Biochemistry-Review of the Basics
... In chemical reactions the energy is usually provided in the form of heat Exothermic reactions result in products with less potential energy than the reactants ...
... In chemical reactions the energy is usually provided in the form of heat Exothermic reactions result in products with less potential energy than the reactants ...
+ H 2 SO 4(aq) - Rothschild Science
... How did you do? MnO2- 86.94 g/mol, Manganese (IV) oxide H2SO4 98.09 g/mol, Sulfuric acid Be sure you go back and review the basics… ...
... How did you do? MnO2- 86.94 g/mol, Manganese (IV) oxide H2SO4 98.09 g/mol, Sulfuric acid Be sure you go back and review the basics… ...
PDF(343KB)
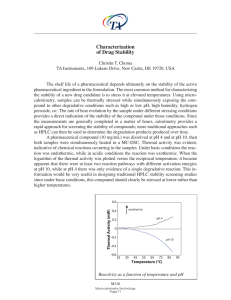
... the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evoluti ...
... the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evoluti ...
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
... They both occur in chloroplasts. They both require sunlight. They both involve organic and inorganic molecules. They both require oxygen and produce carbon dioxide. ...
... They both occur in chloroplasts. They both require sunlight. They both involve organic and inorganic molecules. They both require oxygen and produce carbon dioxide. ...
Organic Chemistry
... Nomenclature for Alkenes 1. Root hydrocarbon name ends in -ene C2H4 is ethene 2. With more than 3 carbons, double bond is indicated by the lowest numbered carbon atom in the bond. C=CCC is 1-butene ...
... Nomenclature for Alkenes 1. Root hydrocarbon name ends in -ene C2H4 is ethene 2. With more than 3 carbons, double bond is indicated by the lowest numbered carbon atom in the bond. C=CCC is 1-butene ...
twelve important naval substances – bonding
... Polymers and Biopolymers Introduction to Polymers A plastic soda bottle, a rubber band, nylon fishing line, a diaper, super glue, proteins, DNA, RNA, and complex carbohydrates are all examples of polymers. Polymer: A molecule of high molar mass formed by the joining of a large number of molecules of ...
... Polymers and Biopolymers Introduction to Polymers A plastic soda bottle, a rubber band, nylon fishing line, a diaper, super glue, proteins, DNA, RNA, and complex carbohydrates are all examples of polymers. Polymer: A molecule of high molar mass formed by the joining of a large number of molecules of ...
Total marks available
... separate test tubes with 5 cm3 of ethanol. These test tubes were placed in the water bath together with a test tube containing aqueous silver nitrate. After about 5 minutes, 1 cm3 of the silver nitrate solution was added to each test tube containing a halogenoalkane and the time taken for a precipit ...
... separate test tubes with 5 cm3 of ethanol. These test tubes were placed in the water bath together with a test tube containing aqueous silver nitrate. After about 5 minutes, 1 cm3 of the silver nitrate solution was added to each test tube containing a halogenoalkane and the time taken for a precipit ...
Biological Molecules Chapter 3: 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids
... Special features of the element Carbon: • can form bonds with up to 4 other atoms • bonds tend to be relatively non-polar, stable • can form complex linear, branched, ringed structures • forms the “skeleton” of biological molecules ...
... Special features of the element Carbon: • can form bonds with up to 4 other atoms • bonds tend to be relatively non-polar, stable • can form complex linear, branched, ringed structures • forms the “skeleton” of biological molecules ...
Organic Dyes as Photoredox Catalysts
... The Nicewicz group recently showed that Mes–Acr+ and derivatives catalyze the direct C–H amination of electron rich arenes with nitrogen heterocyclic nucleophiles.5 The value of this method in drug design and natural product synthesis was demonstrated in the late stage derivatization of biologically ...
... The Nicewicz group recently showed that Mes–Acr+ and derivatives catalyze the direct C–H amination of electron rich arenes with nitrogen heterocyclic nucleophiles.5 The value of this method in drug design and natural product synthesis was demonstrated in the late stage derivatization of biologically ...
Alcohols - ChemistryHSC
... However as the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, solubility decreases, due to more dispersion forces established between the alkyl groups of the alcohol molecules so they are more attracted to each other than the water molecules. Ethanol has polar bonds in its molecule: C - O and O – H. Ox ...
