MB_50_win
... • A condition called hypoglycemia occurs when excessive insulin is stored and not properly delivered to body cells. • This leads to a lowered blood glucose concentration, which can cause such symptoms as overactivity and dizziness. ...
... • A condition called hypoglycemia occurs when excessive insulin is stored and not properly delivered to body cells. • This leads to a lowered blood glucose concentration, which can cause such symptoms as overactivity and dizziness. ...
Chapter 3
... – glandular secretion – some immune functions • Growth & development • Reproduction ...
... – glandular secretion – some immune functions • Growth & development • Reproduction ...
hormones
... – glandular secretion – some immune functions • Growth & development • Reproduction • Hormones have powerful effects when present in very low concentrations. ...
... – glandular secretion – some immune functions • Growth & development • Reproduction • Hormones have powerful effects when present in very low concentrations. ...
opis przypadku - Postępy Nauk Medycznych
... and transplacental passage of TSH receptor stimulating antibodies (3). The other extremely rare causes of fetal hyperthyroidism include activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in McCune-Albright syndrome and activating mutations of the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor (4). Fetal hypothyroid goit ...
... and transplacental passage of TSH receptor stimulating antibodies (3). The other extremely rare causes of fetal hyperthyroidism include activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in McCune-Albright syndrome and activating mutations of the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor (4). Fetal hypothyroid goit ...
Thyroxine (T4): An Overview
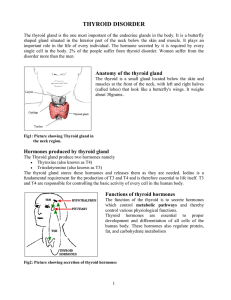
... Background/ About the Molecule: The thyroid gland is located in the anterior region of a neck and contains a large network of blood vessels. It consists of two lobes and extends from the region of the 5th cervical to the 1st thoracic vertebrae. The lobes are composed of follicles which are the struc ...
... Background/ About the Molecule: The thyroid gland is located in the anterior region of a neck and contains a large network of blood vessels. It consists of two lobes and extends from the region of the 5th cervical to the 1st thoracic vertebrae. The lobes are composed of follicles which are the struc ...
Chapter 45 - Endocrine
... glucose levels that triggers signal transduction. 2. Neurosecretory cells, which are neurons (wirelike cells that transmit electrical signals) that secrete hormones. These cells are typically activated by an electrical signal and use electrical signals to secrete their hormones. Most are found in th ...
... glucose levels that triggers signal transduction. 2. Neurosecretory cells, which are neurons (wirelike cells that transmit electrical signals) that secrete hormones. These cells are typically activated by an electrical signal and use electrical signals to secrete their hormones. Most are found in th ...
Document
... • When released into the circulation, only 0.04% of T4 and 0.4% of T3 are unbound by proteins (The free T4 and T3 are physiologically active) • The three major binding proteins, in order of significance, are thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), thyroxine-binding prealbumin, and albumin • The quantity o ...
... • When released into the circulation, only 0.04% of T4 and 0.4% of T3 are unbound by proteins (The free T4 and T3 are physiologically active) • The three major binding proteins, in order of significance, are thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), thyroxine-binding prealbumin, and albumin • The quantity o ...
The Thyroid Connection
... influencing metabolism, body temperature, and growth and development. Healthy thyroid function can be affected by interactions between thyroid hormones and other hormone systems. In particular, excess estrogens can effectively block delivery of thyroid hormones to the cells that need them, as can im ...
... influencing metabolism, body temperature, and growth and development. Healthy thyroid function can be affected by interactions between thyroid hormones and other hormone systems. In particular, excess estrogens can effectively block delivery of thyroid hormones to the cells that need them, as can im ...
Lesson Overview
... Calcitonin’s opposing hormone is parathyroid hormone, which is released by the four parathyroid glands located on the back surface of the thyroid. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the calcium levels in the blood by promoting the release of calcium from bone, the reabsorption of calcium in the kid ...
... Calcitonin’s opposing hormone is parathyroid hormone, which is released by the four parathyroid glands located on the back surface of the thyroid. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the calcium levels in the blood by promoting the release of calcium from bone, the reabsorption of calcium in the kid ...
Ask the Doctor - Advocate Health Care
... Question: Recently my daughter's annual thyroid blood work came back as follows: TSH 9.74 (normal: 0.3 - 5.0), T3 27.8 (normal: 25.0 - 35.0), Free T4 1.7 (normal: 1.0 - 4.3), and T4 6.2 (normal: 4.5 - 12.5). A repeat test six weeks later was similar except the TSH was 6.2. What is the significance a ...
... Question: Recently my daughter's annual thyroid blood work came back as follows: TSH 9.74 (normal: 0.3 - 5.0), T3 27.8 (normal: 25.0 - 35.0), Free T4 1.7 (normal: 1.0 - 4.3), and T4 6.2 (normal: 4.5 - 12.5). A repeat test six weeks later was similar except the TSH was 6.2. What is the significance a ...
The thyroid gland is the most important of the endocrine glands in
... gland which is located in the center of the skull below the brain, senses either a lack of thyroid hormones or a high level of thyroid hormones, it will adjust its own hormone (TSH) and send it to the thyroid to tell it what to do. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which ...
... gland which is located in the center of the skull below the brain, senses either a lack of thyroid hormones or a high level of thyroid hormones, it will adjust its own hormone (TSH) and send it to the thyroid to tell it what to do. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which ...
