Hypothalamus - pituitary
... core called the adrenal medulla, which is surrounded by a much thicker adrenal cortex. a. The adrenal medulla is not fully formed until the age of three, and is actually a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system made up of modified neuron somas. It secretes catecholamines (epinephrine, norepineph ...
... core called the adrenal medulla, which is surrounded by a much thicker adrenal cortex. a. The adrenal medulla is not fully formed until the age of three, and is actually a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system made up of modified neuron somas. It secretes catecholamines (epinephrine, norepineph ...
Thyroid Gland
... To cause muscle contraction and glandular secretion Effect: short duration, measured in seconds, localized ...
... To cause muscle contraction and glandular secretion Effect: short duration, measured in seconds, localized ...
The Endocrine System
... Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
... Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
hormones
... the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetically, the proper hormones must be available for the fetus to develop the appropriate sex organs. Its gonads are fairly inactive at birth, but gradual changes take place each day for years until puberty. Then, changes in the pattern of ...
... the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetically, the proper hormones must be available for the fetus to develop the appropriate sex organs. Its gonads are fairly inactive at birth, but gradual changes take place each day for years until puberty. Then, changes in the pattern of ...
Pathways for nutrient transport in the pitchers of
... chloride (Lu$ ttge, 1971) and calcium (Massa, 1998). However, the origin of these enzymes in pitcher plants has been recently brought into question (Luciano et al., 1998 ; Santo, Massa and Owen, 1998). Either simultaneously, or as a result of these secretions, the glands absorb small byproducts from ...
... chloride (Lu$ ttge, 1971) and calcium (Massa, 1998). However, the origin of these enzymes in pitcher plants has been recently brought into question (Luciano et al., 1998 ; Santo, Massa and Owen, 1998). Either simultaneously, or as a result of these secretions, the glands absorb small byproducts from ...
hormones
... Endocrine System Components • endocrine system - glands, tissues, and cells that secrete hormones • endocrinology – the study of this system and the diagnosis and treatment of its disorders • endocrine glands – organs that produce hormones • hormones - chemical messengers transported by the bloodst ...
... Endocrine System Components • endocrine system - glands, tissues, and cells that secrete hormones • endocrinology – the study of this system and the diagnosis and treatment of its disorders • endocrine glands – organs that produce hormones • hormones - chemical messengers transported by the bloodst ...
Anatomy of salivary glands
... Parotid development Although the parotid anlagen are the first to develop, they ...
... Parotid development Although the parotid anlagen are the first to develop, they ...
Chemical coordina Answer 1: (a) Exocrine gland
... the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Thus, it plays an important role in calcium balance in the body. (b) Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of th ...
... the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Thus, it plays an important role in calcium balance in the body. (b) Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of th ...
Chapter 34 power point chapter 34shortened
... communicate with one another? • In all animals, cells release molecules that influence other cells. Each type of signal acts on all target cells that have receptors for it. Hormones are intercellular signaling molecules that travel in the bloodstream. • Most vertebrates have the same types of hormon ...
... communicate with one another? • In all animals, cells release molecules that influence other cells. Each type of signal acts on all target cells that have receptors for it. Hormones are intercellular signaling molecules that travel in the bloodstream. • Most vertebrates have the same types of hormon ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Interstitial cells of testes are hormone-producing • Produce several androgens • Testosterone is the most important androgen • Responsible for adult male secondary sex characteristics • Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system • Required for sperm cell production ...
... • Interstitial cells of testes are hormone-producing • Produce several androgens • Testosterone is the most important androgen • Responsible for adult male secondary sex characteristics • Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system • Required for sperm cell production ...
Understanding Our Environment - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Hormone is a chemical signal produced in one part of the body that is stable enough to be transported in active form across the body. Three advantages to chemical signals: Can spread to all tissues via blood. Can persist much longer than electrical signals. Many chemicals can act as hormones. ...
... Hormone is a chemical signal produced in one part of the body that is stable enough to be transported in active form across the body. Three advantages to chemical signals: Can spread to all tissues via blood. Can persist much longer than electrical signals. Many chemicals can act as hormones. ...
Nerve Supply
... The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule. The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie ...
... The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule. The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie ...
