Physiology – Biology 219
... Understand the major differences between the fetal circulation and the adult (after birth) circulation pattern. What are two major right-to-left shunts in the fetal circulation? In what parts of the fetal circulation is the blood: a) fully oxygenated; b) mixed oxygenated and deoxygenated; c) deoxyge ...
... Understand the major differences between the fetal circulation and the adult (after birth) circulation pattern. What are two major right-to-left shunts in the fetal circulation? In what parts of the fetal circulation is the blood: a) fully oxygenated; b) mixed oxygenated and deoxygenated; c) deoxyge ...
Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiovascular Physiology
... right atrium and spreads throughout entire heart ...
... right atrium and spreads throughout entire heart ...
Physiological basis of the care of the care of the elderly
... Review of cardiac structure and function Circulation is established by electrical system of the heart Left side of heart produces enough force to overcome systemic resistance Effective circulation due in part to one way valves between the chambers of the heart Effective circulation is also dependen ...
... Review of cardiac structure and function Circulation is established by electrical system of the heart Left side of heart produces enough force to overcome systemic resistance Effective circulation due in part to one way valves between the chambers of the heart Effective circulation is also dependen ...
O2-1 Significance of Premature Restriction or Closure of Foramen
... features. A small aortic isthmus mimicking coarctation of the aorta, relatively small left ventricular cavity imitating hypoplastic left heart, partial obstruction of left ventricular inflow, and premature atrial contractions were other additional findings. One fetus who was born prematurely at 26 w ...
... features. A small aortic isthmus mimicking coarctation of the aorta, relatively small left ventricular cavity imitating hypoplastic left heart, partial obstruction of left ventricular inflow, and premature atrial contractions were other additional findings. One fetus who was born prematurely at 26 w ...
Circulatory System
... ○ Heart Disease: 611,000 people die In the U.S. each year from Heart Disease. ○ Heart Failure: This does not mean that your heart is failing it just means that it is not pumping as fast as it should. This causes water retention which leads to swelling and shortness of breath ○ Cancer: Leukemia also ...
... ○ Heart Disease: 611,000 people die In the U.S. each year from Heart Disease. ○ Heart Failure: This does not mean that your heart is failing it just means that it is not pumping as fast as it should. This causes water retention which leads to swelling and shortness of breath ○ Cancer: Leukemia also ...
cardiovascular system review answer key 2
... ventricle to keep them from being pushed inside the atria during ventricular contraction. » Called your “heart strings” – SEMI-LUNAR valves between ventricle and artery • What are the two valves called between the ventricles and arteries? PULMONARY AND AORTIC_ 9. What supplies the heart muscle itsel ...
... ventricle to keep them from being pushed inside the atria during ventricular contraction. » Called your “heart strings” – SEMI-LUNAR valves between ventricle and artery • What are the two valves called between the ventricles and arteries? PULMONARY AND AORTIC_ 9. What supplies the heart muscle itsel ...
About this Book
... underlying physiologic mechanisms, and treatments for diseases of the heart. The busy bioengineer working on cardiac devices will find here the complete critical background needed to understand cardiac pacing, defibrillation, cardiac repair using stem cell therapy, robotics, less invasive cardiac su ...
... underlying physiologic mechanisms, and treatments for diseases of the heart. The busy bioengineer working on cardiac devices will find here the complete critical background needed to understand cardiac pacing, defibrillation, cardiac repair using stem cell therapy, robotics, less invasive cardiac su ...
Module 5 Cardiac
... More sensitive to fluid volume changes Less cardiac muscle compliance Inability to regulate stroke volume until muscle fibers fully developed at around 5 years of age Increased metabolic rate and increased oxygen demand Little cardiac output reserve H & H concentrations are higher as appropriate for ...
... More sensitive to fluid volume changes Less cardiac muscle compliance Inability to regulate stroke volume until muscle fibers fully developed at around 5 years of age Increased metabolic rate and increased oxygen demand Little cardiac output reserve H & H concentrations are higher as appropriate for ...
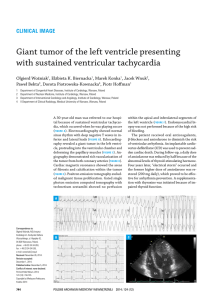
Giant tumor of the left ventricle presenting with sustained ventricular
... POLSKIE ARCHIWUM MEDYCYNY WEWNĘTRZNEJ 2014; 124 (12) ...
... POLSKIE ARCHIWUM MEDYCYNY WEWNĘTRZNEJ 2014; 124 (12) ...
Left Ventricular Regional Contraction Abnormalities by
... Maastricht University Medical Center, Department of Cardiology, Maastricht, The Netherlands Duke University Medical Center, Department of Cardiology, Durham, North Carolina, USA* ...
... Maastricht University Medical Center, Department of Cardiology, Maastricht, The Netherlands Duke University Medical Center, Department of Cardiology, Durham, North Carolina, USA* ...
Download(252)
... • When an impulse originates anywhere in the atria (SA node, atrial cells, AV node, Bundle of His) and then is conducted normally through the ventricles, the QRS will be narrow (0.04 - 0.12 s). ...
