AP Chem – Unit 1 Part 2 AP Chemistry 2016-‐2017 Unit 1
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
0922085
... B The explosivity range of UN No. 1547 ANILINE is 1.2% to 11% (by volume). What would the properties of a mixture of 0.1% (by volume) of aniline and 99.9% (by volume) of air be? A ...
... B The explosivity range of UN No. 1547 ANILINE is 1.2% to 11% (by volume). What would the properties of a mixture of 0.1% (by volume) of aniline and 99.9% (by volume) of air be? A ...
Amine‐Directed Hydrogen‐Bonded Two‐Dimensional
... substrate/adsorbate interactions.[29] The STM image of the 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene supramolecular structure on Au(111) (Figure 4 a) indicates a network with almost the same level of contrast for all the molecules on the surface. On the other hand, 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid (Figure 4 b, inset) i ...
... substrate/adsorbate interactions.[29] The STM image of the 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene supramolecular structure on Au(111) (Figure 4 a) indicates a network with almost the same level of contrast for all the molecules on the surface. On the other hand, 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid (Figure 4 b, inset) i ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... 34) Why are β-lactams, such as penicillins and cephalosporins, unusually reactive amides? 35) Propose a synthesis of benzonitrile from benzene and any other necessary reagents. 36) Propose a synthesis of 2-phenylethylamine from toluene and any other necessary reagents. 37) Propose a synthesis of met ...
... 34) Why are β-lactams, such as penicillins and cephalosporins, unusually reactive amides? 35) Propose a synthesis of benzonitrile from benzene and any other necessary reagents. 36) Propose a synthesis of 2-phenylethylamine from toluene and any other necessary reagents. 37) Propose a synthesis of met ...
No Slide Title
... • monomers join up the with expulsion of small molecules • not all the original atoms are present in the polymer ...
... • monomers join up the with expulsion of small molecules • not all the original atoms are present in the polymer ...
functional group
... Two reaction mechanisms: SN1 and SN2 cation stability and the Hammond Postulate 5) Additional ways to prepare RX from ROH 6) Halogenation of alkanes: reactivityselectivity principle, radical stability and chain reactions Minto - Lectures 7-8 ...
... Two reaction mechanisms: SN1 and SN2 cation stability and the Hammond Postulate 5) Additional ways to prepare RX from ROH 6) Halogenation of alkanes: reactivityselectivity principle, radical stability and chain reactions Minto - Lectures 7-8 ...
POLYPP - Knockhardy
... • monomers join up the with expulsion of small molecules • not all the original atoms are present in the polymer ...
... • monomers join up the with expulsion of small molecules • not all the original atoms are present in the polymer ...
Isomers
... This occurs most often around C=C The most common cases are around asymmetric non-cyclic alkenes ...
... This occurs most often around C=C The most common cases are around asymmetric non-cyclic alkenes ...
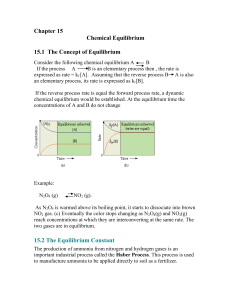
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... nature of the reaction. When K (Kc or Kp) is a very large number, we say that the equilibrium lies to the right. That means that products predominate in the equilibrium mixture. When K is a very small number, we say that the equilibrium lies to the left and reactants predominate in the equilibrium m ...
... nature of the reaction. When K (Kc or Kp) is a very large number, we say that the equilibrium lies to the right. That means that products predominate in the equilibrium mixture. When K is a very small number, we say that the equilibrium lies to the left and reactants predominate in the equilibrium m ...
Chapter 23 The Chemistry of Amines
... two positions “ortho” to the phenolic —OH group, the a-position is the more reactive and gives the observed product. ...
... two positions “ortho” to the phenolic —OH group, the a-position is the more reactive and gives the observed product. ...
Shifting Equilibrium
... The synthesis of ammonia by the Haber-Bosch process is exothermic, as indicated by the energy as heat shown on the product side of the equation. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 92 kJ A high temperature favors the decomposition of ammonia, the endothermic reaction. But at low temperatures, the forward rea ...
... The synthesis of ammonia by the Haber-Bosch process is exothermic, as indicated by the energy as heat shown on the product side of the equation. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 92 kJ A high temperature favors the decomposition of ammonia, the endothermic reaction. But at low temperatures, the forward rea ...
