Lecture 15
... INHIBITORY and RELEASING hormones from hypothalamus III. Thyroid Gland A. Location, Structure and Hormones 1. anterior neck region, overlying the trachea 2. two lateral lobes connected by the isthmus a. thyroid hormone (TH) - regulates rate of metabolism; Iodine key part of hormone b. calcitonin - l ...
... INHIBITORY and RELEASING hormones from hypothalamus III. Thyroid Gland A. Location, Structure and Hormones 1. anterior neck region, overlying the trachea 2. two lateral lobes connected by the isthmus a. thyroid hormone (TH) - regulates rate of metabolism; Iodine key part of hormone b. calcitonin - l ...
Atypical or typical adrenocorticotropic hormone-producing pulmonary carcinoids and the usefulness of 11C-5-hydroxytryptophan
... revealed no central peripheral ratio of adrenocorticotropic hormone. Computed tomography and 111Indiumpentetreoide somatostatin receptor scintigraphy could not visualize any ectopic tumor. The patient was referred for an 11C-5-hydroxytryptophan positron emission tomography, and a small 8mm nodule in ...
... revealed no central peripheral ratio of adrenocorticotropic hormone. Computed tomography and 111Indiumpentetreoide somatostatin receptor scintigraphy could not visualize any ectopic tumor. The patient was referred for an 11C-5-hydroxytryptophan positron emission tomography, and a small 8mm nodule in ...
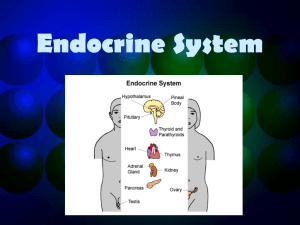
Endocrine System
... • Regulates the effects of hormones on the body functions. • Controls growth, development metabolism and maintaining homeostasis. • Works closely with the nervous system. Nerve impulses direct the secretion of hormones. ...
... • Regulates the effects of hormones on the body functions. • Controls growth, development metabolism and maintaining homeostasis. • Works closely with the nervous system. Nerve impulses direct the secretion of hormones. ...
File ap notes chapter 45
... Reception (signal binds to receptor protein in or on target cell) Water soluble hormones bind to surface receptor triggering activation of internal proteins in ...
... Reception (signal binds to receptor protein in or on target cell) Water soluble hormones bind to surface receptor triggering activation of internal proteins in ...
Endocrine Vocabulary Quiz B Matching Answer Definition Term the
... 15. an enlargement of the thyroid gland that results from a lack of iodine in the diet. Causes a knot to appear in the anterior neck. 16. chemical messengers released into the blood by endocrine glands that affect specific cells or organs. 17. can enter the nucleus, diffuse through the plasma membra ...
... 15. an enlargement of the thyroid gland that results from a lack of iodine in the diet. Causes a knot to appear in the anterior neck. 16. chemical messengers released into the blood by endocrine glands that affect specific cells or organs. 17. can enter the nucleus, diffuse through the plasma membra ...
Endo voc qz
... 16. chemical messengers released into the blood by endocrine glands that affect specific cells or organs. 17. can enter the nucleus, diffuse through the plasma membranes of target cells, activate genes to transcribe mRNA for protein synthesis & bind to receptor proteins in the nucleus. They are also ...
... 16. chemical messengers released into the blood by endocrine glands that affect specific cells or organs. 17. can enter the nucleus, diffuse through the plasma membranes of target cells, activate genes to transcribe mRNA for protein synthesis & bind to receptor proteins in the nucleus. They are also ...
Neuroradiology Neuropatholgy Conference, Dec 2010
... Most often, the CNS tumor is a meningioma. Other reported types of intracranial tumors harboring a metastasis include 8th-nerve schwannoma, glioma, hemangioblastoma, and pituitary adenoma. Breast and lung are the most common primary sites, with breast being the most common site. Renal cell carcinoma ...
... Most often, the CNS tumor is a meningioma. Other reported types of intracranial tumors harboring a metastasis include 8th-nerve schwannoma, glioma, hemangioblastoma, and pituitary adenoma. Breast and lung are the most common primary sites, with breast being the most common site. Renal cell carcinoma ...
multiple endocrine neoplasia
... angiofibromas, collagenomas, and lipomas. They should be sought because they can act as markers for this syndrome. Other lesions Lesions in other tissues have been reported, but their relationship remains controversial. Carcinoid tumors of the foregut, midgut, and thymus occur in about 10%, an ...
... angiofibromas, collagenomas, and lipomas. They should be sought because they can act as markers for this syndrome. Other lesions Lesions in other tissues have been reported, but their relationship remains controversial. Carcinoid tumors of the foregut, midgut, and thymus occur in about 10%, an ...
Chemical signals in animals
... Hormones are compounds produced in one part of the body and transported to another location to produce specific responses; small amount s can induce substantial responses. Chemical signals produced by the body are mostly produced by glands. Hormones either affect a target effector organ directly or ...
... Hormones are compounds produced in one part of the body and transported to another location to produce specific responses; small amount s can induce substantial responses. Chemical signals produced by the body are mostly produced by glands. Hormones either affect a target effector organ directly or ...
Aim: How does the Endocrine System work in our body?
... Work together to maintain stable levels of blood sugar Insulin- released when levels of blood sugar are high Glucagon- causes the liver to release stored glucose from cells into the body when glucose is low ...
