1 - Academics
... In essence, what this means is: a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a p ...
... In essence, what this means is: a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a p ...
Lecture notes
... for different substances. The constant used depends on whether we are considering molar heat capacity, C or specific heat capacity, c. Molar heat capacity of a substance is defined as: the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 M of the substance by 1 ˚C. The specific heat capacity of ...
... for different substances. The constant used depends on whether we are considering molar heat capacity, C or specific heat capacity, c. Molar heat capacity of a substance is defined as: the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 M of the substance by 1 ˚C. The specific heat capacity of ...
California Standards Practice - Student Edition
... 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic ...
... 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic ...
Answers to Selected Problems
... 21. boron-11 22. Silicon-28 must be by far the most abundant. The other two isotopes must be present in very small amounts. ...
... 21. boron-11 22. Silicon-28 must be by far the most abundant. The other two isotopes must be present in very small amounts. ...
What is the pH of a 0.100 M
... What happens if more OH- is added to water? The equilibrium of water, H3O+ and OH- means if we know either the concentration of H3O+ or the concentration of OH- in an aqueous solution, then we know the concentration of the other. Example: What is the pH of 0.150 M CH3NH2? ...
... What happens if more OH- is added to water? The equilibrium of water, H3O+ and OH- means if we know either the concentration of H3O+ or the concentration of OH- in an aqueous solution, then we know the concentration of the other. Example: What is the pH of 0.150 M CH3NH2? ...
2003
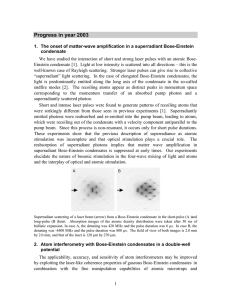
... 10. Distillation of Bose-Einstein condensates in a double-well potential The characteristic feature of Bose-Einstein condensation is the accumulation of a macroscopic number of particles in the lowest quantum state. Condensate fragmentation, the macroscopic occupation of two or more quantum states, ...
... 10. Distillation of Bose-Einstein condensates in a double-well potential The characteristic feature of Bose-Einstein condensation is the accumulation of a macroscopic number of particles in the lowest quantum state. Condensate fragmentation, the macroscopic occupation of two or more quantum states, ...
Alkane
... For RX compound, when X = Cl or F ,the b.p. will be higher than alkane which have the same molecular mass due to the dipole-dipole interaction between the molecules. Solubility As the interaction between water and RX are quite different, (H-bond and dipole-dipole),they are only sightly soluble in wa ...
... For RX compound, when X = Cl or F ,the b.p. will be higher than alkane which have the same molecular mass due to the dipole-dipole interaction between the molecules. Solubility As the interaction between water and RX are quite different, (H-bond and dipole-dipole),they are only sightly soluble in wa ...
Substitution Rxns-a-Sn2-12-quesx
... at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected mechanism. In this new pathway, called the roundabout mechanism, chlor ...
... at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected mechanism. In this new pathway, called the roundabout mechanism, chlor ...
Chapter13
... equilibrium partial pressure of I2(g) is greater than 1.0 atm, the reaction will be spontaneous. B. This process becomes less spontaneous at higher temperatures because more iodine must be vaporized. C. As the temperature increases and the system approaches equilibrium, ΔG° will decrease. When the s ...
... equilibrium partial pressure of I2(g) is greater than 1.0 atm, the reaction will be spontaneous. B. This process becomes less spontaneous at higher temperatures because more iodine must be vaporized. C. As the temperature increases and the system approaches equilibrium, ΔG° will decrease. When the s ...
How QuikSoil 2600 works
... times consistent with the needs of most facilities. Because less carbon dioxide is generated and volatilized, more weight (density) and more carbon remain in the finished product and fewer greenhouse gases are exhausted. Because more ammonia and other free nitrogen compounds are fixed rather than ex ...
... times consistent with the needs of most facilities. Because less carbon dioxide is generated and volatilized, more weight (density) and more carbon remain in the finished product and fewer greenhouse gases are exhausted. Because more ammonia and other free nitrogen compounds are fixed rather than ex ...