... • When an impulse originates anywhere in the atria (SA node, atrial cells, AV node, Bundle of His) and then is conducted normally through the ventricles, the QRS will be narrow (0.04 - 0.12 s). ...
CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA
... tachycardia (AVNRT)- Junctionalarryhythmias These tachycardia are due to re-entry in a circuit involving AV node. It produces regular tachycardia with a rate of 120-240/min. Episode may last from few seconds to many hours ...
... tachycardia (AVNRT)- Junctionalarryhythmias These tachycardia are due to re-entry in a circuit involving AV node. It produces regular tachycardia with a rate of 120-240/min. Episode may last from few seconds to many hours ...
Arrhythmias and Dysrhythmias - American Academy of Family
... • In patients with nonvalvular AF, the CHA2DS2-VASc score is recommended for assessment of stroke risk. (Class 1: LOE B) January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American ...
... • In patients with nonvalvular AF, the CHA2DS2-VASc score is recommended for assessment of stroke risk. (Class 1: LOE B) January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American ...
Chapter 20
... 1. A 56-year-old male presented to the emergency department with chest pain and shortness of breath that occurred suddenly. He was admitted to the unit for management of a myocardial infarction and heart failure. Measurement of his heart size and ejection fraction (EF) at the catheterization showed ...
... 1. A 56-year-old male presented to the emergency department with chest pain and shortness of breath that occurred suddenly. He was admitted to the unit for management of a myocardial infarction and heart failure. Measurement of his heart size and ejection fraction (EF) at the catheterization showed ...
Daisuke Sato, Ph.D.
... cycling. Nonlinear dynamics of cardiac phenomena including alternans, early and delayed afterdepolarizations, Ca sparks, Ca waves. Synopsis: Sudden cardiac death is the leading cause of death in the United States. Our knowledge of sudden cardiac death is still limited. CAST (Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppr ...
... cycling. Nonlinear dynamics of cardiac phenomena including alternans, early and delayed afterdepolarizations, Ca sparks, Ca waves. Synopsis: Sudden cardiac death is the leading cause of death in the United States. Our knowledge of sudden cardiac death is still limited. CAST (Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppr ...
Nursing Consideration
... D -iets high in green leafy vegetables can shorten PT E -xpect 1.5 to 2 times longer PT if on anticoagulation ...
... D -iets high in green leafy vegetables can shorten PT E -xpect 1.5 to 2 times longer PT if on anticoagulation ...
presentation source
... prepares for division into the right and left atria by expanding. At this time, communication between the sinus venosus and the atrium is via the right side of the atrium. This is the first indication that the sinus venosus is becoming a part of the future right atrium. ...
... prepares for division into the right and left atria by expanding. At this time, communication between the sinus venosus and the atrium is via the right side of the atrium. This is the first indication that the sinus venosus is becoming a part of the future right atrium. ...
Peri-operative Cardiac Arrhythmias
... the cause for autonomic changes resulting in intra-operative blood pressure and heart rate changes. The majority of anaesthetic agents have direct myocardial depressant effects, resulting in reduced contractility and reduced sympathetic stimulation of the peripheral vasculature. The net effect is a ...
... the cause for autonomic changes resulting in intra-operative blood pressure and heart rate changes. The majority of anaesthetic agents have direct myocardial depressant effects, resulting in reduced contractility and reduced sympathetic stimulation of the peripheral vasculature. The net effect is a ...
Effects of PPV on the Cardiovascular, Cerebral, Renal and other
... yet it's the most complex of all known living structures. Up to one trillion nerve cells work together and coordinate the physical actions and mental processes that set humans apart from other species. Photograph by Fred Hossler/Getty Images ...
... yet it's the most complex of all known living structures. Up to one trillion nerve cells work together and coordinate the physical actions and mental processes that set humans apart from other species. Photograph by Fred Hossler/Getty Images ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias
... Impulse then travels to Bundle of His, then enters both Right and Left Bundle Branches The impulse is then carried through Purkinje fibers to ventricular myocardial tissue ...
... Impulse then travels to Bundle of His, then enters both Right and Left Bundle Branches The impulse is then carried through Purkinje fibers to ventricular myocardial tissue ...
File
... 1. All of these help conduct the electrical current of the heart (think of one long action potential that causes all of the heart muscle cells to contract). The SA node has an electrical signal that it sends across both atria, causing them to contract simultaneously. When it reaches the AV node (rig ...
... 1. All of these help conduct the electrical current of the heart (think of one long action potential that causes all of the heart muscle cells to contract). The SA node has an electrical signal that it sends across both atria, causing them to contract simultaneously. When it reaches the AV node (rig ...
Heart Dissection Questions
... 1. Why are pig hearts used to study the anatomy of the human heart? 2. How can you tell which side of the heart is the ventral surface? 3. How many chambers are found in the mammalian heart? What other group of organisms would have this same number of chambers? 4. What is the advantage in having thi ...
... 1. Why are pig hearts used to study the anatomy of the human heart? 2. How can you tell which side of the heart is the ventral surface? 3. How many chambers are found in the mammalian heart? What other group of organisms would have this same number of chambers? 4. What is the advantage in having thi ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.