Bio Molecules Carbs Lipids Nuc Acids and Proteins
... (continued) STEP 2 Fold the carbon chain into a hexagon and bond the O on carbon 5 to the carbonyl group. ...
... (continued) STEP 2 Fold the carbon chain into a hexagon and bond the O on carbon 5 to the carbonyl group. ...
Amines
... pyridine or the like) by -ammonium (or anilinium or pyridinium or the like) and add the name of the anion ...
... pyridine or the like) by -ammonium (or anilinium or pyridinium or the like) and add the name of the anion ...
Revised organic chemistry
... poorer symmetry molecules of cis-alkenes do not fit into the crystal lattice so well as in the trans-isomer with the result cis akenes have generally lower melting points than the trans. Chemical properties: Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of π-bond. The π electrons const ...
... poorer symmetry molecules of cis-alkenes do not fit into the crystal lattice so well as in the trans-isomer with the result cis akenes have generally lower melting points than the trans. Chemical properties: Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of π-bond. The π electrons const ...
Instructor`s Guide to General Chemistry: Guided
... of the reactants to the number of molecules/ions that are produced as products. The number of molecules/ions is measured in units of moles. (b) Steps 2 and 3 make clear what information is given and what needs to be found. Molecules/ions react and molecules/ions are produced, so the units to keep tr ...
... of the reactants to the number of molecules/ions that are produced as products. The number of molecules/ions is measured in units of moles. (b) Steps 2 and 3 make clear what information is given and what needs to be found. Molecules/ions react and molecules/ions are produced, so the units to keep tr ...
electrical energy and capacitance
... CHAPTER 9: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (PART 3) CLASS NOTES MOLE TO MOLE CONVERSIONS Chemical equations are quantitative because they tell us how many reactants and products interact in a given reaction. In particular, chemical reactions are written in mole to mole ratios. For example, 3 H2(g) + N2(g) 2 ...
... CHAPTER 9: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (PART 3) CLASS NOTES MOLE TO MOLE CONVERSIONS Chemical equations are quantitative because they tell us how many reactants and products interact in a given reaction. In particular, chemical reactions are written in mole to mole ratios. For example, 3 H2(g) + N2(g) 2 ...
HYBRID MULTIDENTATE PHOSPHINE
... sequentially across all chapters. The main ligands described in this thesis are referred to by either abbreviated names (e.g. Ferrochalcone) and/or by number (32). Complexes are referred to by either a number and/or a formula. ...
... sequentially across all chapters. The main ligands described in this thesis are referred to by either abbreviated names (e.g. Ferrochalcone) and/or by number (32). Complexes are referred to by either a number and/or a formula. ...
Chemistry of Riming: The Retention of Organic and Inorganic
... Abstract. During free fall in clouds ice hydrometeors such as snowflakes and ice particles grow effectively by riming, i.e., the accretion of supercooled droplets. Volatile atmospheric trace constituents dissolved in the supercooled droplets may remain in ice during freezing or may be released back ...
... Abstract. During free fall in clouds ice hydrometeors such as snowflakes and ice particles grow effectively by riming, i.e., the accretion of supercooled droplets. Volatile atmospheric trace constituents dissolved in the supercooled droplets may remain in ice during freezing or may be released back ...
Chem E2b - Organic Chemistry II What is Organic Chemistry?
... As with acidity, inductive effects are generally WEAKER than resonance effects Z = NR2, OR: Strongly Activating (resonance) Z = NHCO2R, OCO2R: Moderately Activating (inductive) Z = R (Alkyl, vinyl): Weakly Activating (inductive) Y = F, Cl, Br, I: Weakly Deactivating (inductive withdrawal/resonance d ...
... As with acidity, inductive effects are generally WEAKER than resonance effects Z = NR2, OR: Strongly Activating (resonance) Z = NHCO2R, OCO2R: Moderately Activating (inductive) Z = R (Alkyl, vinyl): Weakly Activating (inductive) Y = F, Cl, Br, I: Weakly Deactivating (inductive withdrawal/resonance d ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this. – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this. – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
9278654 PS/Chemistry Ja03 - Dolgeville Central School
... 9 An atom of carbon-12 and an atom of carbon-14 differ in (1) atomic number (2) mass number (3) nuclear charge (4) number of electrons ...
