Department of Chemistry - Catalog
... PCM/PBC students are restricted from registering for upper-division (3000- and 4000-level) Chemistry courses without the consent of an undergraduate academic advisor. A student who does not meet all the above requirements after completing the above 16 credit hours will no longer be considered a PCM ...
... PCM/PBC students are restricted from registering for upper-division (3000- and 4000-level) Chemistry courses without the consent of an undergraduate academic advisor. A student who does not meet all the above requirements after completing the above 16 credit hours will no longer be considered a PCM ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... • How would you convey to other scientists what is occurring in the photograph? • A chemical equation is a shorthand way of communicating the reaction that is occurring. • A chemical equation packs a great deal of information into relatively few symbols. Chapter menu ...
... • How would you convey to other scientists what is occurring in the photograph? • A chemical equation is a shorthand way of communicating the reaction that is occurring. • A chemical equation packs a great deal of information into relatively few symbols. Chapter menu ...
Full Text - Journal of the Indian Institute of Science
... The use of Burgess reagent (1) in many occasions leads to unexpected products. Cited below are a few such examples. Cyclopropanone dithioacetals with an additional electron by withdrawing ring substituent are particularly useful, especially if available in optically active form. Apart from substitut ...
... The use of Burgess reagent (1) in many occasions leads to unexpected products. Cited below are a few such examples. Cyclopropanone dithioacetals with an additional electron by withdrawing ring substituent are particularly useful, especially if available in optically active form. Apart from substitut ...
sol-gel chemistry of transition metal oxides
... author proposed a mechanism of hydrolysis in which hydroxyl groups are added to the which leads to the formation of condensed species. ...
... author proposed a mechanism of hydrolysis in which hydroxyl groups are added to the which leads to the formation of condensed species. ...
4. a-Monohalo Ethers in Protection Chemistry
... protection chemistry.[Grenne, 1991] This is partly due to the high reactivity of -halo ethers in nucleophilic displacement reactions, which in many cases assures a complete introduction of the protecting group. Another point of great importance in protection chemistry, is the removal of the protect ...
... protection chemistry.[Grenne, 1991] This is partly due to the high reactivity of -halo ethers in nucleophilic displacement reactions, which in many cases assures a complete introduction of the protecting group. Another point of great importance in protection chemistry, is the removal of the protect ...
Acids, Bases and Salts
... ACIDS, BASES and SALTS the Brønsted-Lowry theory is an acid-base theory, proposed independently by Danish Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and English Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. In this system, an acid is defined as any chemical species (molecule or ion) that is able to lose, or "donate" a hydrogen ion ...
... ACIDS, BASES and SALTS the Brønsted-Lowry theory is an acid-base theory, proposed independently by Danish Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and English Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. In this system, an acid is defined as any chemical species (molecule or ion) that is able to lose, or "donate" a hydrogen ion ...
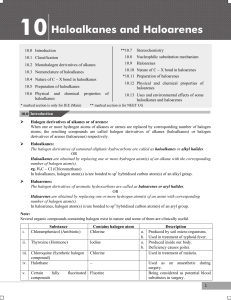
10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
... In the case of unsymmetrical alkenes, carbon atoms involved in double bond are non-equivalent, so the addition of HX in unsymmetrical alkene takes place according to Markownikoff’s rule. According to Markownikoff’s rule, “during addition of an unsymmetrical reagent across the double bond of an unsym ...
... In the case of unsymmetrical alkenes, carbon atoms involved in double bond are non-equivalent, so the addition of HX in unsymmetrical alkene takes place according to Markownikoff’s rule. According to Markownikoff’s rule, “during addition of an unsymmetrical reagent across the double bond of an unsym ...
Energy Foundations for High School Chemistry
... What is energy? Most of us have a feeling that we understand energy and recognize it when we see it, but coming up with a formal definition might be harder for us to do. Here are some of the basic concepts associated with a definition of energy: • Energy is required to make things change. • Energy ...
... What is energy? Most of us have a feeling that we understand energy and recognize it when we see it, but coming up with a formal definition might be harder for us to do. Here are some of the basic concepts associated with a definition of energy: • Energy is required to make things change. • Energy ...
Unit-7-Carboxylic-Acids-Phenols
... which play important roles in biochemistry. These include the carboxylic acids, phenols, amines and amides. We also look at a new type of stereoisomer that figures predominantly in biological chemistry; the optical isomer. ...
... which play important roles in biochemistry. These include the carboxylic acids, phenols, amines and amides. We also look at a new type of stereoisomer that figures predominantly in biological chemistry; the optical isomer. ...
