ECG Workbook - Lakeridge Health
... Most lead II ECG monitoring machines have the ability to look at three different frontal leads. When the lead selection is made by turning the switch to a specific lead, the polarity of the leads changes amongst the white, red and black leads as noted above. ...
... Most lead II ECG monitoring machines have the ability to look at three different frontal leads. When the lead selection is made by turning the switch to a specific lead, the polarity of the leads changes amongst the white, red and black leads as noted above. ...
RECENT TRENDS IN TREATMENT OF ARRHYTHMIAS
... depolarisation in the cardiac muscle. The most recent antiarrhythmic drugs are included togethier. A little is known about it electrophysiologic properties, and more studies are still needed. Some of them e.g. pranolium may be of help in protection in patients who are at high risk of sudden coronary ...
... depolarisation in the cardiac muscle. The most recent antiarrhythmic drugs are included togethier. A little is known about it electrophysiologic properties, and more studies are still needed. Some of them e.g. pranolium may be of help in protection in patients who are at high risk of sudden coronary ...
Definition:
... * Prolonged QT interval . These changes are termed CVA pattern & usually resolved with time . ...
... * Prolonged QT interval . These changes are termed CVA pattern & usually resolved with time . ...
Preview Sample 1 - Test Bank, Manual Solution, Solution Manual
... Give each student one sheet of paper. Then have the students line up in the order in which blood flows. Once they are correctly in line, have students discuss the function of the structures they represent. 3. Have students role-play the qualities of the heart, including automaticity, excitability, c ...
... Give each student one sheet of paper. Then have the students line up in the order in which blood flows. Once they are correctly in line, have students discuss the function of the structures they represent. 3. Have students role-play the qualities of the heart, including automaticity, excitability, c ...
Case study 2 (continued)
... – History of hypertension treated with a diuretic – In the recovery area after an uncomplicated hernia repair – Nurses report the sudden onset of tachycardia ...
... – History of hypertension treated with a diuretic – In the recovery area after an uncomplicated hernia repair – Nurses report the sudden onset of tachycardia ...
EKG Self Study Guide
... -15 large boxes is a three second strip! -30 large boxes represents a six second strip! -For irregularly irregular rhythms, try to calculate rate with a decent time interval, preferably greater than a 3 second strip. ...
... -15 large boxes is a three second strip! -30 large boxes represents a six second strip! -For irregularly irregular rhythms, try to calculate rate with a decent time interval, preferably greater than a 3 second strip. ...
Zool 352 Lecture 33
... • 1. shift activation of L channels to more negative voltages, causing threshold to be reached sooner; increase current carried by L channels. • 2. Increase If, causing hypolarization at beginning of prepotential to be smaller. ...
... • 1. shift activation of L channels to more negative voltages, causing threshold to be reached sooner; increase current carried by L channels. • 2. Increase If, causing hypolarization at beginning of prepotential to be smaller. ...
2-Heart sounds2015-03-08 09:541.7 MB
... • The mitral area (apex): This is found in the left 5th intercostal space, approximately 1 cm medial to the mid-clavicular line. • The tricuspid area: This is found just to the left of the lower border of the sternum. • The pulmonary area: This is found in the left 2nd intercostal space at the ster ...
... • The mitral area (apex): This is found in the left 5th intercostal space, approximately 1 cm medial to the mid-clavicular line. • The tricuspid area: This is found just to the left of the lower border of the sternum. • The pulmonary area: This is found in the left 2nd intercostal space at the ster ...
Electrocardiography
... heart takes over, by default • The closer to the AV node, the more the escape beat will resemble normal QRS • The closer to the ventricle, the more wide and bizarre the QRS will appear ...
... heart takes over, by default • The closer to the AV node, the more the escape beat will resemble normal QRS • The closer to the ventricle, the more wide and bizarre the QRS will appear ...
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block - e
... Previous discussions have focused on first-degree heart block, which is an abnormal slowing of the impulse through the cardiac conduction system, and second-degree heart block, which includes varying degrees of partial blocks. In contrast, third-degree heart block involves a complete blockade of ele ...
... Previous discussions have focused on first-degree heart block, which is an abnormal slowing of the impulse through the cardiac conduction system, and second-degree heart block, which includes varying degrees of partial blocks. In contrast, third-degree heart block involves a complete blockade of ele ...
Arrhythmias 3
... Delayed conduction through/near the AVN Usually asymptomatic Narrow QRS complex indicates block within AVN Wide QRS complex indicates His-Purkinje block. Causes MI Myocarditis/endocarditis SLE ...
... Delayed conduction through/near the AVN Usually asymptomatic Narrow QRS complex indicates block within AVN Wide QRS complex indicates His-Purkinje block. Causes MI Myocarditis/endocarditis SLE ...
08_Cardiac arrhythmyas
... • correct rhythm with frequency of heartbeats 60-100 per 1 min. • the P wave is positive in II, III, AVF leads, negative - in the AVR leads, permanent form of P wave • a complex QRS follows by every P waveR (if there is not а-v-blockade). • Interval of P-Q>0.12 (if there are not additional ways of l ...
