Typical disorders of the endocrine system 1. Choose the correct
... + a) acromegaly; + b) gigantism; + c) hypercortisolism; d) secondary aldosteronism; e) primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insuffi ...
... + a) acromegaly; + b) gigantism; + c) hypercortisolism; d) secondary aldosteronism; e) primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insuffi ...
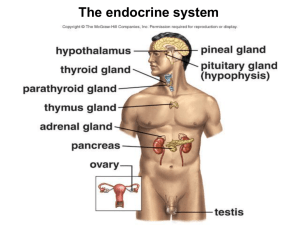
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... • The hormone binds to a receptor protein imbedded in the cell membrane. • A "G protein" is activated by this and detaches from the receptor protein. The "G protein" acts as a catalyst. • Whenever it finds an Adenylate Cyclase molecule embedded in the membrane it "tells" the adenylate cyclase molecu ...
... • The hormone binds to a receptor protein imbedded in the cell membrane. • A "G protein" is activated by this and detaches from the receptor protein. The "G protein" acts as a catalyst. • Whenever it finds an Adenylate Cyclase molecule embedded in the membrane it "tells" the adenylate cyclase molecu ...
Endocrine 112KB 06.09.2016
... The endocrine system relates the most important regulatory systems. It carries out regulatory influence with the help of hormones practically on all functions of an organism – metabolism , growth, reproduction, mental activity, adaptation, functional activity of all organs. The endocrine system cont ...
... The endocrine system relates the most important regulatory systems. It carries out regulatory influence with the help of hormones practically on all functions of an organism – metabolism , growth, reproduction, mental activity, adaptation, functional activity of all organs. The endocrine system cont ...
The Endocrine System
... how birth control and patches work, but an insulin patch would not be effective because it is an amino acid hormone. ...
... how birth control and patches work, but an insulin patch would not be effective because it is an amino acid hormone. ...
ch18 outline
... thyroid and contain principal cells, which produce parathyroid hormone, and oxyphil cells, whose function is unknown (Figure 18.13). B. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates the homeostasis of calcium and phosphate by increasing blood calcium level and decreasing blood phosphate level. C. PTH increase ...
... thyroid and contain principal cells, which produce parathyroid hormone, and oxyphil cells, whose function is unknown (Figure 18.13). B. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates the homeostasis of calcium and phosphate by increasing blood calcium level and decreasing blood phosphate level. C. PTH increase ...
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
... 1. increased cellular uptake of amino acids = increased protein synthesis = growth/maintenance 2. increased lipolysis and gluconeogenesis for energy, leading to hyperglycemia = diabetogenic effect ...
... 1. increased cellular uptake of amino acids = increased protein synthesis = growth/maintenance 2. increased lipolysis and gluconeogenesis for energy, leading to hyperglycemia = diabetogenic effect ...
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia
... sex glands to produce sex hormaones Without these hormones, a person’s sexual development is delayed, a girl’s periods are absent or irregular, and it is difficult to father a child or become pregnant. ...
... sex glands to produce sex hormaones Without these hormones, a person’s sexual development is delayed, a girl’s periods are absent or irregular, and it is difficult to father a child or become pregnant. ...
Chapter 20 - mwsu-wiki
... - Target cell is a cell that is receptive to a specific hormone - Target cell’s have 2 main functions 1. Recognize and bind with high affinity to their particular hormones 2. Initiate a signal to appropriate intracellular effectors - Binding with receptors general stimulates 3 general types of respo ...
... - Target cell is a cell that is receptive to a specific hormone - Target cell’s have 2 main functions 1. Recognize and bind with high affinity to their particular hormones 2. Initiate a signal to appropriate intracellular effectors - Binding with receptors general stimulates 3 general types of respo ...
The Endocrine System
... C. Endothelin and bradykinin are paracrine molecules that are used in the circulatory system for control of vessel constriction and dilation. D. Paracrine molecules are released directly into the circulatory system. E. Nerve growth factor, platelet-growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor are s ...
... C. Endothelin and bradykinin are paracrine molecules that are used in the circulatory system for control of vessel constriction and dilation. D. Paracrine molecules are released directly into the circulatory system. E. Nerve growth factor, platelet-growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor are s ...
hormones and behavior
... • Specific hormones only affect certain c cells and hormones affect different cells in different ways – T Targett cells ll possess receptors t f r specific for ifi h hormones – Target cells vary in the transductio on machinery they possess – Diverse responses to particular ho ormones possible ...
... • Specific hormones only affect certain c cells and hormones affect different cells in different ways – T Targett cells ll possess receptors t f r specific for ifi h hormones – Target cells vary in the transductio on machinery they possess – Diverse responses to particular ho ormones possible ...
Microsoft Word 97
... adapted or designed for producing hormones. This is different in multicellular animals, as there are secretory cells specialized for hormone production alone. In addition, the more complex multicellular organisms have these cells in distinct groupings or glands which are located in specific areas of ...
... adapted or designed for producing hormones. This is different in multicellular animals, as there are secretory cells specialized for hormone production alone. In addition, the more complex multicellular organisms have these cells in distinct groupings or glands which are located in specific areas of ...
