Ch 9 Lecture 2
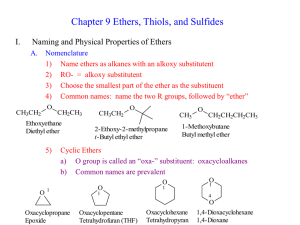
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
Unit F332 - Chemistry of natural resources - Medium band
... Suggest two possible methods that could be used for the capture and storage of carbon dioxide, to prevent its build-up in the atmosphere. ...
... Suggest two possible methods that could be used for the capture and storage of carbon dioxide, to prevent its build-up in the atmosphere. ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
Title
... were studied. We initially studied the behaviour of 1Cl2 and 2(CF3SO3)2 by irradiating with a halogen lamp their water (pH = 7) and acid aqueous solutions (pH = 2, 0). In clean water no reaction was observed, but at pH = 2 and 0 a clear transformation of the starting complexes into a similar compoun ...
... were studied. We initially studied the behaviour of 1Cl2 and 2(CF3SO3)2 by irradiating with a halogen lamp their water (pH = 7) and acid aqueous solutions (pH = 2, 0). In clean water no reaction was observed, but at pH = 2 and 0 a clear transformation of the starting complexes into a similar compoun ...
Chapter 19
... – Oxygen: normally forms two covalent bonds and has two unshared pairs of electrons. ...
... – Oxygen: normally forms two covalent bonds and has two unshared pairs of electrons. ...
Computational Study of Polarizabilities and Second
... electron correlation effects. For γ, the two effects are similarly important. Solvent effects on R and γ caused by subordinate factors other than the dominant electrostatic solute-solvent interactions were studied and assessed to be negligible. Upon solvation, large TM and ligand modification effect ...
... electron correlation effects. For γ, the two effects are similarly important. Solvent effects on R and γ caused by subordinate factors other than the dominant electrostatic solute-solvent interactions were studied and assessed to be negligible. Upon solvation, large TM and ligand modification effect ...
2003 AP Chemistry Form B Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
Glycosyl amines
... Equilibrium mixture of methyl D-xylosides originating from the Fischer glycosidation of D-xylose in methanolic solution of hydrogen chloride at 35º C. Methyl D-xylopyranoside is the major product, due to the anomeric effect, which is characteristic for the tetrahydropyran rings with an electronegati ...
... Equilibrium mixture of methyl D-xylosides originating from the Fischer glycosidation of D-xylose in methanolic solution of hydrogen chloride at 35º C. Methyl D-xylopyranoside is the major product, due to the anomeric effect, which is characteristic for the tetrahydropyran rings with an electronegati ...
Part 2-ICHO-26-30
... The overall catalytic reaction is simple, whereas the reaction mechanism in the homogeneous phase is very complicated with a large number of reaction steps, and the course is difficult to control owing to a distinct chain character. With platinum as catalyst the significant reaction steps are: (i) A ...
... The overall catalytic reaction is simple, whereas the reaction mechanism in the homogeneous phase is very complicated with a large number of reaction steps, and the course is difficult to control owing to a distinct chain character. With platinum as catalyst the significant reaction steps are: (i) A ...
Naming of Alkanes
... – Oxygen: normally forms two covalent bonds and has two unshared pairs of electrons. ...
... – Oxygen: normally forms two covalent bonds and has two unshared pairs of electrons. ...
Directive 2004/42/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council
... VOC is to be determined based on the official stated boiling point specification as provided by the producers/suppliers of these materials within their product and material safety datasheet. Paint industry will apply those data which are assumed to be based on latest methods for boiling point determ ...
... VOC is to be determined based on the official stated boiling point specification as provided by the producers/suppliers of these materials within their product and material safety datasheet. Paint industry will apply those data which are assumed to be based on latest methods for boiling point determ ...
Chemical Equilibrium - 2012 Book Archive
... you need to bail out water. You grab a bucket and begin to bail. After a few minutes, your efforts against the leak keep the water to only about half an inch, but any further bailing doesn’t change the water level; the leak brings in as much water as you bail out. You are at equilibrium. Two opposin ...
... you need to bail out water. You grab a bucket and begin to bail. After a few minutes, your efforts against the leak keep the water to only about half an inch, but any further bailing doesn’t change the water level; the leak brings in as much water as you bail out. You are at equilibrium. Two opposin ...
H2 Adsorption on 3d Transition Metal Clusters
... The experiments have been performed using a molecular beam machine coupled to a beamline of the Free Electron Laser for Infrared eXperiments, FELIX,35 at the FOM Institute for Plasma Physics in Nieuwegein, The Netherlands. The setup and details of the measurement procedure have been discussed in det ...
... The experiments have been performed using a molecular beam machine coupled to a beamline of the Free Electron Laser for Infrared eXperiments, FELIX,35 at the FOM Institute for Plasma Physics in Nieuwegein, The Netherlands. The setup and details of the measurement procedure have been discussed in det ...
CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES
... Cyclic alkanes: general formula CnH2n (if only one ring is present in the compound); all carbons are sp3 hybridized; prefers 109.5Ε bond angles, but rings with three carbons or four carbons or five carbons are forced into bond angles less than 109.5Ε. In cyclopropane, a ring compound made up of thre ...
... Cyclic alkanes: general formula CnH2n (if only one ring is present in the compound); all carbons are sp3 hybridized; prefers 109.5Ε bond angles, but rings with three carbons or four carbons or five carbons are forced into bond angles less than 109.5Ε. In cyclopropane, a ring compound made up of thre ...
Chem12 SM Unit 5 Review final ok
... 42. (a) In P2O5, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of P is +5. (b) In NO2, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of N is +4. (c) In Na2SO4, the oxidation number of Na is +1, the oxidation number of O is –2, and the oxidation number of S is +6. (d) In Cu(NO3) ...
... 42. (a) In P2O5, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of P is +5. (b) In NO2, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of N is +4. (c) In Na2SO4, the oxidation number of Na is +1, the oxidation number of O is –2, and the oxidation number of S is +6. (d) In Cu(NO3) ...
Acidic Environment
... At the equilibrium the concentration of the reactants and products are NOT equal. The system is in a balance. This does not mean that there are 2 moles of reactant and 2 moles of product, for instance. Just that both the forward and reverse reaction is moving at the same rate. ...
... At the equilibrium the concentration of the reactants and products are NOT equal. The system is in a balance. This does not mean that there are 2 moles of reactant and 2 moles of product, for instance. Just that both the forward and reverse reaction is moving at the same rate. ...
O - Montville.net
... 1 mole of O2 is need to react… 1. What relationships can be found in this equation? ...
... 1 mole of O2 is need to react… 1. What relationships can be found in this equation? ...
Document
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...























