Chapter 25 - Austin Community College
... Location: Just inferior to the stomach and in the first loop of the duodenum approximately in the middle of the abdomen. Structure:- mixed gland (endocrine/exocrine); spongy-like appearance. Exocrine cells produce digestive enzymes. Pancreatic “Islet of Langerhans” are endocrine cells. Hormones prod ...
... Location: Just inferior to the stomach and in the first loop of the duodenum approximately in the middle of the abdomen. Structure:- mixed gland (endocrine/exocrine); spongy-like appearance. Exocrine cells produce digestive enzymes. Pancreatic “Islet of Langerhans” are endocrine cells. Hormones prod ...
Wk 7. Assessment of the Endocrine and Metabolic System
... produces melatonin (8) Gonads ovaries (females) and testes (males) 2) Hormones classified into three types: amines, polypeptides, steroids (1) Amines Amines are derived from tyrosine, essential amino acid found in most proteins. (2) Polypeptides protein compounds made of many amino acids connected b ...
... produces melatonin (8) Gonads ovaries (females) and testes (males) 2) Hormones classified into three types: amines, polypeptides, steroids (1) Amines Amines are derived from tyrosine, essential amino acid found in most proteins. (2) Polypeptides protein compounds made of many amino acids connected b ...
Endocrine System
... • Puberty is the transformation from nonreproductive child to a reproductively able adult. • The changes that occur in the body are the results of hormones instructing body parts to produce new things or function new ways. • These changes are long term and happen gradually. • Example – Breast develo ...
... • Puberty is the transformation from nonreproductive child to a reproductively able adult. • The changes that occur in the body are the results of hormones instructing body parts to produce new things or function new ways. • These changes are long term and happen gradually. • Example – Breast develo ...
The Endocrine System
... The thyroid gland is located in the front of the windpipe called the (trachea) and just below the larynx or Adams Apple on the neck. The Thyroid gland regulates your (Metabolism) or your ability to break down food and use it for energy. ...
... The thyroid gland is located in the front of the windpipe called the (trachea) and just below the larynx or Adams Apple on the neck. The Thyroid gland regulates your (Metabolism) or your ability to break down food and use it for energy. ...
Chapter 23: Endocrine Emergencies
... Diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body’s ability to metabolize glucose is impaired. It is characterized by the passage of large quantities of urine containing glucose, significant thirst, and deterioration of body function. Endocrine emergencies can be difficult to assess because they af ...
... Diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body’s ability to metabolize glucose is impaired. It is characterized by the passage of large quantities of urine containing glucose, significant thirst, and deterioration of body function. Endocrine emergencies can be difficult to assess because they af ...
Ready for Review - Paramedic EMS Zone
... hormones produced by these glands. Secondary adrenal insufficiency is defined as a lack of ACTH secretion from the pituitary gland. Acute adrenal insufficiency is referred to as an Addisonian crisis, which may result from an acute exacerbation of chronic insufficiency, usually brought on by a period ...
... hormones produced by these glands. Secondary adrenal insufficiency is defined as a lack of ACTH secretion from the pituitary gland. Acute adrenal insufficiency is referred to as an Addisonian crisis, which may result from an acute exacerbation of chronic insufficiency, usually brought on by a period ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... – a structure of both the nervous and endocrine systems – produces releasing hormones, sent to pituitary gland ...
... – a structure of both the nervous and endocrine systems – produces releasing hormones, sent to pituitary gland ...
physiology hormone-1
... Proteins, peptides and amines are not lipid soluble thus they cannot pass across the plasma membranes of cells. The receptors for such hormones are present on the outside of the cell membrane. Binding of the hormone with its membrane receptor causes the production within the cell of a second messeng ...
... Proteins, peptides and amines are not lipid soluble thus they cannot pass across the plasma membranes of cells. The receptors for such hormones are present on the outside of the cell membrane. Binding of the hormone with its membrane receptor causes the production within the cell of a second messeng ...