THE MOLE (pp. 159
... 2. But, they do not always tell exactly how many atoms of each element are present in a molecule of the compound. For that one needs the _______________________________. 3. Molecular formula – a formula that gives the type and actual number of atoms in a chemical compound. 4. The molecular formula c ...
... 2. But, they do not always tell exactly how many atoms of each element are present in a molecule of the compound. For that one needs the _______________________________. 3. Molecular formula – a formula that gives the type and actual number of atoms in a chemical compound. 4. The molecular formula c ...
Synopsis
... diastereomeric sulfilimines behave in a stereoconvergent fashion and afford products with the same configuration at carbon. An efficient route to αhydroxy-β-amino acid derivatives AHDA and AHPBA was developed using a common advanced intermediate. The methodology provides aminoalcohol derivatives wit ...
... diastereomeric sulfilimines behave in a stereoconvergent fashion and afford products with the same configuration at carbon. An efficient route to αhydroxy-β-amino acid derivatives AHDA and AHPBA was developed using a common advanced intermediate. The methodology provides aminoalcohol derivatives wit ...
Topic 4
... 2.) All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3.) All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, or Hg22+. 4.) All sulfates are soluble except those containing Hg22+, Pb2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, or Ca2+. Ag2SO4 is slightly soluble. 5.) Al ...
... 2.) All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3.) All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, or Hg22+. 4.) All sulfates are soluble except those containing Hg22+, Pb2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, or Ca2+. Ag2SO4 is slightly soluble. 5.) Al ...
Balancing Reaction Equations Oxidation State Reduction
... Balance each of these two reactions using the eight steps we discussed. Assume that the reactions take place in alkaline solution. ...
... Balance each of these two reactions using the eight steps we discussed. Assume that the reactions take place in alkaline solution. ...
Lesson Plan
... acidic. Strong acids are acids (bases) that have a higher degree of ionization. Thus, even small amount of molecules can produce large number of hydrogen ions (hydroxide ions) resulting in strong acidity (basicity). Even weak acid can produce large number of hydrogen ions when a large amount of mole ...
... acidic. Strong acids are acids (bases) that have a higher degree of ionization. Thus, even small amount of molecules can produce large number of hydrogen ions (hydroxide ions) resulting in strong acidity (basicity). Even weak acid can produce large number of hydrogen ions when a large amount of mole ...
solute
... dissolved in water (aqueous) In order for a solution to carry an electrical current, it must contain ions that are free to move. ...
... dissolved in water (aqueous) In order for a solution to carry an electrical current, it must contain ions that are free to move. ...
Chemistry A level transition - baseline assessment
... we need to know how heavy each atom is. From the periodic table: Mg = 24.3 and S = 32.1 If I weigh out exactly 24.3g of magnesium this will be 1 mole of magnesium, if we counted how many atoms were present in this mass it would be a huge number (6.02 x 1023!!!!), if I weigh out 32.1g of sulfur then ...
... we need to know how heavy each atom is. From the periodic table: Mg = 24.3 and S = 32.1 If I weigh out exactly 24.3g of magnesium this will be 1 mole of magnesium, if we counted how many atoms were present in this mass it would be a huge number (6.02 x 1023!!!!), if I weigh out 32.1g of sulfur then ...
AP Chemistry
... Anion is larger than atom and cation is smaller than atom. Elements in the same column in the periodic table have similar chemical properties. Lattice energy is a measure of ionic bond strength, which is proportional to charge and inversely proportional to size. Single bonds are the weakest (CO, O= ...
... Anion is larger than atom and cation is smaller than atom. Elements in the same column in the periodic table have similar chemical properties. Lattice energy is a measure of ionic bond strength, which is proportional to charge and inversely proportional to size. Single bonds are the weakest (CO, O= ...
Carboxylic Acids - BSAK Chemistry weebly
... happens in two steps. In the first, the carbonoxygen double bond reforms and a chloride ion is pushed off. ...
... happens in two steps. In the first, the carbonoxygen double bond reforms and a chloride ion is pushed off. ...
Substitution and Elimination Reactions . 7.1. Definitions.
... intermediate. Before we talk about how different compounds undergo substitution reactions at different rates, we need to discuss factors that affect the stability of carbocations. Let’s look at the electronic structure of a carbocation, for example the t-Bu cation. The central C atom is electron-def ...
... intermediate. Before we talk about how different compounds undergo substitution reactions at different rates, we need to discuss factors that affect the stability of carbocations. Let’s look at the electronic structure of a carbocation, for example the t-Bu cation. The central C atom is electron-def ...