Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... • Carboxylic acid derivatives have an acyl carbon bonded to a group Y that can leave • A tetrahedral intermediate is formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
... • Carboxylic acid derivatives have an acyl carbon bonded to a group Y that can leave • A tetrahedral intermediate is formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
Reaction Energy
... • The enthalpy change that occurs during the complete combustion of one mole of a substance is called the enthalpy of combustion of the substance. • Enthalpy of combustion is defined in terms of one mole of reactant, whereas the enthalpy of formation is defined in terms of one mole of product. • ∆H ...
... • The enthalpy change that occurs during the complete combustion of one mole of a substance is called the enthalpy of combustion of the substance. • Enthalpy of combustion is defined in terms of one mole of reactant, whereas the enthalpy of formation is defined in terms of one mole of product. • ∆H ...
440400 - IDEALS @ Illinois
... increase with successive ring fluorine substitution, and the sequence follows aqueous phase acidity of the fluorophenols. This behavior is similar to what has been observed in the case of phenol-water complexes. The major contributions to binding interactions of phenol-benzene and phenol-water com ...
... increase with successive ring fluorine substitution, and the sequence follows aqueous phase acidity of the fluorophenols. This behavior is similar to what has been observed in the case of phenol-water complexes. The major contributions to binding interactions of phenol-benzene and phenol-water com ...
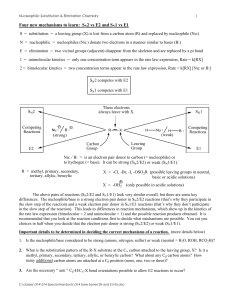
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
Non-native transition metal monoxide nanostructures
... h-CoO phase is significant due to not only fundamental scientific interest in synthetic strategies and mechanisms for new materials but also technological interest in newly emerging unique magnetic and electrochemical properties of these materials. Selective syntheses of colloidal h-CoO and c-CoO Ther ...
... h-CoO phase is significant due to not only fundamental scientific interest in synthetic strategies and mechanisms for new materials but also technological interest in newly emerging unique magnetic and electrochemical properties of these materials. Selective syntheses of colloidal h-CoO and c-CoO Ther ...
File
... Measuring Equilibrium Concentrations - We often need to find the concentration of each chemical in an equilibrium mixture. Equilibrium concentrations can be obtained in ______ steps: 1. Find the ______ concentration of each species. 2. Use the balanced chemical equation to find the ________ in each ...
... Measuring Equilibrium Concentrations - We often need to find the concentration of each chemical in an equilibrium mixture. Equilibrium concentrations can be obtained in ______ steps: 1. Find the ______ concentration of each species. 2. Use the balanced chemical equation to find the ________ in each ...
Carbonyl Compounds - Thomas Tallis Science
... Carboxylic acids are named using the suffix –oic acid. Methanoic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid and is found in bee and ant stings. Ethanoic acid is the acid that gives vinegar its sharp taste and smell. It is also important in the chemical industry and about 6.5 million tonnes are used worldw ...
... Carboxylic acids are named using the suffix –oic acid. Methanoic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid and is found in bee and ant stings. Ethanoic acid is the acid that gives vinegar its sharp taste and smell. It is also important in the chemical industry and about 6.5 million tonnes are used worldw ...
honors chemistry harvard-westlake second semester final exam
... of 30 multiple choice questions, 4 major required problems, your choice of 4 out of 6 minor problems, and your choice of 1 out of 32 essays. The essays are somewhat more involved than usual. For the exam you will be provided with a periodic table, an electronegativity table, the Standard Reduction P ...
... of 30 multiple choice questions, 4 major required problems, your choice of 4 out of 6 minor problems, and your choice of 1 out of 32 essays. The essays are somewhat more involved than usual. For the exam you will be provided with a periodic table, an electronegativity table, the Standard Reduction P ...
1 Introduction to Hybrid Materials
... selective, directional directional nonselective predominantly irreversible ...