Document
... The anterior, or front, lobe of the pituitary gland produces six hormones. These hormones include somatotropic, or growth, A gonad is hormone, thyroid stimulating another name hormone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. for the ovary and testes. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormo ...
... The anterior, or front, lobe of the pituitary gland produces six hormones. These hormones include somatotropic, or growth, A gonad is hormone, thyroid stimulating another name hormone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. for the ovary and testes. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormo ...
Lesson 1
... The anterior, or front, lobe of the pituitary gland produces six hormones. These hormones include somatotropic, or growth, A gonad is hormone, thyroid stimulating another name hormone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. for the ovary and testes. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormo ...
... The anterior, or front, lobe of the pituitary gland produces six hormones. These hormones include somatotropic, or growth, A gonad is hormone, thyroid stimulating another name hormone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. for the ovary and testes. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormo ...
9 - Mr-Js-Science
... Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary • Gonadotropic hormones • Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) • Stimulates follicle development in ovaries • Stimulates sperm development in testes • Luteinizing hormone (LH) • Triggers ovulation of an egg in females • Stim ...
... Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary • Gonadotropic hormones • Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) • Stimulates follicle development in ovaries • Stimulates sperm development in testes • Luteinizing hormone (LH) • Triggers ovulation of an egg in females • Stim ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... Causes contraction of the pregnant uterus ...
... Causes contraction of the pregnant uterus ...
Parotid gland
... located on either side of the face between the buccinators muscle and several more superficial muscles ( including the masseter, the zygomaticus major, and the zygomaticus minor). The inferior portion of the buccal fat pad is contained within the buccal space. The buccal fat pad formation begins at ...
... located on either side of the face between the buccinators muscle and several more superficial muscles ( including the masseter, the zygomaticus major, and the zygomaticus minor). The inferior portion of the buccal fat pad is contained within the buccal space. The buccal fat pad formation begins at ...
Unit One – Concept Two - Calgary Christian School
... endocrine: non-ducted: goes into extracellular fluid (ECF), secretion ends up in the blood stream where it is picked up by capillaries exocrine: ducted – materials end up outside (saliva, sweat, mammary glands) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VBwCBdd0ru8& playnext=1&list=PLEEE5A627695E1E4A ...
... endocrine: non-ducted: goes into extracellular fluid (ECF), secretion ends up in the blood stream where it is picked up by capillaries exocrine: ducted – materials end up outside (saliva, sweat, mammary glands) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VBwCBdd0ru8& playnext=1&list=PLEEE5A627695E1E4A ...
The Endocrine System
... Made of modified nerve tissue that is under direct regulation of sympathetic nerves of the autonomic nervous system. ...
... Made of modified nerve tissue that is under direct regulation of sympathetic nerves of the autonomic nervous system. ...
Slide 1
... Epithelial cells can form glands • A gland- a collection of cells which secrete a product • Exocrine- release substances through ducts or tubes ...
... Epithelial cells can form glands • A gland- a collection of cells which secrete a product • Exocrine- release substances through ducts or tubes ...
PAROTID REGION.
... nerve (V3)) to reach the parotid gland. Sympathetic nerves originating from Superior Cervical Ganglion and giving rise to the external carotid nerve plexus reach the gland. Parasympathetic stimulation produces a water rich, serous saliva. Sympathetic stimulation leads to the production of a lo ...
... nerve (V3)) to reach the parotid gland. Sympathetic nerves originating from Superior Cervical Ganglion and giving rise to the external carotid nerve plexus reach the gland. Parasympathetic stimulation produces a water rich, serous saliva. Sympathetic stimulation leads to the production of a lo ...
Endocrinology Pituitary gland Hypothalamic control
... Synthesis, transport, & mechanism of action of GH Synthesized in ER of glandular cells as preprohormone; & stored in secretory vesicles in its active form until stimulated. Dissolve freely in the blood. Its receptors are found ON or IN cell membrane of target cells. Stimulates G-proteins in ...
... Synthesis, transport, & mechanism of action of GH Synthesized in ER of glandular cells as preprohormone; & stored in secretory vesicles in its active form until stimulated. Dissolve freely in the blood. Its receptors are found ON or IN cell membrane of target cells. Stimulates G-proteins in ...
hormones of the pituitary and thyroid
... Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus and pituitary are all peptides Hormones of the anterior and posterior pituitary are administered either IM, SC or intranasally but not orally ...
... Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus and pituitary are all peptides Hormones of the anterior and posterior pituitary are administered either IM, SC or intranasally but not orally ...
7. Endocrine System
... Lipid droplets are abundant in these steroid-secreting cells. Cholesterol precursors for steroid hormones are stored in lipid droplets. Also SER would be abundant in these cells to provide the enzymes for steroid production. ...
... Lipid droplets are abundant in these steroid-secreting cells. Cholesterol precursors for steroid hormones are stored in lipid droplets. Also SER would be abundant in these cells to provide the enzymes for steroid production. ...
BIO 262 Unit 4 Review Sheet
... ___3. Which pair of glands produces hormones that have opposing effects? a. anterior pituitary-posterior pituitary ...
... ___3. Which pair of glands produces hormones that have opposing effects? a. anterior pituitary-posterior pituitary ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.