Document
... Hydrocarbon names are based on: 1) type, 2) # of carbons, 3) side chain type and position 1) name will end in -ane, -ene, or -yne 2) the number of carbons is given by a “prefix” 1 meth- 2 eth- 3 prop- 4 but- 5 pent6 hex- 7 hept- 8 oct- 9 non- 10 decActually, all end in a, but a is dropped when next ...
... Hydrocarbon names are based on: 1) type, 2) # of carbons, 3) side chain type and position 1) name will end in -ane, -ene, or -yne 2) the number of carbons is given by a “prefix” 1 meth- 2 eth- 3 prop- 4 but- 5 pent6 hex- 7 hept- 8 oct- 9 non- 10 decActually, all end in a, but a is dropped when next ...
Solving Problems: A Chemistry Handbook
... sunburn. Ultraviolet radiation can also harm other animals and plants. In the 1980s, scientists documented that the ozone layer around Earth was becoming measurably thinner in some spots. In the 1970s, scientists had observed that large quantities of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) had accumulated in Ear ...
... sunburn. Ultraviolet radiation can also harm other animals and plants. In the 1980s, scientists documented that the ozone layer around Earth was becoming measurably thinner in some spots. In the 1970s, scientists had observed that large quantities of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) had accumulated in Ear ...
Document
... Hydrocarbon names are based on: 1) type, 2) # of carbons, 3) side chain type and position 1) name will end in -ane, -ene, or -yne 2) the number of carbons is given by a “prefix” 1 meth- 2 eth- 3 prop- 4 but- 5 pent6 hex- 7 hept- 8 oct- 9 non- 10 decActually, all end in a, but a is dropped when next ...
... Hydrocarbon names are based on: 1) type, 2) # of carbons, 3) side chain type and position 1) name will end in -ane, -ene, or -yne 2) the number of carbons is given by a “prefix” 1 meth- 2 eth- 3 prop- 4 but- 5 pent6 hex- 7 hept- 8 oct- 9 non- 10 decActually, all end in a, but a is dropped when next ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 3 Carbon and the
... 8) What determines whether a carbon atom's covalent bonds to other atoms are in a tetrahedral configuration or a planar configuration? A) the presence or absence of bonds with oxygen atoms B) the presence or absence of double bonds between the carbon atom and other atoms C) the polarity of the cova ...
... 8) What determines whether a carbon atom's covalent bonds to other atoms are in a tetrahedral configuration or a planar configuration? A) the presence or absence of bonds with oxygen atoms B) the presence or absence of double bonds between the carbon atom and other atoms C) the polarity of the cova ...
AMIDES AND AMINES: ORGANIC NITROGEN COMPOUNDS
... Amides: Unsubstituted amides (except formamide) are solids at room temperature. Many are odorless and colorless. Low molar-mass amides are water soluble. Solubility in water decreases as the molar mass increases. Amides are neutral compounds. The group is capable of hydrogen bonding. Amines: Low mol ...
... Amides: Unsubstituted amides (except formamide) are solids at room temperature. Many are odorless and colorless. Low molar-mass amides are water soluble. Solubility in water decreases as the molar mass increases. Amides are neutral compounds. The group is capable of hydrogen bonding. Amines: Low mol ...
Ch14b: Carboxylic Acids
... effect makes it difficult to use in many cases. ‣ Phenols and carboxylic acids are acidic, but other substances with these functional groups don’t have the same side effect. ‣ In salicylic acid, the functional groups interact to create that greater acidity. ...
... effect makes it difficult to use in many cases. ‣ Phenols and carboxylic acids are acidic, but other substances with these functional groups don’t have the same side effect. ‣ In salicylic acid, the functional groups interact to create that greater acidity. ...
PART 6-ICHO-26-30
... The overall catalytic reaction is simple, whereas the reaction mechanism in the homogeneous phase is very complicated with a large number of reaction steps, and the course is difficult to control owing to a distinct chain character. With platinum as catalyst the significant reaction steps are: (i) A ...
... The overall catalytic reaction is simple, whereas the reaction mechanism in the homogeneous phase is very complicated with a large number of reaction steps, and the course is difficult to control owing to a distinct chain character. With platinum as catalyst the significant reaction steps are: (i) A ...
CHAPTER 22 ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 1
... Cyclic alkanes: general formula CnH2n (if only one ring is present in the compound); all carbons are sp3 hybridized; prefers 109.5 bond angles, but rings with three carbons or four carbons or five carbons are forced into bond angles less than 109.5. In cyclopropane, a ring compound made up of thre ...
... Cyclic alkanes: general formula CnH2n (if only one ring is present in the compound); all carbons are sp3 hybridized; prefers 109.5 bond angles, but rings with three carbons or four carbons or five carbons are forced into bond angles less than 109.5. In cyclopropane, a ring compound made up of thre ...
Photoelectron Spectroscopy of SO3 at 355 and 266 nm
... observed. The geometry and normal-mode frequencies of SO3- and SO3 as well as the adiabatic electron affinity (AEA) and vertical detachment energy (VDE) of SO3 have also been calculated with ab initio (MP2 and CCSD(T)) and DFT methods. Using theoretical predictions and experimental data, Franck-Cond ...
... observed. The geometry and normal-mode frequencies of SO3- and SO3 as well as the adiabatic electron affinity (AEA) and vertical detachment energy (VDE) of SO3 have also been calculated with ab initio (MP2 and CCSD(T)) and DFT methods. Using theoretical predictions and experimental data, Franck-Cond ...