... selective, directional directional nonselective predominantly irreversible ...
Experiment 22
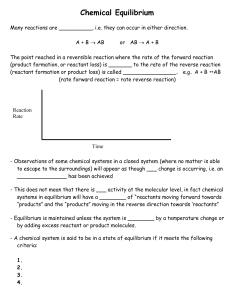
... equilibrium system will shift to the left on being heated if the reaction is exothermic (H < 0, Kc goes down). It will shift to the right if the reaction is endothermic (H > 0, Kc goes up). Again, since we can change temperatures very markedly, we can shift equilibria a long, long way. An endother ...
... equilibrium system will shift to the left on being heated if the reaction is exothermic (H < 0, Kc goes down). It will shift to the right if the reaction is endothermic (H > 0, Kc goes up). Again, since we can change temperatures very markedly, we can shift equilibria a long, long way. An endother ...
Fundamentals
... It’s easier to check your result (and memorize equations) when you know what the units are. ...
... It’s easier to check your result (and memorize equations) when you know what the units are. ...
Chemistry - Bulletin < Brown
... Concentration Requirements How does life work at the molecular level? This question is at the core of the concentration program Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. In earlier years of this discipline, the focus was on structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates and small ...
... Concentration Requirements How does life work at the molecular level? This question is at the core of the concentration program Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. In earlier years of this discipline, the focus was on structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates and small ...
the chemistry of smell
... 1. R-Carvone and S-Carvone are special isomers of each other. They have the same chemical formula and very similar structures, but they have distinct smells. R-Carvone has a minty smell, while S-Carvone smells like caraway seeds (as you’ve seen in Part B) or dill. The difference in smell is subtle f ...
... 1. R-Carvone and S-Carvone are special isomers of each other. They have the same chemical formula and very similar structures, but they have distinct smells. R-Carvone has a minty smell, while S-Carvone smells like caraway seeds (as you’ve seen in Part B) or dill. The difference in smell is subtle f ...
13_lecture_ppt
... corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
... corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
Chemical bonding
... subtraction. Let ψA and ψB represent the wave functions of the two combining atomic orbitals A and B taking part in chemical combination. 21) Ans: Atomic orbitals 1. Atomic orbitals are monocentric. 2. Atomic orbitals have simple shapes like spherical or dumb-bell. Molecular orbitals 1. Molecular o ...
... subtraction. Let ψA and ψB represent the wave functions of the two combining atomic orbitals A and B taking part in chemical combination. 21) Ans: Atomic orbitals 1. Atomic orbitals are monocentric. 2. Atomic orbitals have simple shapes like spherical or dumb-bell. Molecular orbitals 1. Molecular o ...
Organic compounds containing Nitrogen
... (iii) Aniline and N-methylamiline. Ans. i) Methylamine and dimethyl amine by isocyanide test: Methyl amine (primary) responds to carbyl amaine reaction. When heated with chloroform and KOH, it produces foul smell. Dimethyl amine (secondary) does not respond to this test. ...
... (iii) Aniline and N-methylamiline. Ans. i) Methylamine and dimethyl amine by isocyanide test: Methyl amine (primary) responds to carbyl amaine reaction. When heated with chloroform and KOH, it produces foul smell. Dimethyl amine (secondary) does not respond to this test. ...
IPC: Essential Learning Outcomes By the IPC District Team
... • Use Bohr’s model to place the electrons in their energy levels. • Compare and contrast Bohr’s model with the modern model of the atom. • Understand the organization of the periodic table and the periodic law. • Distinguish between atomic number, atomic mass and mass number. • Explain and calculate ...
... • Use Bohr’s model to place the electrons in their energy levels. • Compare and contrast Bohr’s model with the modern model of the atom. • Understand the organization of the periodic table and the periodic law. • Distinguish between atomic number, atomic mass and mass number. • Explain and calculate ...