... Work together to maintain stable levels of blood sugar Insulin- released when levels of blood sugar are high Glucagon- causes the liver to release stored glucose from cells into the body when glucose is low ...
Science Grade (Unit 6)
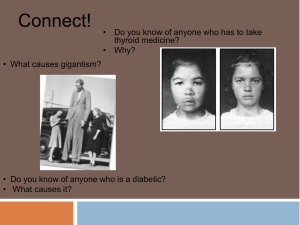
... 3. What is gigantism, dwarfism, and acromegaly and what hormone is involved in their development? 4. What are the true names of the hormones that are abbreviated GH, TSH, FSH, LH, PRL, and ACTH? 5. Release of eggs from the ovaries is controlled by what hormone? 6. Which glands does the anterior pitu ...
... 3. What is gigantism, dwarfism, and acromegaly and what hormone is involved in their development? 4. What are the true names of the hormones that are abbreviated GH, TSH, FSH, LH, PRL, and ACTH? 5. Release of eggs from the ovaries is controlled by what hormone? 6. Which glands does the anterior pitu ...
File
... 1) The endocrine system: a) releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body b) releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs c) produces effects that can last for hours, days, or even longer d) can alter gene activity of cells ...
... 1) The endocrine system: a) releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body b) releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs c) produces effects that can last for hours, days, or even longer d) can alter gene activity of cells ...
chapter-16-worksheet
... Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1. Sort the list into major endocrine glands and secondary endocrine tissues: Pituitary, adipose cells, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, cells in the cell intestine, stomach, kidney, heart) Major endocrine glands ...
... Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1. Sort the list into major endocrine glands and secondary endocrine tissues: Pituitary, adipose cells, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, cells in the cell intestine, stomach, kidney, heart) Major endocrine glands ...
Endocrine System
... Functions of Hormones – The varying actions performed by hormones may be fast-acting (e.g. Adrenaline is a hormone that up the heart and breathing rates when we get a fright), or may be slow-acting (e.g. Human Growth Hormone regulates the many body processes involved in ...
... Functions of Hormones – The varying actions performed by hormones may be fast-acting (e.g. Adrenaline is a hormone that up the heart and breathing rates when we get a fright), or may be slow-acting (e.g. Human Growth Hormone regulates the many body processes involved in ...
The Endocrine System
... CNS controls hypothalamus, which regulates release of hormones from pituitary Hormones can act on nearby cells or be transported through blood until they reach a cell with matching receptor (target cell) Target cell carries the receptor protein which will bind to hormone, changing its shape Cellular ...
... CNS controls hypothalamus, which regulates release of hormones from pituitary Hormones can act on nearby cells or be transported through blood until they reach a cell with matching receptor (target cell) Target cell carries the receptor protein which will bind to hormone, changing its shape Cellular ...
AMEND AMEND - Association for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
... Tumors of the pancreatic islet cells occur in up to 75% (3 in 4) of MEN1 patients. The pancreas is responsible for producing juices (digestive enzymes) to aid food digestion. It also produces hormones to ...
... Tumors of the pancreatic islet cells occur in up to 75% (3 in 4) of MEN1 patients. The pancreas is responsible for producing juices (digestive enzymes) to aid food digestion. It also produces hormones to ...
Endocrine System
... The hypothalamus is a tiny cluster of brain cells which transmits messages from the body to the brain. The pituitary gland releases many hormones which affect growth, sexual development, metabolism and the system of reproduction. The pineal gland (or pineal body) produces melatonin, a hormone which ...
... The hypothalamus is a tiny cluster of brain cells which transmits messages from the body to the brain. The pituitary gland releases many hormones which affect growth, sexual development, metabolism and the system of reproduction. The pineal gland (or pineal body) produces melatonin, a hormone which ...
The Pituitary Gland
... kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, this hormone is responsible for initiating uterine contractions, mild during monthly menstrual flow and strong during labor contractions. ...
... kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, this hormone is responsible for initiating uterine contractions, mild during monthly menstrual flow and strong during labor contractions. ...
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 4
... tumors originated from studies of MENX, a MEN-like syndrome in the rat. This multitumor syndrome was discovered about 10 years ago when a Sprague-Dawleyderived rat colony spontaneously started to develop multiple neuroendocrine tumors at a young age, including anterior pituitary adenoma, adrenal and ...
... tumors originated from studies of MENX, a MEN-like syndrome in the rat. This multitumor syndrome was discovered about 10 years ago when a Sprague-Dawleyderived rat colony spontaneously started to develop multiple neuroendocrine tumors at a young age, including anterior pituitary adenoma, adrenal and ...
Hormones & Endocrine System
... Introduction Endocrine System – Sum of all hormone secreting cells and ...
... Introduction Endocrine System – Sum of all hormone secreting cells and ...
Differences Similarities
... •How is the endocrine system similar to the nervous system? •How is the endocrine system different from the nervous system? •How do hormones get to where they are needed? •Name some endocrine glands. ...
... •How is the endocrine system similar to the nervous system? •How is the endocrine system different from the nervous system? •How do hormones get to where they are needed? •Name some endocrine glands. ...
endocrine system ppt
... Create a Poster on an endocrine organ including the following information: ...
... Create a Poster on an endocrine organ including the following information: ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.