Endocrine Lab - Winona State University
... The gland itself is butterfly shaped where the two wings create the glands bulk as it wraps the trachea. The two lobes (i.e., the left and right lobes) are attached inferiorly by a bridge-like structure called the isthmus (figure 17.9a). Remove slide #4 from the slide box, place the slide on the sta ...
... The gland itself is butterfly shaped where the two wings create the glands bulk as it wraps the trachea. The two lobes (i.e., the left and right lobes) are attached inferiorly by a bridge-like structure called the isthmus (figure 17.9a). Remove slide #4 from the slide box, place the slide on the sta ...
Endocrine Virtual Lab! AP Biology
... sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in the female as do hi ...
... sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in the female as do hi ...
chapt11_lecture
... Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. ...
... Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. ...
Lecture Outline ()
... – nervous system reacts quickly (1 - 10 msec) and stops quickly – endocrine system reacts slowly (hormone release in seconds or days), effect may continue for weeks ...
... – nervous system reacts quickly (1 - 10 msec) and stops quickly – endocrine system reacts slowly (hormone release in seconds or days), effect may continue for weeks ...
Milk Let Down
... Carrying out a teat preparation routine for cows which are slow to let down (e.g. teat washing and drying or massage) as it is a strong stimulus for let down. Check for interrupted milk flow in a rotary by going back around about 10-20 cows from cup attachment, depending on the size of the platform, ...
... Carrying out a teat preparation routine for cows which are slow to let down (e.g. teat washing and drying or massage) as it is a strong stimulus for let down. Check for interrupted milk flow in a rotary by going back around about 10-20 cows from cup attachment, depending on the size of the platform, ...
ch18 Endocrine System
... 1. Alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon which increases blood glucose levels. 2. Beta cells secrete the hormone insulin which decreases blood glucose levels. 3. Delta cells secrete growth hormone inhibiting hormone or somatostatin, which acts as a paracrine to inhibit the secretion of insulin an ...
... 1. Alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon which increases blood glucose levels. 2. Beta cells secrete the hormone insulin which decreases blood glucose levels. 3. Delta cells secrete growth hormone inhibiting hormone or somatostatin, which acts as a paracrine to inhibit the secretion of insulin an ...
notes - Main
... 1. Alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon which increases blood glucose levels. 2. Beta cells secrete the hormone insulin which decreases blood glucose levels. 3. Delta cells secrete growth hormone inhibiting hormone or somatostatin, which acts as a paracrine to inhibit the secretion of insulin an ...
... 1. Alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon which increases blood glucose levels. 2. Beta cells secrete the hormone insulin which decreases blood glucose levels. 3. Delta cells secrete growth hormone inhibiting hormone or somatostatin, which acts as a paracrine to inhibit the secretion of insulin an ...
Endocrine System
... • Access to every cell because hormones circulate in the blood • Each hormone acts only on specific cells (target cells) because only the hormone’s target cells have the appropriate receptor to fit it; • Endocrine control slower than nervous system • Endocrine and nervous systems interact i.e. timin ...
... • Access to every cell because hormones circulate in the blood • Each hormone acts only on specific cells (target cells) because only the hormone’s target cells have the appropriate receptor to fit it; • Endocrine control slower than nervous system • Endocrine and nervous systems interact i.e. timin ...
eprint_3_16309_960
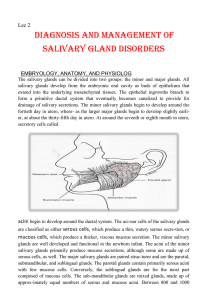
... EMBRYOLOGY, ANATOMY, AND PHYSIOLOG The salivary glands can be divided into two groups: the minor and major glands. All salivary glands develop from the embryonic oral cavity as buds of epithelium that extend into the underlying mesenchymal tissues. The epithelial ingrowths branch to form a primitive ...
... EMBRYOLOGY, ANATOMY, AND PHYSIOLOG The salivary glands can be divided into two groups: the minor and major glands. All salivary glands develop from the embryonic oral cavity as buds of epithelium that extend into the underlying mesenchymal tissues. The epithelial ingrowths branch to form a primitive ...
Slide 1
... associated with > metabolic costs at this time? S. tiburo highest levels- placental formation ...
... associated with > metabolic costs at this time? S. tiburo highest levels- placental formation ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.