... 9 An atom of carbon-12 and an atom of carbon-14 differ in (1) atomic number (2) mass number (3) nuclear charge (4) number of electrons ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this. – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this. – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
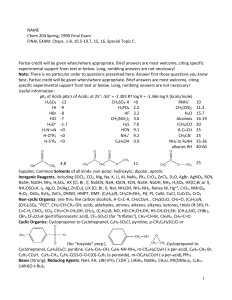
NAME Chem 204 Spring, 1990 Final Exam FINAL EXAM: Chaps. 1
... alkyl chloride, there is NO one reaction that will convert a chiral alcohol into its alkyl chloride with "retained" configuration. Thus, it is necessary to use several reaction steps, each of 100% inversion or 100% retention of configuration, in order to convert (X) into (XI). Outlines below a serie ...
... alkyl chloride, there is NO one reaction that will convert a chiral alcohol into its alkyl chloride with "retained" configuration. Thus, it is necessary to use several reaction steps, each of 100% inversion or 100% retention of configuration, in order to convert (X) into (XI). Outlines below a serie ...
Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acid
... reactions due to steric and electronic reasons (or inductive effect). Electronic Effect: Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two ...
... reactions due to steric and electronic reasons (or inductive effect). Electronic Effect: Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two ...
An efficient acetylation of dextran using in situ activated acetic
... of polysaccharides under homogeneous reaction conditions is a current area of research. However, the fact that solvent systems used to dissolve polysaccharides are quite expensive cannot be neglected; therefore, such methods cannot be readily commercialized. Another important aspect of commercial sy ...
... of polysaccharides under homogeneous reaction conditions is a current area of research. However, the fact that solvent systems used to dissolve polysaccharides are quite expensive cannot be neglected; therefore, such methods cannot be readily commercialized. Another important aspect of commercial sy ...
Stoichiometry - Taylor County Schools
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this. – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this. – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Multiple Choice Exam Review June 2016
... ____ 34. Catalysts can be used to speed up a reaction. _________________________ ____ 35. The value of the rate constant, k, is valid only for a specific reaction at a specific temperature. _________________________ ____ 36. An ineffective collision is one that has sufficient energy and correct orie ...
... ____ 34. Catalysts can be used to speed up a reaction. _________________________ ____ 35. The value of the rate constant, k, is valid only for a specific reaction at a specific temperature. _________________________ ____ 36. An ineffective collision is one that has sufficient energy and correct orie ...
Chapter 6 Quantities in Chemical Reactions
... atoms at a time. How can we keep track of so many atoms (and molecules) at a time? We do it by using mass rather than by counting individual atoms. A hydrogen atom has a mass of approximately 1 u. An oxygen atom has a mass of approximately 16 u. The ratio of the mass of an oxygen atom to the mass of ...
... atoms at a time. How can we keep track of so many atoms (and molecules) at a time? We do it by using mass rather than by counting individual atoms. A hydrogen atom has a mass of approximately 1 u. An oxygen atom has a mass of approximately 16 u. The ratio of the mass of an oxygen atom to the mass of ...
Reduction of CuO in H2: in situ time
... mass spectrometer. This experiment was repeated many times and no diffraction lines for Cu4 O3 [16] or Cu2 O [17] were seen during the reduction. We also investigated the reduction process at lower temperatures, as shown in figure 2. The decrease in reaction temperature led to an increase in the magni ...
... mass spectrometer. This experiment was repeated many times and no diffraction lines for Cu4 O3 [16] or Cu2 O [17] were seen during the reduction. We also investigated the reduction process at lower temperatures, as shown in figure 2. The decrease in reaction temperature led to an increase in the magni ...
Document
... reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of NH3will decrease D) The concentration of both N ...
... reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of NH3will decrease D) The concentration of both N ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... double bond in ethene (CH2=CH2)? Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. D ...
... double bond in ethene (CH2=CH2)? Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. D ...
FREE Sample Here
... double bond in ethene (CH2=CH2)? Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. D ...
... double bond in ethene (CH2=CH2)? Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. D ...
x - SharpSchool
... hydrogen. Evidence indicates that this reaction establishes an equilibrium with only partial conversion of reactants to products. Initially, 2.00 mol of each reactant is placed in the vessel. Kc for this reaction is 4.20 at 900C. Calculate the concentration of each substance at equilibrium. ...
... hydrogen. Evidence indicates that this reaction establishes an equilibrium with only partial conversion of reactants to products. Initially, 2.00 mol of each reactant is placed in the vessel. Kc for this reaction is 4.20 at 900C. Calculate the concentration of each substance at equilibrium. ...