7echap45guidedreading
... Study the table on page 949 – it is overwhelming when presented with a long list of information – the easier way to approach the memorization is first look through the list for what you already know and would associate together – for example pancreas and insulin/glucagon. Then attack the glands wit ...
... Study the table on page 949 – it is overwhelming when presented with a long list of information – the easier way to approach the memorization is first look through the list for what you already know and would associate together – for example pancreas and insulin/glucagon. Then attack the glands wit ...
Endocrine System
... messenger within cell triggers appropriate cellular changes Most use cAMP as second messenger Operates more quickly than steroid mechanism ...
... messenger within cell triggers appropriate cellular changes Most use cAMP as second messenger Operates more quickly than steroid mechanism ...
ap biology ch - Birdville ISD
... -hormones released to whole system…only target organs effected…how? -how is it determined when to release hormones? -many endocrine glands controlled via autonomic nervous system -what about hormonal disorders?…causes = # of hormones OR # of receptors ...
... -hormones released to whole system…only target organs effected…how? -how is it determined when to release hormones? -many endocrine glands controlled via autonomic nervous system -what about hormonal disorders?…causes = # of hormones OR # of receptors ...
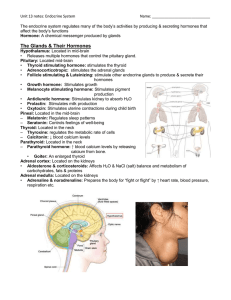
The Endocrine System
... • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. ...
... • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. ...
The Endocrine System
... Very rare disease, caused by the autoimmune destruction of the Adrenal Glands. – High levels of ____________ and _____________ In the blood, craving for ______________due to excessive sodium loss, low ___________ ____________ Also, abnormal darkening of the skin due to elevated ACTH levels and no ...
... Very rare disease, caused by the autoimmune destruction of the Adrenal Glands. – High levels of ____________ and _____________ In the blood, craving for ______________due to excessive sodium loss, low ___________ ____________ Also, abnormal darkening of the skin due to elevated ACTH levels and no ...
Nrsg 407 Disorders of the Endocrine Glands
... Thyroid cont’d • Regulates body metabolism • Thermal regulation • Regulation of physical/mental development ...
... Thyroid cont’d • Regulates body metabolism • Thermal regulation • Regulation of physical/mental development ...
Adrenal Glands
... Cortisol is the major glucocorticoid in humans. Levels are highest in the morning and lowest in the middle of the night. Cortisol helps control carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. For example, cortisol increases glucose levels in the blood by stimulating gluconeogenesis and promotes the for ...
... Cortisol is the major glucocorticoid in humans. Levels are highest in the morning and lowest in the middle of the night. Cortisol helps control carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. For example, cortisol increases glucose levels in the blood by stimulating gluconeogenesis and promotes the for ...
File
... Hormone: a chemical substance produced by the body that affects growth and development, sexual function, mood, metabolism and many other processes Metabolism: the sum of all chemical and physical processes occurring within living cells ...
... Hormone: a chemical substance produced by the body that affects growth and development, sexual function, mood, metabolism and many other processes Metabolism: the sum of all chemical and physical processes occurring within living cells ...
22-Endocrine
... Three advantages to using chemical signals 1. Can spread to all tissues via the blood 2. Can persist much longer than electric signals 3. Many can act as hormones Different hormones can target different tissues ...
... Three advantages to using chemical signals 1. Can spread to all tissues via the blood 2. Can persist much longer than electric signals 3. Many can act as hormones Different hormones can target different tissues ...
Endocrine System Guide
... Thyroid Gland • ____________________gland • Located in the neck just below the ________________________________________ Thyroid Hormone – ____________________ – Produced by the thyroid which ________________________________________ – ________________________________________ The ability of cells to _ ...
... Thyroid Gland • ____________________gland • Located in the neck just below the ________________________________________ Thyroid Hormone – ____________________ – Produced by the thyroid which ________________________________________ – ________________________________________ The ability of cells to _ ...
Endocrine ,cells are distributed in three different ways
... A-Groups of endocrine cells may be present in organs that have other functions , such as the islets of pancreas, interstitial cells of the testis, the follicles and corpora lutea of the ovary , some cells of the kidney ,and of the thymus ,and the placenta. ...
