File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... electrons in the central metal atom or ion. 1/2M The unpaired electrons show d-d transition by jumping between t2g and eg orbitals. 1/2M Q3. Write the structures of the each of the following alcohols. 1)3,3-dimethyl cyclopentanol 2)3-chloro-2-methyl-1-butanol ...
... electrons in the central metal atom or ion. 1/2M The unpaired electrons show d-d transition by jumping between t2g and eg orbitals. 1/2M Q3. Write the structures of the each of the following alcohols. 1)3,3-dimethyl cyclopentanol 2)3-chloro-2-methyl-1-butanol ...
VOLUME 3 - ICHO 41-45 _opravené_
... graphs used for grading of practical problems). Nevertheless, the mentioned corrections and changes do not concern the contents and language of the competition problems. The practical problems set in the IChO competitions, contain as a rule some instructions, list of apparatuses available, chemicals ...
... graphs used for grading of practical problems). Nevertheless, the mentioned corrections and changes do not concern the contents and language of the competition problems. The practical problems set in the IChO competitions, contain as a rule some instructions, list of apparatuses available, chemicals ...
Ion Exchange Resins: Catalyst Recovery and Recycle
... onto ion-exchange resin is an equilibrium process driven by noncovalent electrostatic interactions (Scheme 2, strong cation exchanger example). The affinity and selectivity of resins varies with the ionic size and charge of the ions. Generally, the affinity is greatest for large ions with high valen ...
... onto ion-exchange resin is an equilibrium process driven by noncovalent electrostatic interactions (Scheme 2, strong cation exchanger example). The affinity and selectivity of resins varies with the ionic size and charge of the ions. Generally, the affinity is greatest for large ions with high valen ...
Oxidation numbers
... 3. In a molecule or compound, the sum of the oxidation numbers for each element in the molecule or compound will be zero. For example the sum of the oxidation numbers for the elements in water will be 0. 4. In a polyatomic ion the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge. For example the ...
... 3. In a molecule or compound, the sum of the oxidation numbers for each element in the molecule or compound will be zero. For example the sum of the oxidation numbers for the elements in water will be 0. 4. In a polyatomic ion the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge. For example the ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
SCH4U TEXT BOOK
... examples of three types of structural diagrams that are used to depict organic molecules. (The Concepts and Skills Review contains a further review of these types of structural diagrams.) ...
... examples of three types of structural diagrams that are used to depict organic molecules. (The Concepts and Skills Review contains a further review of these types of structural diagrams.) ...
13: Carbonyl Compounds: Ketones, Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids
... Details of Oxidation Number Calculations. The rules used to calculate these numbers are similar to those used for inorganic molecules. The H atoms are assigned an oxidation number of +1 when they are bonded to C or to more electronegative atoms. In contrast, oxygen atoms, whether singly or doubly bo ...
... Details of Oxidation Number Calculations. The rules used to calculate these numbers are similar to those used for inorganic molecules. The H atoms are assigned an oxidation number of +1 when they are bonded to C or to more electronegative atoms. In contrast, oxygen atoms, whether singly or doubly bo ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... – Acids and bases are some of the most important electrolytes. – They can cause color changes in certain dyes called acid-base indicators. – Household acids and bases. – Red cabbage juice as an acid-base indicator. ...
... – Acids and bases are some of the most important electrolytes. – They can cause color changes in certain dyes called acid-base indicators. – Household acids and bases. – Red cabbage juice as an acid-base indicator. ...
Limiting Reactants and Percentage Yield
... Place the balls on an ungreased cookie sheet. 5. Bake at 350 °F for about 10 minutes, or until the cookies are light brown. ...
... Place the balls on an ungreased cookie sheet. 5. Bake at 350 °F for about 10 minutes, or until the cookies are light brown. ...
Naming Aldehydes & Ketones
... 3. Form the parent aldehyde name by dropping the –e from the corresponding alkane name and adding the suffix –al. 4. Other groups attached to the parent chain are named and numbered as we have done before. ...
... 3. Form the parent aldehyde name by dropping the –e from the corresponding alkane name and adding the suffix –al. 4. Other groups attached to the parent chain are named and numbered as we have done before. ...
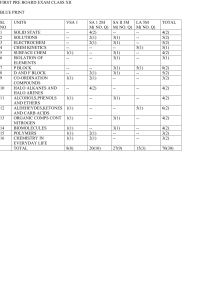
Final Exam
... ____ 15. If the energy of 1.00 mole of photons is 441 kJ, what is the wavelength of the light? a. 271 nm b. 451 nm c. 680 nm d. 732 nm e. 891 nm ____ 16. What type of orbital is designated n = 4, = 3, m = -3? a. 4s b. 4p c. 4d d. 4f e. none ____ 17. Which of the following orbitals might have m = ...
... ____ 15. If the energy of 1.00 mole of photons is 441 kJ, what is the wavelength of the light? a. 271 nm b. 451 nm c. 680 nm d. 732 nm e. 891 nm ____ 16. What type of orbital is designated n = 4, = 3, m = -3? a. 4s b. 4p c. 4d d. 4f e. none ____ 17. Which of the following orbitals might have m = ...
Unit 2
... Members of the alkane family share some distinct chemical and physical properties. Due to their non-polar nature, alkanes are _______in water. They generally have low boiling points, but boiling points ___________ as the number of carbon atoms in the molecule rises. This is due to the fact that when ...
... Members of the alkane family share some distinct chemical and physical properties. Due to their non-polar nature, alkanes are _______in water. They generally have low boiling points, but boiling points ___________ as the number of carbon atoms in the molecule rises. This is due to the fact that when ...
U6B _13-14
... contains only products -the point where the acid and the base are equal in equal moles ...
... contains only products -the point where the acid and the base are equal in equal moles ...
Synthesis and thermal decarbonylation of W(CO)5 complexes
... {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.6[NP(O–C6H4–CO2Prn)(O–C5H4N)]0.4}n (3) have been synthesized by sequential substitution from [NPCl2]n. Their reactions with [W(MeOH)(CO)5] gives the corresponding tungsten carbonyl complexes {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.5[NP(O–C6H4–CO2Prn)(O–C6H4–CN)(W(CO)5)0.4]0.5}n (4), {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.5[NP(O-C ...
... {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.6[NP(O–C6H4–CO2Prn)(O–C5H4N)]0.4}n (3) have been synthesized by sequential substitution from [NPCl2]n. Their reactions with [W(MeOH)(CO)5] gives the corresponding tungsten carbonyl complexes {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.5[NP(O–C6H4–CO2Prn)(O–C6H4–CN)(W(CO)5)0.4]0.5}n (4), {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.5[NP(O-C ...