adrenal insufficiency - Hormone Health Network
... They check blood levels of cortisol, other hormones, sodium, potassium, and glucose to detect AI and help find the cause. They also look at the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland with imaging tests, such as x-rays, ultrasound, and CT or MRI scans. ...
... They check blood levels of cortisol, other hormones, sodium, potassium, and glucose to detect AI and help find the cause. They also look at the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland with imaging tests, such as x-rays, ultrasound, and CT or MRI scans. ...
The Endocrine System
... Hormones affects its target cells or target organs For a target cell to respond to a hormone, specific receptor to which hormone can attach must be present on the cell membrane Only when this binding occur, the hormone influence the working of the cell ...
... Hormones affects its target cells or target organs For a target cell to respond to a hormone, specific receptor to which hormone can attach must be present on the cell membrane Only when this binding occur, the hormone influence the working of the cell ...
Anat3_09_Endocrine_System
... cell receptors may decrease. Down-regulation decreases the responsiveness of the target cell to the hormone. ...
... cell receptors may decrease. Down-regulation decreases the responsiveness of the target cell to the hormone. ...
Endocrine System
... glands and the hormones they produce. – What stimulates the release of medullary hormones (hormones released from the adrenal medulla). – What causes the release of hormones released from the Adrenal cortex (aldosterone, cortisol and sex hormones). – Whats the function of aldosterone, cortisol and h ...
... glands and the hormones they produce. – What stimulates the release of medullary hormones (hormones released from the adrenal medulla). – What causes the release of hormones released from the Adrenal cortex (aldosterone, cortisol and sex hormones). – Whats the function of aldosterone, cortisol and h ...
Tài liệu PDF
... discussed above, dietary iodine is required for the synthesis of T3 and T4. But for much of the world’s population, foods do not provide adequate levels of this mineral, because the amount varies according to the level in the soil in which the food was grown, as well as the irrigation and fertilizer ...
... discussed above, dietary iodine is required for the synthesis of T3 and T4. But for much of the world’s population, foods do not provide adequate levels of this mineral, because the amount varies according to the level in the soil in which the food was grown, as well as the irrigation and fertilizer ...
adrenal insufficiency - Hormone Health Network
... • Low blood pressure and fainting You also should tell family and friends what to do if a crisis occurs. Always wear a medical alert bracelet or tag. ...
... • Low blood pressure and fainting You also should tell family and friends what to do if a crisis occurs. Always wear a medical alert bracelet or tag. ...
Chapter 14 Assignments, Study Guide, Word List, Pronunciation
... a constriction or narrow passage connecting two larger parts of an organ or other anatomical structure. a high level of this substance in the blood occurs in diabetes mellitus as the body metabolizes fat instead of glucose a subdivision of a body organ or part bounded by fissures, connective tissu ...
... a constriction or narrow passage connecting two larger parts of an organ or other anatomical structure. a high level of this substance in the blood occurs in diabetes mellitus as the body metabolizes fat instead of glucose a subdivision of a body organ or part bounded by fissures, connective tissu ...
Human Physiology/The endocrine system
... within acceptable limits from opposite extremes are called antagonistic hormones. The two glands that are the most responsible for homeostasis is the thyroid and the parathyroid. The regulation of blood glucose concentration (through negative feedback) illustrates how the endocrine system maintains ...
... within acceptable limits from opposite extremes are called antagonistic hormones. The two glands that are the most responsible for homeostasis is the thyroid and the parathyroid. The regulation of blood glucose concentration (through negative feedback) illustrates how the endocrine system maintains ...
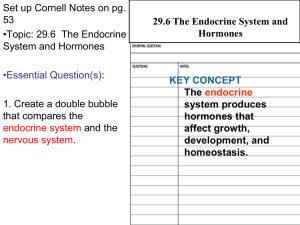
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... Hormonal imbalances can cause severe illness. • Abnormal hormone levels affect homeostasis. • Hormonal imbalances might be treated with surgery or ...
... Hormonal imbalances can cause severe illness. • Abnormal hormone levels affect homeostasis. • Hormonal imbalances might be treated with surgery or ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Stephen G
... 5. What are the eicosanoids? Is their activity considered being local or general? Mechanisms of Hormone Action 6. How do hormones bring about their effects on cells? What are five ways a hormone may produce a change? 7. There are two major mechanisms by which hormone-receptor binding places intracel ...
... 5. What are the eicosanoids? Is their activity considered being local or general? Mechanisms of Hormone Action 6. How do hormones bring about their effects on cells? What are five ways a hormone may produce a change? 7. There are two major mechanisms by which hormone-receptor binding places intracel ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... was removal of the testes to eliminate testosterone production. The two rats (normal and castrate) of each group were treated alike in all other ways (food, water, etc). All rats, except for those in the control group were injected with a hormone (ACTH, cortisol, LH, TRH, testosterone or TSH) on a d ...
... was removal of the testes to eliminate testosterone production. The two rats (normal and castrate) of each group were treated alike in all other ways (food, water, etc). All rats, except for those in the control group were injected with a hormone (ACTH, cortisol, LH, TRH, testosterone or TSH) on a d ...
Endocrine Physiology - e-safe
... Control of pituitary secretion by the hypothalamus Almost all hormone secretion by the pituitary is controlled by either hormonal or nervous signals from the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus receives signals from almost all possible sources in the nervous system, and is itself under negative feedback ...