... A-Groups of endocrine cells may be present in organs that have other functions , such as the islets of pancreas, interstitial cells of the testis, the follicles and corpora lutea of the ovary , some cells of the kidney ,and of the thymus ,and the placenta. ...
The Endocrine System
... The Endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream. Their products deliver messages throughout the body. (like broadcasting via radio) Hormones: The “chemicals” released from glands to carry messages They are releases in one part of the body and travel thr ...
... The Endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream. Their products deliver messages throughout the body. (like broadcasting via radio) Hormones: The “chemicals” released from glands to carry messages They are releases in one part of the body and travel thr ...
Notes_Endocrine2013
... chemicals travel to target tissue, which has receptor proteins slow, long-lasting response ...
... chemicals travel to target tissue, which has receptor proteins slow, long-lasting response ...
Title: The Endocrine System
... receptive to the hormone. However, if a hormone is deficient the number of receptor site will grow in order to make the cells more sensitive. 4- Chemical Classes of Hormones a- Hormones can be broadly classified into hormones that are water soluble and those that are fat soluble 1- Fat-soluble hormo ...
... receptive to the hormone. However, if a hormone is deficient the number of receptor site will grow in order to make the cells more sensitive. 4- Chemical Classes of Hormones a- Hormones can be broadly classified into hormones that are water soluble and those that are fat soluble 1- Fat-soluble hormo ...
Lecture 1. Introduction
... Hormones (modern, broad definition): any substance that is released by a cell and acts on another cell (to regulate its function). The means of intercellular communication. This definition includes: - Gap junctions: direct flow of various chemicals from one cell to another - Autocrines - Paracrines ...
... Hormones (modern, broad definition): any substance that is released by a cell and acts on another cell (to regulate its function). The means of intercellular communication. This definition includes: - Gap junctions: direct flow of various chemicals from one cell to another - Autocrines - Paracrines ...
Hormones - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Hormones are chemical signals produced by endocrine cells that can be grouped in endocrine glands. Hormones circulate in the blood stream and affect the activity of target cells that exhibit specific receptors. There are peptide, steroid and amino acid derived hormones. They can be water-soluble (th ...
... Hormones are chemical signals produced by endocrine cells that can be grouped in endocrine glands. Hormones circulate in the blood stream and affect the activity of target cells that exhibit specific receptors. There are peptide, steroid and amino acid derived hormones. They can be water-soluble (th ...
Objectives for Chapter 9
... Objectives for Chapter 9: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) ...
... Objectives for Chapter 9: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) ...
Endocrine System
... • Glucagon is a polypeptide made of 29 amino acids. It has the opposite effect of insulin: It raises the blood glucose levels. • Glucagon stimulates breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver. When blood glucose levels are high, large amounts of glucose are taken up by the liver and stored in form of ...
... • Glucagon is a polypeptide made of 29 amino acids. It has the opposite effect of insulin: It raises the blood glucose levels. • Glucagon stimulates breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver. When blood glucose levels are high, large amounts of glucose are taken up by the liver and stored in form of ...
Chapter 51 The Endocrine System
... controls skeletal and muscular growth, while other cells secrete prolactin, which stimulates the production of breast milk during lactation. 2. Thyroid Gland – located near the lower part of the larynx. The anterior pituitary releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyro ...
... controls skeletal and muscular growth, while other cells secrete prolactin, which stimulates the production of breast milk during lactation. 2. Thyroid Gland – located near the lower part of the larynx. The anterior pituitary releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyro ...
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands make hormones • Hormones are chemical messengers transported in the bloodstream. • Hormones bring about a response, or change, in cells with matching receptors called target cells. ...
... • Endocrine glands make hormones • Hormones are chemical messengers transported in the bloodstream. • Hormones bring about a response, or change, in cells with matching receptors called target cells. ...
Chapter 25 - Austin Community College
... Location: Just inferior to the stomach and in the first loop of the duodenum approximately in the middle of the abdomen. Structure:- mixed gland (endocrine/exocrine); spongy-like appearance. Exocrine cells produce digestive enzymes. Pancreatic “Islet of Langerhans” are endocrine cells. Hormones prod ...
... Location: Just inferior to the stomach and in the first loop of the duodenum approximately in the middle of the abdomen. Structure:- mixed gland (endocrine/exocrine); spongy-like appearance. Exocrine cells produce digestive enzymes. Pancreatic “Islet of Langerhans” are endocrine cells. Hormones prod ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.