... • correct rhythm with frequency of heartbeats 60-100 per 1 min. • the P wave is positive in II, III, AVF leads, negative - in the AVR leads, permanent form of P wave • a complex QRS follows by every P waveR (if there is not а-v-blockade). • Interval of P-Q>0.12 (if there are not additional ways of l ...
template - Developing Anaesthesia
... The nomenclature is actually misleading, as the pathology is a delay in conduction rather than a total “block”. 1 The abnormality of itself is clinically benign. It may be a normal finding in some people such as athletes, however it may also indicate an underlying cardiac abnormality that may or may ...
... The nomenclature is actually misleading, as the pathology is a delay in conduction rather than a total “block”. 1 The abnormality of itself is clinically benign. It may be a normal finding in some people such as athletes, however it may also indicate an underlying cardiac abnormality that may or may ...
ECG Waveform tip.pdf
... Q wave represents septal depolarization. First negative deflection after P wave. R wave is first positive deflection after P wave. S wave is first negative deflection after R wave. Measured from beginning of first waveform to end of last waveform in complex Duration: Less than .10 second (use .12 fo ...
... Q wave represents septal depolarization. First negative deflection after P wave. R wave is first positive deflection after P wave. S wave is first negative deflection after R wave. Measured from beginning of first waveform to end of last waveform in complex Duration: Less than .10 second (use .12 fo ...
File - Health Careers
... When the sinus node and atria both fail When the sinus node, atria and AV node all fail ...
... When the sinus node and atria both fail When the sinus node, atria and AV node all fail ...
Care of Patient With Dysrhythmias
... – Review medications as some (Digoxin) can cause dysrhythmias. – Conducts a physical assessment to observe for signs of diminished cardiac output (changes in LOC. Inspect the skin (may be pale and cool). Assess signs of fluid retention (neck vein distention; crackles and wheezes in the lungs). – Aus ...
... – Review medications as some (Digoxin) can cause dysrhythmias. – Conducts a physical assessment to observe for signs of diminished cardiac output (changes in LOC. Inspect the skin (may be pale and cool). Assess signs of fluid retention (neck vein distention; crackles and wheezes in the lungs). – Aus ...
Physiology 5
... during a cardiac cycle that keeps repeating itself each time. It does not record any of the mechanical changes , muscle contraction or relaxation that occurs in the heart. During this cycle, there is atrial depolarization followed by ventricular depolarization then atrial and ventricular repolarizat ...
... during a cardiac cycle that keeps repeating itself each time. It does not record any of the mechanical changes , muscle contraction or relaxation that occurs in the heart. During this cycle, there is atrial depolarization followed by ventricular depolarization then atrial and ventricular repolarizat ...
Stage #1 - IEEE Real World Engineering Projects
... – Often regarded as the traditional form of ECG recording ...
... – Often regarded as the traditional form of ECG recording ...
pace-maker
... generator of normal sinus rhythm. It is a group of cells positioned on the wall of the right atrium, near the entrance of the superior vena cava. These cells are modified cardiac myocytes. Though they possess some contractile filaments, they do not contract. Although all of the heart's cells have th ...
... generator of normal sinus rhythm. It is a group of cells positioned on the wall of the right atrium, near the entrance of the superior vena cava. These cells are modified cardiac myocytes. Though they possess some contractile filaments, they do not contract. Although all of the heart's cells have th ...
The Multiphase Functional Cardiogram A Clinical
... electrical power-generating source, reduced to a dipole with a pair of + & - signs. Conventionally, each lead is sampled at a rate of 200-500Hz, and then analyzed individually and sequentially in the time domain. This produces a simple model of the heart – a signal of millivolts over microseconds – ...
... electrical power-generating source, reduced to a dipole with a pair of + & - signs. Conventionally, each lead is sampled at a rate of 200-500Hz, and then analyzed individually and sequentially in the time domain. This produces a simple model of the heart – a signal of millivolts over microseconds – ...
Slide ()
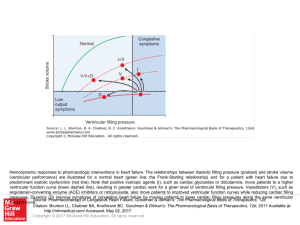
... Hemodynamic responses to pharmacologic interventions in heart failure. The relationships between diastolic filling pressure (preload) and stroke volume (ventricular performance) are illustrated for a normal heart (green line; the Frank-Starling relationship) and for a patient with heart failure due ...
... Hemodynamic responses to pharmacologic interventions in heart failure. The relationships between diastolic filling pressure (preload) and stroke volume (ventricular performance) are illustrated for a normal heart (green line; the Frank-Starling relationship) and for a patient with heart failure due ...
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II —ECG
... The electrocardiogram is useful because it provides a non-invasive, if indirect, snapshot of heart function. The horizontal axis represents time. Heart rate can be determined by measuring the time between successive R peaks. Myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) produce changes in the ECG such as a ...
... The electrocardiogram is useful because it provides a non-invasive, if indirect, snapshot of heart function. The horizontal axis represents time. Heart rate can be determined by measuring the time between successive R peaks. Myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) produce changes in the ECG such as a ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.