... Control of pituitary secretion by the hypothalamus Almost all hormone secretion by the pituitary is controlled by either hormonal or nervous signals from the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus receives signals from almost all possible sources in the nervous system, and is itself under negative feedback ...
Endocrine Disorders
... endocrine cells which secrete: insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and others. Purpose: Control blood sugar and overall glucose metabolism, help control other endocrine cells of the digestive tract. parathyroid, parathyroid surgery, parathyroid hormone • Pituitary Gland. The pituitary is located at the ...
... endocrine cells which secrete: insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and others. Purpose: Control blood sugar and overall glucose metabolism, help control other endocrine cells of the digestive tract. parathyroid, parathyroid surgery, parathyroid hormone • Pituitary Gland. The pituitary is located at the ...
What is the median eminence? The median eminence is the nucleus
... 69. What does this picture mean? (Explain it in words) a. Estrogen, LH and FSH hormone cycles begin before puberty, but they increase in amplitude during puberty 70. What does Frisch suggest about body fat and menarche? a. Body fat is a determinant of menarche (have to reach a certain percentage to ...
... 69. What does this picture mean? (Explain it in words) a. Estrogen, LH and FSH hormone cycles begin before puberty, but they increase in amplitude during puberty 70. What does Frisch suggest about body fat and menarche? a. Body fat is a determinant of menarche (have to reach a certain percentage to ...
Describe the development of the thyroid gland
... external to the fibrous thyroid capsule on the medial half of the posterior surface of each lobe of the thyroid, but within its sheath. The number of glands can vary from two to six. These glands produce parathormone also a regulator of serum calcium increasing levels by resorption of bone. There ar ...
... external to the fibrous thyroid capsule on the medial half of the posterior surface of each lobe of the thyroid, but within its sheath. The number of glands can vary from two to six. These glands produce parathormone also a regulator of serum calcium increasing levels by resorption of bone. There ar ...
Chapter 6
... Figure 6.5 Hypothalamic and anterior pituitary tropic hormones. The hypothalamus secretes into the hypothalamic-pituitary portal vein seven tropic hormones that are either releasing hormone [-RH] or inhibiting hormones [-IH]. These tropic hormones act on endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary to ...
... Figure 6.5 Hypothalamic and anterior pituitary tropic hormones. The hypothalamus secretes into the hypothalamic-pituitary portal vein seven tropic hormones that are either releasing hormone [-RH] or inhibiting hormones [-IH]. These tropic hormones act on endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary to ...
Chapter 6 The endocrine system
... Figure 6.5 Hypothalamic and anterior pituitary tropic hormones. The hypothalamus secretes into the hypothalamic-pituitary portal vein seven tropic hormones that are either releasing hormone [-RH] or inhibiting hormones [-IH]. These tropic hormones act on endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary to ...
... Figure 6.5 Hypothalamic and anterior pituitary tropic hormones. The hypothalamus secretes into the hypothalamic-pituitary portal vein seven tropic hormones that are either releasing hormone [-RH] or inhibiting hormones [-IH]. These tropic hormones act on endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary to ...
Unit 7_Endocrine System
... Hormonal release is regulated by releasing & inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus Hypothalamus produces two hormones: ...
... Hormonal release is regulated by releasing & inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus Hypothalamus produces two hormones: ...
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... hormone (ACTH)/cortisol, glucagon/insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, and describe how they maintain homeostasis through feedback 30–A2.3k explain the metabolic roles hormones may play in homeostasis; i.e., thyroxine in metabolism; insulin, gluc ...
... hormone (ACTH)/cortisol, glucagon/insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, and describe how they maintain homeostasis through feedback 30–A2.3k explain the metabolic roles hormones may play in homeostasis; i.e., thyroxine in metabolism; insulin, gluc ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 22
... increase the level of calcium in blood. It promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Hence, it plays an important role in maintaining calcium balance in the body. (b) Thyroid hormones - Thyroid hormones such as thyroxine, trii ...
... increase the level of calcium in blood. It promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Hence, it plays an important role in maintaining calcium balance in the body. (b) Thyroid hormones - Thyroid hormones such as thyroxine, trii ...
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #1
... pituitary by small blood vessels, or venules, where they control the release of six different hormones: growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle stimulating hormone. Look at figure 17.4b and note the extensive capillary ne ...
... pituitary by small blood vessels, or venules, where they control the release of six different hormones: growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle stimulating hormone. Look at figure 17.4b and note the extensive capillary ne ...
Parotid duct
... ***Frey's Sdromeyn • Frey's syndrome is an interesting complication • that sometimes develops after penetrating wounds of the parotid gland. When the patient eats, beads of perspiration appear on the skin covering the parotid. This condition is caused by damage to the auriculotemporal and great aur ...
... ***Frey's Sdromeyn • Frey's syndrome is an interesting complication • that sometimes develops after penetrating wounds of the parotid gland. When the patient eats, beads of perspiration appear on the skin covering the parotid. This condition is caused by damage to the auriculotemporal and great aur ...
Chapter 17
... • Autocrine chemical signals – released by cells and have a local effect of the same cell type. Example are prostaglandins and platelets. • Paracrine chemical signals – released by cells and effect local other cell types. Somatostatin from pancreas. ...
... • Autocrine chemical signals – released by cells and have a local effect of the same cell type. Example are prostaglandins and platelets. • Paracrine chemical signals – released by cells and effect local other cell types. Somatostatin from pancreas. ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.