... However as the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, solubility decreases, due to more dispersion forces established between the alkyl groups of the alcohol molecules so they are more attracted to each other than the water molecules. Ethanol has polar bonds in its molecule: C - O and O – H. Ox ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... 2. Assuming a s’more requires two graham crackers, one marshmallow, and one piece of chocolate, how many s’mores could you make with the ingredients shown? _____________ Gizmo Warm-up In a chemical reaction, reactants interact to form products. This process is summarized by a chemical equation. In t ...
... 2. Assuming a s’more requires two graham crackers, one marshmallow, and one piece of chocolate, how many s’mores could you make with the ingredients shown? _____________ Gizmo Warm-up In a chemical reaction, reactants interact to form products. This process is summarized by a chemical equation. In t ...
Chemistry
... Molecular formula and Kekule’s structure. Stability and carbon-carbon bond lengths of benzene, resonance structure, MO picture. Aromaticity: Huckel rule, aromatic ions, Aromatic electrophilic substitution –Mechanism of nitration, halogenation, sulphonation, Friedel-Craft reaction. Effect of substitu ...
... Molecular formula and Kekule’s structure. Stability and carbon-carbon bond lengths of benzene, resonance structure, MO picture. Aromaticity: Huckel rule, aromatic ions, Aromatic electrophilic substitution –Mechanism of nitration, halogenation, sulphonation, Friedel-Craft reaction. Effect of substitu ...
CHM2210 Organic Chemistry 1
... diastereomers, resonance structures, identical or unrelated 11. predicting the relative stability of alkane and substituted alkane conformers ,substituted cyclohexane conformers, cycloalkanes, alkenes, dienes, polyenes, carbocations and free radicals Competency 2: The student will demonstrate knowl ...
... diastereomers, resonance structures, identical or unrelated 11. predicting the relative stability of alkane and substituted alkane conformers ,substituted cyclohexane conformers, cycloalkanes, alkenes, dienes, polyenes, carbocations and free radicals Competency 2: The student will demonstrate knowl ...
Biology Name: TEACHER KEY Life Substances Notes
... 1.) Organic compounds- Contain carbon and hydrogen atoms 2.) Inorganic compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms A. Most of your body’s molecules are organic compounds. a. Macromolecules are built from small organic compounds the same way a railroad trai ...
... 1.) Organic compounds- Contain carbon and hydrogen atoms 2.) Inorganic compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms A. Most of your body’s molecules are organic compounds. a. Macromolecules are built from small organic compounds the same way a railroad trai ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
Name: Period
... 3. What are the shapes of an s and p orbitals? 4. What is a principal energy level, sublevel and atomic orbital? 5. What is the maximum number in each s, p, d and f orbitals? 6. What types of atomic orbitals are in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd principal energy levels? 7. If the spin of one electron is clock ...
... 3. What are the shapes of an s and p orbitals? 4. What is a principal energy level, sublevel and atomic orbital? 5. What is the maximum number in each s, p, d and f orbitals? 6. What types of atomic orbitals are in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd principal energy levels? 7. If the spin of one electron is clock ...
malhotra book depot
... Three states of matter, intermolecular interactions, types of bonding, melting and boiling points, role of gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Gay Lussac’s law, Avogadro’s law, ideal behaviour, empirical derivation of gas equation, Avogadro’s number, ideal ...
... Three states of matter, intermolecular interactions, types of bonding, melting and boiling points, role of gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Gay Lussac’s law, Avogadro’s law, ideal behaviour, empirical derivation of gas equation, Avogadro’s number, ideal ...
CH 10
... • Alkane + Cl2 or Br2, heat or light replaces C-H with C-X but gives mixtures – Hard to control – Via free radical mechanism ...
... • Alkane + Cl2 or Br2, heat or light replaces C-H with C-X but gives mixtures – Hard to control – Via free radical mechanism ...
2 - Glow Blogs
... When this reaction was studied at different temperatures, the data shown in the table below were obtained. The data could be used to determine the activation energy for the forward reaction. Temperature/K ...
... When this reaction was studied at different temperatures, the data shown in the table below were obtained. The data could be used to determine the activation energy for the forward reaction. Temperature/K ...