: Some reactions require more energy than is produced; others produce more energy then is required. A Heat energy Exothermic Reactions – when energy is released during a reaction it is called an exothermic reaction. When atoms combine to form a compound, energy is re ...
... III. Energy in chemical reactions: Some reactions require more energy than is produced; others produce more energy then is required. A Heat energy Exothermic Reactions – when energy is released during a reaction it is called an exothermic reaction. When atoms combine to form a compound, energy is re ...
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 1998 - University of Waterloo
... With six electrons in its outer shell the sulfur atom can either gain electrons from other elements or share its electrons with other ...
... With six electrons in its outer shell the sulfur atom can either gain electrons from other elements or share its electrons with other ...
Chapter 5
... enzymatically catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell Metabolic pathways are determined by enzymes Enzymes are encoded by genes ...
... enzymatically catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell Metabolic pathways are determined by enzymes Enzymes are encoded by genes ...
unit 5 hw packet - District 196 e
... 1. Add the number of valence electrons in each atom to determine the total number of valence electrons. (For polyatomic anions, add one electron for each unit of negative charge. For polyatomic cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge.) 2. Put electrons around each atom. Start ...
... 1. Add the number of valence electrons in each atom to determine the total number of valence electrons. (For polyatomic anions, add one electron for each unit of negative charge. For polyatomic cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge.) 2. Put electrons around each atom. Start ...
pcc-sio2.alcohol.oxi..
... overoxidation is avoided using Swern conditions, the annoying odor of by-products and troublesome removal of DMSO may make the purification of products lengthy. The anhydrous conditions maintained by a PCC/silica gel oxidation serve to minimize the formation of carboxylic acids as products of the si ...
... overoxidation is avoided using Swern conditions, the annoying odor of by-products and troublesome removal of DMSO may make the purification of products lengthy. The anhydrous conditions maintained by a PCC/silica gel oxidation serve to minimize the formation of carboxylic acids as products of the si ...
Unit 1 - Cells: The Functional Unit of Life
... rate of chemical reactions through the use of biological catalysts Organisms must store energy in a usable form so again control the rate of chemical reactions ...
... rate of chemical reactions through the use of biological catalysts Organisms must store energy in a usable form so again control the rate of chemical reactions ...
Oxacyclopropane (Epoxide) Synthesis: Epoxidation by
... Hydrogen bromide can add to alkenes in anti-Markovnikov fashion: a change in mechanism. The reaction products from the treatment of 1-butene with HBr depend upon the presence or absence of molecular oxygen in the reaction mixture: ...
... Hydrogen bromide can add to alkenes in anti-Markovnikov fashion: a change in mechanism. The reaction products from the treatment of 1-butene with HBr depend upon the presence or absence of molecular oxygen in the reaction mixture: ...
Study Guide for Lab Quiz
... take place at a useful rate. 2) It acid-catalyzed dehydration occurs via an SN1 mechanism, which type of alcohols dehydrate most rapidly, 1°, 2°, or 3°. 3) Acid catalyzed dehydration is an equilibrium - the reverse is the hydration of alkenes. How did you shift the equilibrium to favor the formation ...
... take place at a useful rate. 2) It acid-catalyzed dehydration occurs via an SN1 mechanism, which type of alcohols dehydrate most rapidly, 1°, 2°, or 3°. 3) Acid catalyzed dehydration is an equilibrium - the reverse is the hydration of alkenes. How did you shift the equilibrium to favor the formation ...