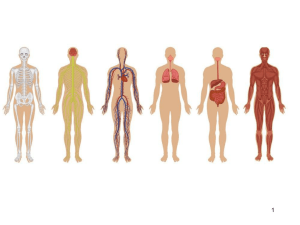
chapter 8 - Mrs. Aymami`s Class
... • Tooth subdivided into crown and root; crown is part of tooth visible above gum line; root is below gum line; root anchored in bony socket of jaw by cementum and tiny periodontal ligaments • Crown of tooth is covered by layer of enamel, hardest substance in body; under enamel layer is dentin, subst ...
... • Tooth subdivided into crown and root; crown is part of tooth visible above gum line; root is below gum line; root anchored in bony socket of jaw by cementum and tiny periodontal ligaments • Crown of tooth is covered by layer of enamel, hardest substance in body; under enamel layer is dentin, subst ...
Neuro Anatomy Lec.4 أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي Blood supply of the
... Blood supply of the brain: The brain form about 2% of total body weight, but it receive about 10% of the cardiac output as it is the most actively metabolic structure in the body & can’t with stand poor perfusion or cut of its blood supply for more than 20-30 seconds, & if last for a minute there wi ...
... Blood supply of the brain: The brain form about 2% of total body weight, but it receive about 10% of the cardiac output as it is the most actively metabolic structure in the body & can’t with stand poor perfusion or cut of its blood supply for more than 20-30 seconds, & if last for a minute there wi ...
41C The Mammalian Digestive System
... • The general principles of food processing are similar for a diversity of animals, including the mammalian system which we will use as a representative example. • The mammalian digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and various accessory glands that secrete digestive juices into the cana ...
... • The general principles of food processing are similar for a diversity of animals, including the mammalian system which we will use as a representative example. • The mammalian digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and various accessory glands that secrete digestive juices into the cana ...
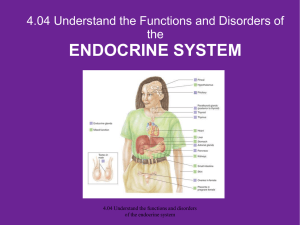
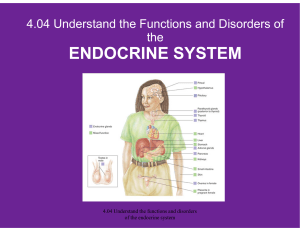
The Endocrine System
... Diabetes Mellitus (Type I) How is it treated? Insulin and monitor daily glucose levels ...
... Diabetes Mellitus (Type I) How is it treated? Insulin and monitor daily glucose levels ...
fd endocrine system
... Diabetes Mellitus (Type I) How is it treated? Insulin and monitor daily glucose levels ...
... Diabetes Mellitus (Type I) How is it treated? Insulin and monitor daily glucose levels ...
Anatomy of the Reproductive System (Chapter 42) Lab Objectives
... Be able to label the arteries and veins from the lecture notes on the slides marked “Know these arteries” and “Know these veins” and the other vessels noted with an asterisk Histology: be able to differentiate between vein and artery cross section Blood (covered on final exam only, not the lab prac ...
... Be able to label the arteries and veins from the lecture notes on the slides marked “Know these arteries” and “Know these veins” and the other vessels noted with an asterisk Histology: be able to differentiate between vein and artery cross section Blood (covered on final exam only, not the lab prac ...
Surgical Science Generic Examination Anatomy MCQ Sample Paper
... The questions that follow consist of an assertion or statement (S) in the left-hand column and a reason (R) in the right-hand column. For each question select the most appropriate response and blacken the circle according to the rules below: Blacken A if S is correct and R is correct and is a valid ...
... The questions that follow consist of an assertion or statement (S) in the left-hand column and a reason (R) in the right-hand column. For each question select the most appropriate response and blacken the circle according to the rules below: Blacken A if S is correct and R is correct and is a valid ...
gastroduodenal_ulcer_disease
... prostaglandins; binding is greater in upper small intestinal (duodenal) ulcers than in stomach ulcers • Antibiotic(s) should be given by injection, if a break in the lining of the stomach or upper small intestine is suspected or if aspiration pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs, caused by accidenta ...
... prostaglandins; binding is greater in upper small intestinal (duodenal) ulcers than in stomach ulcers • Antibiotic(s) should be given by injection, if a break in the lining of the stomach or upper small intestine is suspected or if aspiration pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs, caused by accidenta ...
Sample Chapter
... enzyme in turn activates several others, and so on. These intracellular enzymes cause the changes in the cell that are associated with the hormone. Because of the second messenger system, the binding of a single peptide hormone can result in as much as a thousandfold response. The cellular response ...
... enzyme in turn activates several others, and so on. These intracellular enzymes cause the changes in the cell that are associated with the hormone. Because of the second messenger system, the binding of a single peptide hormone can result in as much as a thousandfold response. The cellular response ...
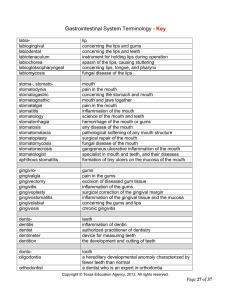
Gastrointestinal System Terminology - Key
... psychiatric condition involving self-deprivation of food, lack of appetite, and pathological weight loss cessation of digestion inability to swallow accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity congenital absence or closure of a normal opening abnormal slowness in eating a neurotic disorder charac ...
