XeCu Covalent Bonding in XeCuF and XeCuCl, Characterized by
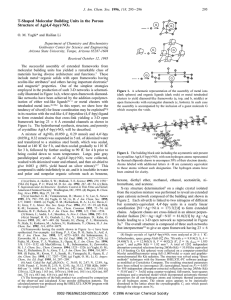
... Abstract: XeCu covalent bonding has been found in the complexes XeCuF and XeCuCl. The molecules were characterized by Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy, supported by MP2 ab initio calculations. The complexes were prepared by laser ablation of Cu in the presence of Xe and SF6 or Cl2 and stabil ...
... Abstract: XeCu covalent bonding has been found in the complexes XeCuF and XeCuCl. The molecules were characterized by Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy, supported by MP2 ab initio calculations. The complexes were prepared by laser ablation of Cu in the presence of Xe and SF6 or Cl2 and stabil ...
Catalyst characterization: characterization techniques
... Usually mercury porosimetry based on that principle allows to study pores in the range 7.5-1.5 X lo4 nm (2000 atm). The technique utilizes only commercial apparatuses. Working under pressure requires some care because it can cause compression of the solid or breakage of the pore walls (this occurs i ...
... Usually mercury porosimetry based on that principle allows to study pores in the range 7.5-1.5 X lo4 nm (2000 atm). The technique utilizes only commercial apparatuses. Working under pressure requires some care because it can cause compression of the solid or breakage of the pore walls (this occurs i ...
Unit 4 Chemistry of Carbon
... Solid, does not boil Boiling point decreases with an increase in branching. Very low solubility in water as they are nonpolar. ...
... Solid, does not boil Boiling point decreases with an increase in branching. Very low solubility in water as they are nonpolar. ...
ch17
... K therefore indicates the extent of a reaction, i.e., how far a reaction proceeds towards the products at a given temperature. A small value for K indicates that the reaction yields little product before reaching equilibrium. The reaction favors the reactants. ...
... K therefore indicates the extent of a reaction, i.e., how far a reaction proceeds towards the products at a given temperature. A small value for K indicates that the reaction yields little product before reaching equilibrium. The reaction favors the reactants. ...
Organic Chemistry II Introduction
... Named by adding -nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name, Nitrile carbon is numbered 1 Complex nitriles are named as derivatives of carboxylic acids. Replace -ic acid or -oic acid ending with -onitrile ...
... Named by adding -nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name, Nitrile carbon is numbered 1 Complex nitriles are named as derivatives of carboxylic acids. Replace -ic acid or -oic acid ending with -onitrile ...
Acyl Anions Derived from Enol Ethers
... Reversal of carbonyl group polarity (Umpolung) The carbonyl group is electrophilic at the carbon atom and hence is susceptible to attack by nucleophilic reagents. Thus, the carbonyl group reacts as a formyl cation or as an acyl cation. A reversal of the positive polarity of the carbonyl group so it ...
... Reversal of carbonyl group polarity (Umpolung) The carbonyl group is electrophilic at the carbon atom and hence is susceptible to attack by nucleophilic reagents. Thus, the carbonyl group reacts as a formyl cation or as an acyl cation. A reversal of the positive polarity of the carbonyl group so it ...
www.fahadsacademy.com
... 1. Ionic compounds are hard crystalline solids with flat sides and regular shapes because the ions are arrnged in straight rows in strong ionic bonds. 2. Ionic compounds have very high melting points and boiling points. 3. The strong forces holding ionic compounds prevents them to evaporate easily. ...
... 1. Ionic compounds are hard crystalline solids with flat sides and regular shapes because the ions are arrnged in straight rows in strong ionic bonds. 2. Ionic compounds have very high melting points and boiling points. 3. The strong forces holding ionic compounds prevents them to evaporate easily. ...
metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactoins
... transition metals for cross-coupling reactions.7 The rate, yield, and scope of palladium-catalyzed crosscoupling reactions are influenced by both the reaction partners and the choice of ligands, allowing for a wide substrate scope through judicious choice of these parameters. Historically, palladiu ...
