4.03-4.04 Endocrine System PPP
... 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
21 Endocrine Flashcards MtSAC
... Type I (insulin dependent, develops in children) Type II (insulin resistance, develops in adults) Diet and exercise ...
... Type I (insulin dependent, develops in children) Type II (insulin resistance, develops in adults) Diet and exercise ...
Endocrine System
... converted to glucose, leading to increased blood glucose 2. Immune system may be suppressed ...
... converted to glucose, leading to increased blood glucose 2. Immune system may be suppressed ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... converted to glucose, leading to increased blood glucose 2. Immune system may be suppressed ...
... converted to glucose, leading to increased blood glucose 2. Immune system may be suppressed ...
01 - ALCA
... 08.1 Endocrine System Introduction A. Nervous System vs. Endocrine System The Endocrine System is one of the ‘silent’ systems that plays a major role in our lives every day. It works much quieter than the nervous system, but its role is to communicate and coordinate organs and tissues in the body. W ...
... 08.1 Endocrine System Introduction A. Nervous System vs. Endocrine System The Endocrine System is one of the ‘silent’ systems that plays a major role in our lives every day. It works much quieter than the nervous system, but its role is to communicate and coordinate organs and tissues in the body. W ...
The Endocrine System - Part 1
... Hormones transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. Glands produce and secrete chemicals. They select and remove materials from the blood, process them and secrete the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. Pituitary gland - the major endocrine gland. A ...
... Hormones transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. Glands produce and secrete chemicals. They select and remove materials from the blood, process them and secrete the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. Pituitary gland - the major endocrine gland. A ...
The Endocrine System
... built-in physiological mechanisms to maintain them at desirable levels. When a change occurs in the body, there are two general ways that the body can respond. In negative feedback, the body responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Because this tends to keep things constant, it ...
... built-in physiological mechanisms to maintain them at desirable levels. When a change occurs in the body, there are two general ways that the body can respond. In negative feedback, the body responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Because this tends to keep things constant, it ...
Chapter 47
... Exocrine glands release their secretions into ducts. Some neurons secrete hormones (neurohormones) and are known are neuroendocrine cells. Some cells release hormones that act on nearby cells. This is called paracrine regulation. ...
... Exocrine glands release their secretions into ducts. Some neurons secrete hormones (neurohormones) and are known are neuroendocrine cells. Some cells release hormones that act on nearby cells. This is called paracrine regulation. ...
02 Endocrine and Cell Communication
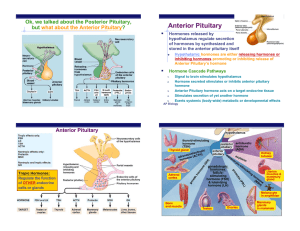
... • Hormone production in the anterior pituitary is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus. • For example, prolactin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete prolactin (PRL), which has a role in milk production and secretion. • ...
... • Hormone production in the anterior pituitary is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus. • For example, prolactin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete prolactin (PRL), which has a role in milk production and secretion. • ...
Chapter 18 - Illini West High School
... • Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of death, after lung cancer for women in the United States • The American Cancer Society recommends that females examine their breasts once a month, right after the menstrual period ...
... • Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of death, after lung cancer for women in the United States • The American Cancer Society recommends that females examine their breasts once a month, right after the menstrual period ...
Lecture_36_2014_noquiz
... There are lots of other elements of the fish that differ, possibly due to thyroid hormone. -initiation of migration (for marine fish) -activity levels ...
... There are lots of other elements of the fish that differ, possibly due to thyroid hormone. -initiation of migration (for marine fish) -activity levels ...
Lesson 10 - MsBakerGHS
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) – stimulates the thyroid gland to make and release thyroid hormone. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin) – stimulates the adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids. Luteinizing hormone (LH) – stimulates the release of steroid hormones i ...
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) – stimulates the thyroid gland to make and release thyroid hormone. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin) – stimulates the adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids. Luteinizing hormone (LH) – stimulates the release of steroid hormones i ...
Summary - Union High School
... After a few days, the egg reaches the uterus. The uterus is connected to the outside of the body by a canal called the vagina. One egg develops each month during the menstrual cycle. The cycle is controlled by hormones. It has four phases: follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, and menstruation. ...
... After a few days, the egg reaches the uterus. The uterus is connected to the outside of the body by a canal called the vagina. One egg develops each month during the menstrual cycle. The cycle is controlled by hormones. It has four phases: follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, and menstruation. ...
Endocrine System
... – Most cells respond by increasing rate of cell growth and protein production – effects are by indirect and direct stimulation – Indirect – in response to GH, liver cells synthesize and release insulin-like growth factors (IGF’s) • The IGF’s increase amino acid uptake and subsequent protein synthesi ...
... – Most cells respond by increasing rate of cell growth and protein production – effects are by indirect and direct stimulation – Indirect – in response to GH, liver cells synthesize and release insulin-like growth factors (IGF’s) • The IGF’s increase amino acid uptake and subsequent protein synthesi ...
File
... -substances produced by a response to changes will go back and turn off the system when HOMEOSTASIS is achieved. NEGATIVE = OPPOSITE Hormone produced by Pituitary ...
... -substances produced by a response to changes will go back and turn off the system when HOMEOSTASIS is achieved. NEGATIVE = OPPOSITE Hormone produced by Pituitary ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... • Lies at the base of the brain in the sella turcica, small depression in the sphenoid bone of the skull • Known as the “master gland” because of its major influence on body’s activities (but still controlled by the hypothalamus) • Size of a grape • Connected to hypothalamus by a stalk called infund ...
... • Lies at the base of the brain in the sella turcica, small depression in the sphenoid bone of the skull • Known as the “master gland” because of its major influence on body’s activities (but still controlled by the hypothalamus) • Size of a grape • Connected to hypothalamus by a stalk called infund ...
Endocrine System
... reproductive system only • 3. anabolic hormone— stimulate anabolism of their target cells ...
... reproductive system only • 3. anabolic hormone— stimulate anabolism of their target cells ...
The Endocrine System
... secrete glucocorticoids, which are important in glucose, fat, and protein metabolism o Prolactin After a woman gives birth, it stimulates the mammary glands to secrete milk In males, it makes the testes more sensitive to luteinizing hormone, which enhances secretion of testosterone o Growth Horm ...
... secrete glucocorticoids, which are important in glucose, fat, and protein metabolism o Prolactin After a woman gives birth, it stimulates the mammary glands to secrete milk In males, it makes the testes more sensitive to luteinizing hormone, which enhances secretion of testosterone o Growth Horm ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.