13.1 Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Alcohols and Phenols 13.1
... If the alcohol is converted into a better leaving group, then a strong base can be used to promote E2. ...
... If the alcohol is converted into a better leaving group, then a strong base can be used to promote E2. ...
Redox Reactions C12-1-10
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
Organic Nomenclature
... nonmetals such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, or the halogens. The term organic comes from the old idea that all carbon containing compounds had to be produced by a living organism. While living organisms produce a vast number of organic compounds, many of these compounds, as well as many compounds ...
... nonmetals such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, or the halogens. The term organic comes from the old idea that all carbon containing compounds had to be produced by a living organism. While living organisms produce a vast number of organic compounds, many of these compounds, as well as many compounds ...
Organic Chemistry
... CH3OH methyl alcohol, methanol, “wood alcohol”. Impurity in moonshine; causes blindness CH3CH2OH ethyl alcohol, ethanol, “alcohol” Prepared by fermentation of sugar-containing plant material. ...
... CH3OH methyl alcohol, methanol, “wood alcohol”. Impurity in moonshine; causes blindness CH3CH2OH ethyl alcohol, ethanol, “alcohol” Prepared by fermentation of sugar-containing plant material. ...
Balancing Redox Equations
... Before we balance a Redox equation lets first refresh our memory on how to calculate oxidation numbers. Oxidation Number - The charge that an atom would have if the compound in which it were found were ionic. The rules: 1) The sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a molecule must be equal to ...
... Before we balance a Redox equation lets first refresh our memory on how to calculate oxidation numbers. Oxidation Number - The charge that an atom would have if the compound in which it were found were ionic. The rules: 1) The sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a molecule must be equal to ...
Test-tube Reactions - University of Manitoba
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
... electrons are partially transferred from hydrogen to oxygen. Oxygen is a more electronegative element than hydrogen. The electron pair in the covalent bond is shifted toward oxygen resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on hydrogen. Both reactions above are exam ...
Quantum Energy Regression using Scattering Transforms
... chemical nature of atom k which determines its nuclear charge zk , and hence which atomic density should be substituted. Isolated atomic densities are pre-computed from Density Functional Theory calculations for every distinct atomic species present in a molecular database. The electron density mode ...
... chemical nature of atom k which determines its nuclear charge zk , and hence which atomic density should be substituted. Isolated atomic densities are pre-computed from Density Functional Theory calculations for every distinct atomic species present in a molecular database. The electron density mode ...
File
... 5.E.3 If a chemical or physical process is not driven by both entropy and enthalpy changes, then the Gibbs free energy change can be used to determine whether the process is thermodynamically favored. 5.E.4 External sources of energy can be used to drive change in cases where the Gibbs free ener ...
... 5.E.3 If a chemical or physical process is not driven by both entropy and enthalpy changes, then the Gibbs free energy change can be used to determine whether the process is thermodynamically favored. 5.E.4 External sources of energy can be used to drive change in cases where the Gibbs free ener ...
United States Patent
... in the IS-position. Osuka et al .• "Synthesis of Benzochlorin Monomer. Dimer, and Porphyrin-Benzochlorin Heterodimer from 5-Aryl- and 5J5-Diaryloctaethylporphyrins," Bull. Chem. Soc. lpn., 65.3322-30 (1992). Some of these derivatives have shown strong absorptions in the visible region around 700 run ...
... in the IS-position. Osuka et al .• "Synthesis of Benzochlorin Monomer. Dimer, and Porphyrin-Benzochlorin Heterodimer from 5-Aryl- and 5J5-Diaryloctaethylporphyrins," Bull. Chem. Soc. lpn., 65.3322-30 (1992). Some of these derivatives have shown strong absorptions in the visible region around 700 run ...
Exam 2
... • Detach the data sheet from the centre of this book during reading time. • Write your student number in the space provided above on this page. • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provide ...
... • Detach the data sheet from the centre of this book during reading time. • Write your student number in the space provided above on this page. • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provide ...