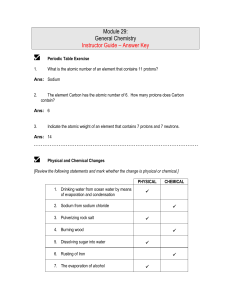
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
... Ans: A physical change in matter is a change in the form of matter but not in its chemical identity. A chemical change in matter is a change in which one or more kinds of matter transform into a new kind of matter. ...
... Ans: A physical change in matter is a change in the form of matter but not in its chemical identity. A chemical change in matter is a change in which one or more kinds of matter transform into a new kind of matter. ...
Kinetic study on carbonation of crude Li2CO3 with CO2
... High purity Li2CO3 can be used for the production of medicines, electronic grade crystals, such as LiNbO3 and LiTaO3 crystals, and high purity lithium metal. With the development of batteries and single crystal industries in the world, the demand for it has been dramatically growing in recent years, ...
... High purity Li2CO3 can be used for the production of medicines, electronic grade crystals, such as LiNbO3 and LiTaO3 crystals, and high purity lithium metal. With the development of batteries and single crystal industries in the world, the demand for it has been dramatically growing in recent years, ...
2011 HSC Examination - Chemistry
... acid. The concentration of the citric acid is determined by titration with NaOH. The sodium hydroxide solution is prepared by dissolving 4.000 g of NaOH pellets in water to give 1.000 L of solution. This solution is standardised by titrating 25.00 mL with a 0.1011 mol L–1 standardised solution of HC ...
... acid. The concentration of the citric acid is determined by titration with NaOH. The sodium hydroxide solution is prepared by dissolving 4.000 g of NaOH pellets in water to give 1.000 L of solution. This solution is standardised by titrating 25.00 mL with a 0.1011 mol L–1 standardised solution of HC ...
19_Worked_Examples
... (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transferred from the hotter object to the colder one. (Section 5.1) Thus, heat is transferred from the hot metal to the cooler water. The final temperature, after the metal and water ach ...
... (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transferred from the hotter object to the colder one. (Section 5.1) Thus, heat is transferred from the hot metal to the cooler water. The final temperature, after the metal and water ach ...
Chemistry HSC - The Bored of Studies Community
... and can be synthesised from many different hydrocarbons. Three ways: 1. Thermal cracking – requires very high temps and generally not used. End products hard to control since many places where bonds could break, early method. Accelerates reaction and drives equilibrium to reactants. 2. Catalytic cra ...
... and can be synthesised from many different hydrocarbons. Three ways: 1. Thermal cracking – requires very high temps and generally not used. End products hard to control since many places where bonds could break, early method. Accelerates reaction and drives equilibrium to reactants. 2. Catalytic cra ...
Academic Assessment Unit Academic Assessment Unit Course
... Description of the course: - This course deals with study of the general principles of physical chemistry, including thermodynamics, solution, kinetics, thermo chemistry, spontaneity of reaction, electrochemistry, and nuclear reactions. Teaching methodology: - white board, discussions, & solving ...
... Description of the course: - This course deals with study of the general principles of physical chemistry, including thermodynamics, solution, kinetics, thermo chemistry, spontaneity of reaction, electrochemistry, and nuclear reactions. Teaching methodology: - white board, discussions, & solving ...
Equilibrium 5
... 5. At a certain temperature, a 1.00-L flask initially contained 0.298 moles of PCl3 (g) and 8.7 x 10-3 moles of PCl5 (g). After the system had reached equilibrium, 2.00 x 10-3 moles of Cl2 (g) was found in the flask. Gaseous PCl5 decomposes according to the reaction: PCl5 (g) ...
... 5. At a certain temperature, a 1.00-L flask initially contained 0.298 moles of PCl3 (g) and 8.7 x 10-3 moles of PCl5 (g). After the system had reached equilibrium, 2.00 x 10-3 moles of Cl2 (g) was found in the flask. Gaseous PCl5 decomposes according to the reaction: PCl5 (g) ...
CHemiStrY - Cabrillo College
... Repeatability: May be taken a total of 1 time. Presents a one semester survey of general and organic chemistry as preparation for careers in the allied health sciences. It is not appropriate for premed, dental or veterinary students nor is it intended for allied health students requiring two semeste ...
... Repeatability: May be taken a total of 1 time. Presents a one semester survey of general and organic chemistry as preparation for careers in the allied health sciences. It is not appropriate for premed, dental or veterinary students nor is it intended for allied health students requiring two semeste ...
Qsp Ksp Qsp > Ksp
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
- Lancaster EPrints
... methodology employed in the obtention of the density to be analysed: in fact, such analyses can be applied to experimental densities derived from low temperature X-ray diffraction (XRD) data [6]. The most popular of these density-based approaches is the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIM) a ...
... methodology employed in the obtention of the density to be analysed: in fact, such analyses can be applied to experimental densities derived from low temperature X-ray diffraction (XRD) data [6]. The most popular of these density-based approaches is the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIM) a ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... species, both ionic and molecular present in aqueous solution for the reaction. H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- --> Na+ + Cl- + H2O ...
... species, both ionic and molecular present in aqueous solution for the reaction. H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- --> Na+ + Cl- + H2O ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical reactions to occur energy is needed. The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the activation energy. A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction ...
... ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical reactions to occur energy is needed. The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the activation energy. A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction ...
Possible pieces of introduction:
... doctrine, in chemistry, and on the mountains.” This description allows the reader to connect to Levi’s world, a world in which chemistry is an essential part of life, by listing his trade juxtaposed with nature and religion, one of which is likely to be connected as intimately to the reader’s life a ...
... doctrine, in chemistry, and on the mountains.” This description allows the reader to connect to Levi’s world, a world in which chemistry is an essential part of life, by listing his trade juxtaposed with nature and religion, one of which is likely to be connected as intimately to the reader’s life a ...
Mechanistic notation
... The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed. Tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary, which are more stable than primary, which are more stable than methyl. Tertiary alcohols react faster than secondary, which react faster than primary, which react faster than methanol. ...
... The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed. Tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary, which are more stable than primary, which are more stable than methyl. Tertiary alcohols react faster than secondary, which react faster than primary, which react faster than methanol. ...
Science SOL CH
... Students can do research on radioactive isotopes to explore the following questions: o What factors influence the stability of a nuclide? o What are the different types of nuclear decay? o What happens when an atom undergoes nuclear decay? o Is there a way to predict what type of decay a particular ...
... Students can do research on radioactive isotopes to explore the following questions: o What factors influence the stability of a nuclide? o What are the different types of nuclear decay? o What happens when an atom undergoes nuclear decay? o Is there a way to predict what type of decay a particular ...