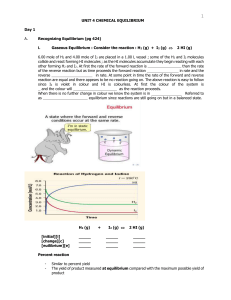
Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
... Recognizing Equilibrium (pg 424) Gaseous Equilibrium : Consider the reaction : H2 (g) + I2 (g) ...
... Recognizing Equilibrium (pg 424) Gaseous Equilibrium : Consider the reaction : H2 (g) + I2 (g) ...
Unit-7-Carboxylic-Acids-Phenols
... which play important roles in biochemistry. These include the carboxylic acids, phenols, amines and amides. We also look at a new type of stereoisomer that figures predominantly in biological chemistry; the optical isomer. ...
... which play important roles in biochemistry. These include the carboxylic acids, phenols, amines and amides. We also look at a new type of stereoisomer that figures predominantly in biological chemistry; the optical isomer. ...
File
... 5. Explain the term “homologous series.” 6. How can you tell the difference between a “cis” and “trans” isomer? In what types of hydrocarbons can they be found? 7. What is an aromatic compound, and what is the simplest aromatic structure? 8. Do aromatic hydrocarbons react more than saturated or unsa ...
... 5. Explain the term “homologous series.” 6. How can you tell the difference between a “cis” and “trans” isomer? In what types of hydrocarbons can they be found? 7. What is an aromatic compound, and what is the simplest aromatic structure? 8. Do aromatic hydrocarbons react more than saturated or unsa ...
431 KB / 47 pages
... (a) The description of this gold electroplating system gives the reduction half reaction that occurs at the surface to be plated, so the object to be plated must be the cathode in the electroplating cell. The sheet of gold must be the anode, so the anode reaction is oxidation of gold, which enters t ...
... (a) The description of this gold electroplating system gives the reduction half reaction that occurs at the surface to be plated, so the object to be plated must be the cathode in the electroplating cell. The sheet of gold must be the anode, so the anode reaction is oxidation of gold, which enters t ...
IIT-JEE - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Point defects: When ions or atoms do not hold the theoretical position, this is called point defect. Point defects are of two types: Stoichiometric defects: Schottky defect: Due to missing of ions from lattice point in pairs. Frenkel defect: It is caused due to the creation of lattice vacancy as a r ...
... Point defects: When ions or atoms do not hold the theoretical position, this is called point defect. Point defects are of two types: Stoichiometric defects: Schottky defect: Due to missing of ions from lattice point in pairs. Frenkel defect: It is caused due to the creation of lattice vacancy as a r ...
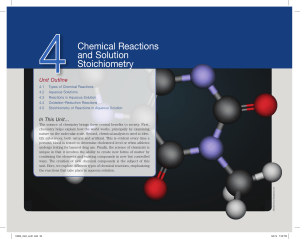
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... closer to oxygen than hydrogen. As a result, each H2O molecule has a buildup of partial negative charge near the oxygen end of the molecule and partial positive charge near the hydrogen atoms. Thus, the negative end of a water molecule is strongly attracted to positively charged cations, and the pos ...
... closer to oxygen than hydrogen. As a result, each H2O molecule has a buildup of partial negative charge near the oxygen end of the molecule and partial positive charge near the hydrogen atoms. Thus, the negative end of a water molecule is strongly attracted to positively charged cations, and the pos ...
top organomet chem-2006-19-207 pauson
... ies support this mechanism while it explains the regio- and stereochemical results of numerous examples. Thus, Nakamura [53] and Milet and Gimbert [54] have performed high-level theoretical calculations on the cobaltacycle formation step, showing that the insertion of the olefin is the critical stere ...
... ies support this mechanism while it explains the regio- and stereochemical results of numerous examples. Thus, Nakamura [53] and Milet and Gimbert [54] have performed high-level theoretical calculations on the cobaltacycle formation step, showing that the insertion of the olefin is the critical stere ...
Question Bank for Pre Board Exam(XII Chemistry)
... 39.Which point defect is observed in a crystal when a vacancy is created by an atom missing from a lattice site. 40. Why does conductivity of silicon increase with the rise in temperature? 41.Name the crystal defect which lowers the density of an ionic crystal. 42 What makes the crystal of KCl somet ...
... 39.Which point defect is observed in a crystal when a vacancy is created by an atom missing from a lattice site. 40. Why does conductivity of silicon increase with the rise in temperature? 41.Name the crystal defect which lowers the density of an ionic crystal. 42 What makes the crystal of KCl somet ...