ECG Rhythm Interpretation Workbook
... Tachycardia is > 100 bpm. All of us can increase our heart rate, for example when we exercise. This is physiological and is called Sinus Tachycardia. This is not an arrhythmia. There are other tachycardia’s which are caused by different rhythms, many of which are pathological. It can be very difficu ...
... Tachycardia is > 100 bpm. All of us can increase our heart rate, for example when we exercise. This is physiological and is called Sinus Tachycardia. This is not an arrhythmia. There are other tachycardia’s which are caused by different rhythms, many of which are pathological. It can be very difficu ...
The Construction of a Volumetric Cardiac Model for Real-time ECG Simulation
... The electrocardiograph is one of the most useful diagnostic medical devices ever created. It offers a real-time non-invasive technique for monitoring cardiac activity. Figure 1 illustrates the heart’s electrical conduction system and also describes the typical arrangement of the 3 standard ECG leads ...
... The electrocardiograph is one of the most useful diagnostic medical devices ever created. It offers a real-time non-invasive technique for monitoring cardiac activity. Figure 1 illustrates the heart’s electrical conduction system and also describes the typical arrangement of the 3 standard ECG leads ...
How does the heart function?
... Disorders of the heart . . . • When a coronary blood vessel becomes blocked, heart tissue can die from lack of oxygen in minutes • This region of dead tissue is called an infarct • A “heart attack” is technically a myocardial infarction • If recognized and treated early, the heart tissue may suffer ...
... Disorders of the heart . . . • When a coronary blood vessel becomes blocked, heart tissue can die from lack of oxygen in minutes • This region of dead tissue is called an infarct • A “heart attack” is technically a myocardial infarction • If recognized and treated early, the heart tissue may suffer ...
Chest pain and syncope key slides
... • If there is ST elevation, it will be a STEMI if: • Any ST dep except V1 or aVR (allowed in acute pericarditis) • ST elevation III > II • Horizontal or convex up ST elevation • New Q waves ...
... • If there is ST elevation, it will be a STEMI if: • Any ST dep except V1 or aVR (allowed in acute pericarditis) • ST elevation III > II • Horizontal or convex up ST elevation • New Q waves ...
234 Electrocardio
... Read through all of the following passage and then fill in the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The cardiac cycle is initiated and controlled by the heart itself. Cardiac muscle is said to be ......................... since it will contract and relax of its own accord. The beat is ini ...
... Read through all of the following passage and then fill in the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The cardiac cycle is initiated and controlled by the heart itself. Cardiac muscle is said to be ......................... since it will contract and relax of its own accord. The beat is ini ...
Chapter 7 Basic ECG Monitoring
... • In the mid 1800s, it was discovered that the heart’s electrical activity could be measured externally by placing an electrode on a person’s skin. • In 1901 Dr. Einthoven improved the hearts measurement with electrical activity with a timed record. He named these measured waves or rhythmic movement ...
... • In the mid 1800s, it was discovered that the heart’s electrical activity could be measured externally by placing an electrode on a person’s skin. • In 1901 Dr. Einthoven improved the hearts measurement with electrical activity with a timed record. He named these measured waves or rhythmic movement ...
Experiment 4 - UniMAP Portal
... The electrical activity of the heart Cardiac contractions are not dependent upon a nerve supply. However, innervation by the parasympathetic (vagus) and sympathetic nerves does modify the basic cardiac rhythm. Thus the central nervous system can affect this rhythm. The best known example of this is ...
... The electrical activity of the heart Cardiac contractions are not dependent upon a nerve supply. However, innervation by the parasympathetic (vagus) and sympathetic nerves does modify the basic cardiac rhythm. Thus the central nervous system can affect this rhythm. The best known example of this is ...
Intrinsic Conduction System
... • Initiates the depolarization impulse which, in turn, generates an action potential that spreads throughout the atria to the AV node. • Sets the overall pace of the heartbeat. Internodal Pathway • Located in the walls of the atria. • Links the SA node to the AV node. • Distributes the action potent ...
... • Initiates the depolarization impulse which, in turn, generates an action potential that spreads throughout the atria to the AV node. • Sets the overall pace of the heartbeat. Internodal Pathway • Located in the walls of the atria. • Links the SA node to the AV node. • Distributes the action potent ...
File
... An electrical impulse originates in the modified myocardial tissue of the sinoatrial(SA) node, causing the atria to contact This is known as atrial depolarization(this is the first part of the cardiac cycle) The first impulse as recorded on the graph paper is termed the P wave, the impulses continue ...
... An electrical impulse originates in the modified myocardial tissue of the sinoatrial(SA) node, causing the atria to contact This is known as atrial depolarization(this is the first part of the cardiac cycle) The first impulse as recorded on the graph paper is termed the P wave, the impulses continue ...
File
... contracts, and repolarises (regains charge) when it relaxes. - Patches with wires are placed on the patients chest and wires are connected to a monitor. - Electric charges are recorded by an electrocardiograph, as a electrocardiogram/ECG which shows the patients normal heart rhythm. ...
... contracts, and repolarises (regains charge) when it relaxes. - Patches with wires are placed on the patients chest and wires are connected to a monitor. - Electric charges are recorded by an electrocardiograph, as a electrocardiogram/ECG which shows the patients normal heart rhythm. ...