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
2.3 Chemical Communication by Hisrich
... name for an organ that secretes something) that signals a system to do something. Some hormones are short-term (like adrenalin speeding up heart rate) and some are long term (like growth hormone) The same hormone can be secreted by multiple organs (for example, the ovaries and adrenal glands bot ...
... name for an organ that secretes something) that signals a system to do something. Some hormones are short-term (like adrenalin speeding up heart rate) and some are long term (like growth hormone) The same hormone can be secreted by multiple organs (for example, the ovaries and adrenal glands bot ...
endocrine1
... 2. Starting with the arrival of carbohydrates in the stomach list the sequence of events, cell types, and hormone(s) that comprise a feedforward mechanism. What is the purpose of this feedforward mechanism? 3. Beginning with the ingestion of a large amount of sugar, list the sequence of events in a ...
... 2. Starting with the arrival of carbohydrates in the stomach list the sequence of events, cell types, and hormone(s) that comprise a feedforward mechanism. What is the purpose of this feedforward mechanism? 3. Beginning with the ingestion of a large amount of sugar, list the sequence of events in a ...
Book`s PowerPoint on Chapter 37
... Starr/Taggart’s Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life, Chapter 37 ...
... Starr/Taggart’s Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life, Chapter 37 ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... acromegaly: no height increase due to bones ossifying; but diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary ...
... acromegaly: no height increase due to bones ossifying; but diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary ...
GLANDS AT A GLANCE
... • Goiter is an enlargement of the gland due to either excess or deficiency of dietary iodine, the essential ingredient of thyroxine. Foals may be born with goiter when their dams get too little or too much iodine in their diets. Often the cause is an iodine excess from kelp-containing feed supplemen ...
... • Goiter is an enlargement of the gland due to either excess or deficiency of dietary iodine, the essential ingredient of thyroxine. Foals may be born with goiter when their dams get too little or too much iodine in their diets. Often the cause is an iodine excess from kelp-containing feed supplemen ...
endocrine system
... Exocrine System: produce chemicals (not hormones) which move through ducts in organs Ex. Salivary glands (spit) Eye Ducts (tears) Sweat Glands (sweat) ...
... Exocrine System: produce chemicals (not hormones) which move through ducts in organs Ex. Salivary glands (spit) Eye Ducts (tears) Sweat Glands (sweat) ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
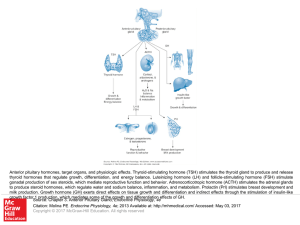
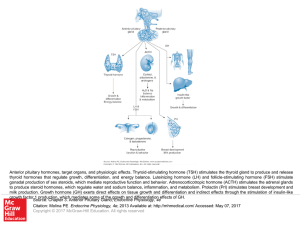
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Slide ()
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Comparison of coordination by hormones and the nervous system
... A system which matches specific responses to particular stimuli to ensure “the right thing happens in the right place at the right time to the right degree ...
... A system which matches specific responses to particular stimuli to ensure “the right thing happens in the right place at the right time to the right degree ...
Endocrine System
... bursts) by endocrine glands – Negative feedback system (levels of hormones increase until signals are sent to glands to stop secretion of that hormone) • Endocrine glands: – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas ...
... bursts) by endocrine glands – Negative feedback system (levels of hormones increase until signals are sent to glands to stop secretion of that hormone) • Endocrine glands: – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas ...
Chapter 39 - Midway ISD
... Attached to thyroid, maintain homeostasis and calcium levels in blood Ex: if blood calcium levels are high, releases calcitonin to reduce calcium absorption; if levels are low, releases PTH to increase absorption of calcium ...
... Attached to thyroid, maintain homeostasis and calcium levels in blood Ex: if blood calcium levels are high, releases calcitonin to reduce calcium absorption; if levels are low, releases PTH to increase absorption of calcium ...
Ch. 45 Endocrine System
... – Proteins and peptides – Amines derived from amino acids – Steroids ...
... – Proteins and peptides – Amines derived from amino acids – Steroids ...
Endocrine system
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). ...
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.