... transition metals for cross-coupling reactions.7 The rate, yield, and scope of palladium-catalyzed crosscoupling reactions are influenced by both the reaction partners and the choice of ligands, allowing for a wide substrate scope through judicious choice of these parameters. Historically, palladiu ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... geometry or orientation, is wrong and successful collision cannot occur. ...
... geometry or orientation, is wrong and successful collision cannot occur. ...
First Semester Final Review
... a. Mg(OH)2(s) b. (NH4)2CO3(s) c. CuSO4(s) d. (NH4)2SO4(s) e. Sr(NO3)2(s) 45. In which of the following processes are covalent bonds broken? a. I2(s) I2(g) b. CO2(s) CO2(g) c. NaCl(s) NaCl(l) d. C(diamond) C(g) e. Fe(s) Fe(l) 46. What is the final concentration of barium ions, [Ba2+], in so ...
... a. Mg(OH)2(s) b. (NH4)2CO3(s) c. CuSO4(s) d. (NH4)2SO4(s) e. Sr(NO3)2(s) 45. In which of the following processes are covalent bonds broken? a. I2(s) I2(g) b. CO2(s) CO2(g) c. NaCl(s) NaCl(l) d. C(diamond) C(g) e. Fe(s) Fe(l) 46. What is the final concentration of barium ions, [Ba2+], in so ...
graduate school of pharmaceutical sciences faculty of
... The comprehensive structural reorganization of the entire Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences was completed in 1997. The Graduate School, which is known as the Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, offers courses for advanced instruction and opportunity for research; the staff includes ...
... The comprehensive structural reorganization of the entire Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences was completed in 1997. The Graduate School, which is known as the Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, offers courses for advanced instruction and opportunity for research; the staff includes ...
Organics – Naming the Molecules
... stuff added to it. These might be extra carbon branches or halogens. It is important for us to be able to know exactly what and where they are. This forms the very first part of the name (before the prefix). Here is how we do it: Count the number of carbons in from the closest side (along the ...
... stuff added to it. These might be extra carbon branches or halogens. It is important for us to be able to know exactly what and where they are. This forms the very first part of the name (before the prefix). Here is how we do it: Count the number of carbons in from the closest side (along the ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structure
... related to the fact that valence shells contain a single s orbital and three p orbitals that can accommodate up to eight electrons, and it is these orbitals that are most often involved in forming covalent bonds between nonmetals in covalent compounds. When determining whether elements have satisfie ...
... related to the fact that valence shells contain a single s orbital and three p orbitals that can accommodate up to eight electrons, and it is these orbitals that are most often involved in forming covalent bonds between nonmetals in covalent compounds. When determining whether elements have satisfie ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
... formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
無投影片標題 - SKHSBS
... Nomenclature of Alkenes 1. Determine the stem name by selecting the longest possible straight chain containing the C = C double bond and use the ending ‘-ene’ 2. Number the parent chain so as to include both carbon atoms of the double bond, and begin numbering with the end of the chain nearer the C ...
... Nomenclature of Alkenes 1. Determine the stem name by selecting the longest possible straight chain containing the C = C double bond and use the ending ‘-ene’ 2. Number the parent chain so as to include both carbon atoms of the double bond, and begin numbering with the end of the chain nearer the C ...
DNA/RNA nucleotides and nucleosides: direct measurement of
... Because we monitor the population loss to the ground state, these measurements provide accurate description of the non-radiative decay by internal conversion. The range of lifetimes measured is from 520 to 980 fs. Vibrational relaxation and solvation occur on a time scale less than or comparable to ...
... Because we monitor the population loss to the ground state, these measurements provide accurate description of the non-radiative decay by internal conversion. The range of lifetimes measured is from 520 to 980 fs. Vibrational relaxation and solvation occur on a time scale less than or comparable to ...