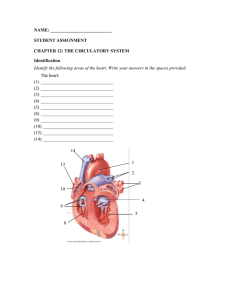
NAME
... C. aortic semilunar D. pulmonary semilunar 27. To where does the superior vena cava carry blood? A. left ventricle B. coronary arteries C. right atrium D. pulmonary veins 28. What is the innermost coat of an artery that comes into direct contact with blood called? A. lumen B. tunica externa C. tunic ...
... C. aortic semilunar D. pulmonary semilunar 27. To where does the superior vena cava carry blood? A. left ventricle B. coronary arteries C. right atrium D. pulmonary veins 28. What is the innermost coat of an artery that comes into direct contact with blood called? A. lumen B. tunica externa C. tunic ...
ELEKTROCARDIOGRAFI LEARNING OUTCOME TINJAUAN TEORI
... ST segment distinct from the T wave is usually absent. More often the ST-T wave is a smooth, continuous waveform beginning with the J-point (end of QRS), slowly rising to the peak of the T and followed by a rapid descent to the isoelectric baseline or the onset of the U wave. This gives rise to an a ...
... ST segment distinct from the T wave is usually absent. More often the ST-T wave is a smooth, continuous waveform beginning with the J-point (end of QRS), slowly rising to the peak of the T and followed by a rapid descent to the isoelectric baseline or the onset of the U wave. This gives rise to an a ...
8228 PM-783-HCG
... The new HeartScan ECG Monitor senses the heart waveform and indicates potential ECG abnormalities. The ECG waveform from the heart shows when the heart contracts and relaxes and gives the heart rhythm of consecutive heartbeats. In a healthy heart the waveform pattern shows a regular shape and rhythm ...
... The new HeartScan ECG Monitor senses the heart waveform and indicates potential ECG abnormalities. The ECG waveform from the heart shows when the heart contracts and relaxes and gives the heart rhythm of consecutive heartbeats. In a healthy heart the waveform pattern shows a regular shape and rhythm ...
Just Move It
... heart rate, conversational pace Vigorous PA: breathing and heart rate, only words or short sentences possible ...
... heart rate, conversational pace Vigorous PA: breathing and heart rate, only words or short sentences possible ...
MiniLab Analyzing EKGs
... An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in the right atrium (the sinoatrial node) which initiates an electrical sequence. This impulse then passes down natural conduction pathways ...
... An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in the right atrium (the sinoatrial node) which initiates an electrical sequence. This impulse then passes down natural conduction pathways ...
12 Analyzing Heart EKG KJ
... An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in the right atrium (the sinoatrial node) which initiates an electrical sequence. This impulse then passes down natural conduction pathways ...
... An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in the right atrium (the sinoatrial node) which initiates an electrical sequence. This impulse then passes down natural conduction pathways ...
12 Analyzing Heart EKG
... An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in the right atrium (the sinoatrial node) which initiates an electrical sequence. This impulse then passes down natural conduction pathways ...
... An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in the right atrium (the sinoatrial node) which initiates an electrical sequence. This impulse then passes down natural conduction pathways ...
myocardial infarction
... phase, the T waves become tall and narrow. This configuration is referred to as hyperacute or peaked T waves. Within a few hours, these hyperacute T waves invert. Next, the ST segments elevate, a pattern that usually lasts from several hours to several days. In addition to the ST segment elevations ...
... phase, the T waves become tall and narrow. This configuration is referred to as hyperacute or peaked T waves. Within a few hours, these hyperacute T waves invert. Next, the ST segments elevate, a pattern that usually lasts from several hours to several days. In addition to the ST segment elevations ...
Intraoperative Detection of Rate Dependent Left Bundle Branch Block
... Rate dependent left bundle branch block (RDLBBB) is an uncommon case. RDLBBB is defined as an intraventricular conduction defect that may return, if only temporarily, to sinus rhythm at lower heart rates. It appears when the heart rate exceeds a certain critical value. Although RDLBBB is usually ben ...
... Rate dependent left bundle branch block (RDLBBB) is an uncommon case. RDLBBB is defined as an intraventricular conduction defect that may return, if only temporarily, to sinus rhythm at lower heart rates. It appears when the heart rate exceeds a certain critical value. Although RDLBBB is usually ben ...
Myocardial infarction - Philadelphia University
... phase, the T waves become tall and narrow. This configuration is referred to as hyperacute or peaked T waves. Within a few hours, these hyperacute T waves invert. Next, the ST segments elevate, a pattern that usually lasts from several hours to several days. In addition to the ST segment elevations ...
... phase, the T waves become tall and narrow. This configuration is referred to as hyperacute or peaked T waves. Within a few hours, these hyperacute T waves invert. Next, the ST segments elevate, a pattern that usually lasts from several hours to several days. In addition to the ST segment elevations ...
DOC
... Exercise and the heart How does the heart move blood around the body? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Where in the body would you find the heart? (be exact) __________________________________________ ...
... Exercise and the heart How does the heart move blood around the body? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Where in the body would you find the heart? (be exact) __________________________________________ ...
Digital High Pass Filter - webwww03 - poseidon.heig
... • Testing of circuit for tachycardia and bradycardia could be easier as database has records of such arrhythmias • WAV files are transferred to circuit via a modified speaker phone. The right and left ear pieces correspond to the right arm and left arm ...
... • Testing of circuit for tachycardia and bradycardia could be easier as database has records of such arrhythmias • WAV files are transferred to circuit via a modified speaker phone. The right and left ear pieces correspond to the right arm and left arm ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.