Cardiovascular Effects of Octreotide, a Long‐Acting Somatostatin
... Institute in 1973 (4), is a tetradecapeptide that inhibits growth hormone (GH) release from the pituitary gland (Fig. 1). Large amounts of somatostatin are found in many human tissues, including the D cells of the stomach, intestine, and pancreatic islets; the central nervous system; and the neurons ...
... Institute in 1973 (4), is a tetradecapeptide that inhibits growth hormone (GH) release from the pituitary gland (Fig. 1). Large amounts of somatostatin are found in many human tissues, including the D cells of the stomach, intestine, and pancreatic islets; the central nervous system; and the neurons ...
Document
... Effect on active mammary glands: Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of musclelike myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts Forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible for nursing/m ...
... Effect on active mammary glands: Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of musclelike myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts Forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible for nursing/m ...
Production, Regulation, and Action of Thyroid Hormones
... More on Receptor Coactivators and Corepressors When not bound to hormone, the thyroid hormone receptor binds to target DNA (TRE on 5’ flanking region). It is associated with corepressor proteins that cause DNA to be tightly wound and inhibit transcription. Binding of hormone causes a conformation ...
... More on Receptor Coactivators and Corepressors When not bound to hormone, the thyroid hormone receptor binds to target DNA (TRE on 5’ flanking region). It is associated with corepressor proteins that cause DNA to be tightly wound and inhibit transcription. Binding of hormone causes a conformation ...
Production, Regulation, and Action of Thyroid Hormones
... More on Receptor Coactivators and Corepressors When not bound to hormone, the thyroid hormone receptor binds to target DNA (TRE on 5’ flanking region). It is associated with corepressor proteins that cause DNA to be tightly wound and inhibit transcription. Binding of hormone causes a conformation ...
... More on Receptor Coactivators and Corepressors When not bound to hormone, the thyroid hormone receptor binds to target DNA (TRE on 5’ flanking region). It is associated with corepressor proteins that cause DNA to be tightly wound and inhibit transcription. Binding of hormone causes a conformation ...
Thyroid Gland
... The thyroid gland is one of the most responsive organs in the body and contains the largest store of hormones of any endocrine gland. The gland responds to many stimuli and is in a constant state of adaptation. During puberty, pregnancy, and physiologic stress from any source, the gland increases in ...
... The thyroid gland is one of the most responsive organs in the body and contains the largest store of hormones of any endocrine gland. The gland responds to many stimuli and is in a constant state of adaptation. During puberty, pregnancy, and physiologic stress from any source, the gland increases in ...
Answer Key to Short Answer Questions for
... “My Brother Calls Me ‘Bug Eyes’: A Case Study on the Endocrine System” 1. Name the two hormones commonly referred to as “thyroid hormone” and describe their general actions. Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyr ...
... “My Brother Calls Me ‘Bug Eyes’: A Case Study on the Endocrine System” 1. Name the two hormones commonly referred to as “thyroid hormone” and describe their general actions. Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyr ...
ch_18_Case Study_Answer_Key
... “My Brother Calls Me ‘Bug Eyes’: A Case Study on the Endocrine System” 1. Name the two hormones commonly referred to as “thyroid hormone” and describe their general actions. Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyr ...
... “My Brother Calls Me ‘Bug Eyes’: A Case Study on the Endocrine System” 1. Name the two hormones commonly referred to as “thyroid hormone” and describe their general actions. Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyr ...
The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
... larger prohormone. It contains a single disulfide bond, which causes the amino terminus to assume the shape of a ring. Alternative splicing of the calcitonin pre-mRNA can yield a mRNA encoding calcitonin gene-related peptide; that peptide appears to function in the nervous and vascular systems. The ...
... larger prohormone. It contains a single disulfide bond, which causes the amino terminus to assume the shape of a ring. Alternative splicing of the calcitonin pre-mRNA can yield a mRNA encoding calcitonin gene-related peptide; that peptide appears to function in the nervous and vascular systems. The ...
******* 1
... drains into the sinusoidal plexus of the cortex. There is no direct supply to middle and inner zones. Venous drainage from the central vein displays laterality. After crossing the medulla, the right adrenal vein empties into the inferior vena cava, and the left adrenal vein drains into the left ...
... drains into the sinusoidal plexus of the cortex. There is no direct supply to middle and inner zones. Venous drainage from the central vein displays laterality. After crossing the medulla, the right adrenal vein empties into the inferior vena cava, and the left adrenal vein drains into the left ...
ENDOCRINE.Thyroid
... Iodine uptake is an index of thyroid function Uptake can be measured by using tracer doses of radioactive isotopes of iodine that have no effect on thyroid gland. Tracer is administered orally Gamma ray counter placed over the neck Large amount of radioactive iodine destroys the thyroid tissue. Radi ...
... Iodine uptake is an index of thyroid function Uptake can be measured by using tracer doses of radioactive isotopes of iodine that have no effect on thyroid gland. Tracer is administered orally Gamma ray counter placed over the neck Large amount of radioactive iodine destroys the thyroid tissue. Radi ...
Direct stimulation from the nervous system
... a.k.a. somatotropin and somatotropic hormone Promotes body growth in young animals Helps regulate metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids in all body cells The effect of GH on protein metabolism is to encourage anabolism (synthesis of proteins by body cells) The effects of GH on carb and l ...
... a.k.a. somatotropin and somatotropic hormone Promotes body growth in young animals Helps regulate metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids in all body cells The effect of GH on protein metabolism is to encourage anabolism (synthesis of proteins by body cells) The effects of GH on carb and l ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.