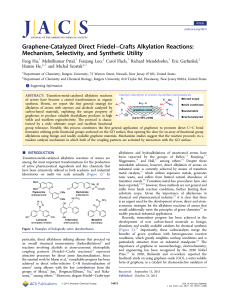
Graphene-Catalyzed Direct Friedel–Crafts Alkylation Reactions
... CC bonds (from 37.0% to 52.0%). Notably, these changes include loss of CO and C−O functions from the GO surface (epoxide, hydroxyl) during the reaction, as well as the reduction of anhydride and carboxylic acid functional groups on the GO surface (from 13.6% to 7.2%). (7) Film conductivity measure ...
... CC bonds (from 37.0% to 52.0%). Notably, these changes include loss of CO and C−O functions from the GO surface (epoxide, hydroxyl) during the reaction, as well as the reduction of anhydride and carboxylic acid functional groups on the GO surface (from 13.6% to 7.2%). (7) Film conductivity measure ...
å¾è湿çå¦
... solution prepared by dissolving 0.10 mol HCOOH in water to make 1.0 L of solution, approximately 4.1% of the HCOOH molecules ionize. What is the pH of this ...
... solution prepared by dissolving 0.10 mol HCOOH in water to make 1.0 L of solution, approximately 4.1% of the HCOOH molecules ionize. What is the pH of this ...
INŻYNIERIA POWIERZCHNI - AGH University of Science and
... Corrosion and corrosion protection Natural rubber - used in the form of derivatives: chloro-rubber and cyclo-rubber. Protective coatings of derivatives of natural rubber are non-flammable, resistant to acids and alkalis, have high gloss and good adhesion. Chlorinated rubber is widely used in antico ...
... Corrosion and corrosion protection Natural rubber - used in the form of derivatives: chloro-rubber and cyclo-rubber. Protective coatings of derivatives of natural rubber are non-flammable, resistant to acids and alkalis, have high gloss and good adhesion. Chlorinated rubber is widely used in antico ...
organic coatings - chemia.odlew.agh.edu.pl
... Corrosion and corrosion protection Natural rubber - used in the form of derivatives: chloro-rubber and cyclo-rubber. Protective coatings of derivatives of natural rubber are non-flammable, resistant to acids and alkalis, have high gloss and good adhesion. Chlorinated rubber is widely used in antico ...
... Corrosion and corrosion protection Natural rubber - used in the form of derivatives: chloro-rubber and cyclo-rubber. Protective coatings of derivatives of natural rubber are non-flammable, resistant to acids and alkalis, have high gloss and good adhesion. Chlorinated rubber is widely used in antico ...
- Catalyst
... Determining the Molecular Formula from Elemental Composition and Molar Mass - I Problem: The sugar burned for energy in cells of the body is glucose (MM = 180.16 g/mol), elemental analysis shows that it contains 40.00 mass % C, 6.729 mass % H, and 53.27 mass % O. (a) Determine the empirical formula ...
... Determining the Molecular Formula from Elemental Composition and Molar Mass - I Problem: The sugar burned for energy in cells of the body is glucose (MM = 180.16 g/mol), elemental analysis shows that it contains 40.00 mass % C, 6.729 mass % H, and 53.27 mass % O. (a) Determine the empirical formula ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... The problem: •Rearrangement of carbon skeleton which usually indicates carbocations. •Reacting alcohol is primary; do not expect carbocation. •Time to adjust our thinking a bit…. H3C ...
... The problem: •Rearrangement of carbon skeleton which usually indicates carbocations. •Reacting alcohol is primary; do not expect carbocation. •Time to adjust our thinking a bit…. H3C ...
4.9 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen Halides
... hybridized carbon is attached to C+, but is not availabe when H is attached to C+. Therefore,alkyl groups stabilize carbocations better than H does. ...
... hybridized carbon is attached to C+, but is not availabe when H is attached to C+. Therefore,alkyl groups stabilize carbocations better than H does. ...
Stoichiometry - AaronFreeman
... The coefficients in the balanced equation give the ratio of moles of reactants and products. Stoichiometry ...
... The coefficients in the balanced equation give the ratio of moles of reactants and products. Stoichiometry ...
For metals
... Most active metals, only found in compounds in nature React violently with water to form hydrogen gas and a strong base: 2 Na (s) + H2O (l) 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) 1 valence electron Form +1 ion by losing that valence electron Form oxides like Na2O, Li2O, K2O ...
... Most active metals, only found in compounds in nature React violently with water to form hydrogen gas and a strong base: 2 Na (s) + H2O (l) 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) 1 valence electron Form +1 ion by losing that valence electron Form oxides like Na2O, Li2O, K2O ...
File - Chemistry Workshop
... 4. Use italicized N- for each additional substituent(s) on the nitrogen ...
... 4. Use italicized N- for each additional substituent(s) on the nitrogen ...
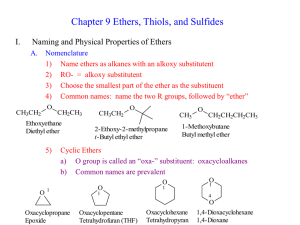
Ch 9 Lecture 2
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...













![Chem Soc Rev - [ RSC ] Publishing](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022750285_1-eab192c7d8bd21532ac3979b6ccdf310-300x300.png)