... psychiatric condition involving self-deprivation of food, lack of appetite, and pathological weight loss cessation of digestion inability to swallow accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity congenital absence or closure of a normal opening abnormal slowness in eating a neurotic disorder charac ...
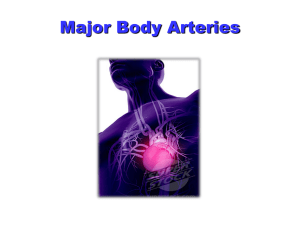
17. Major Vessels of the Head & Neck
... Supplies structures in the neck, face, and scalp; it also supplies the tongue and the maxilla. Begins at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage Terminates in the substance of the parotid gland behind the neck of the mandible by dividing into the superficial temporal and maxillary art ...
... Supplies structures in the neck, face, and scalp; it also supplies the tongue and the maxilla. Begins at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage Terminates in the substance of the parotid gland behind the neck of the mandible by dividing into the superficial temporal and maxillary art ...
L1-Esophagus and stomach2014-11-16 00:5710.6 MB
... Cardiac orifice lies opposite the left seventh costal cartilage 2.5 cm. from the sternum ,(T10). Pyloric orifice lies on transpyloric plane1 cm. to the right of the middle line, at the level of L1. Lesser curvature a curved line, concave to the right joining these 2 points. The fundus : reaches to t ...
... Cardiac orifice lies opposite the left seventh costal cartilage 2.5 cm. from the sternum ,(T10). Pyloric orifice lies on transpyloric plane1 cm. to the right of the middle line, at the level of L1. Lesser curvature a curved line, concave to the right joining these 2 points. The fundus : reaches to t ...
Topic: Ecological Issues Aim : How do we take part in solving
... have built-in physiological mechanisms to maintain them at desirable levels. When a change occurs in the body, there are two general ways that the body can respond. In negative feedback, the body responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Because this tends to keep things constant ...
... have built-in physiological mechanisms to maintain them at desirable levels. When a change occurs in the body, there are two general ways that the body can respond. In negative feedback, the body responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Because this tends to keep things constant ...
Common Surgical Problems of the Stomach and Small Intestine
... Via female GU tract. Through peritoneal surface via a procedure. Intraperitoneal source, such as abscess rupture or gas-forming microbes. ...
... Via female GU tract. Through peritoneal surface via a procedure. Intraperitoneal source, such as abscess rupture or gas-forming microbes. ...
Anatomy - Digestion - Clackamas Career and Technical Education
... be reduced by maintaining at least 50% of the stand as grass. Also, cattle should not be turned out onto a pasture with a high percentage of legumes when cattle are hungry or the pasture is wet. Once cattle are adapted to legume/grass pastures, they can graze it even when wet. A final option is to u ...
... be reduced by maintaining at least 50% of the stand as grass. Also, cattle should not be turned out onto a pasture with a high percentage of legumes when cattle are hungry or the pasture is wet. Once cattle are adapted to legume/grass pastures, they can graze it even when wet. A final option is to u ...
ANHIS digestive system#1 010115
... “wisdom teeth,” in the late teens or early 20’s. Often the jaw lacks space to accommodate these final molars, and they may either emerge only partially or grow at an angle and become impacted. Impacted teeth cannot erupt properly because of the angle of ...
... “wisdom teeth,” in the late teens or early 20’s. Often the jaw lacks space to accommodate these final molars, and they may either emerge only partially or grow at an angle and become impacted. Impacted teeth cannot erupt properly because of the angle of ...
Lecture 1
... Cardiac orifice lies opposite the left seventh costal cartilage 2.5 cm. from the sternum ,(T10). Pyloric orifice lies on transpyloric plane1 cm. to the right of the middle line, at the level of L1. Lesser curvature a curved line, concave to the right joining these 2 points. The fundus : reaches to t ...
... Cardiac orifice lies opposite the left seventh costal cartilage 2.5 cm. from the sternum ,(T10). Pyloric orifice lies on transpyloric plane1 cm. to the right of the middle line, at the level of L1. Lesser curvature a curved line, concave to the right joining these 2 points. The fundus : reaches to t ...
Blood Supply of Barin
... tissues and carries away metabolites. Loss of consciousness occurs in less than 15 seconds after blood flow to the brain has stopped, and irreparable damage to the brain tissue occurs within 5 minutes. Cerebrovascular disease, or stroke, occurs as a result of vascular compromise or hemorrhage an ...
... tissues and carries away metabolites. Loss of consciousness occurs in less than 15 seconds after blood flow to the brain has stopped, and irreparable damage to the brain tissue occurs within 5 minutes. Cerebrovascular disease, or stroke, occurs as a result of vascular compromise or hemorrhage an ...
Ch 9 glands
... • Adrenal Medulla • Secretes epinephrin (adrenalin) and norepinephrin (collectively called catecholamines). Chief hormones that respond to stress quickly. Fight or flight response. ...
... • Adrenal Medulla • Secretes epinephrin (adrenalin) and norepinephrin (collectively called catecholamines). Chief hormones that respond to stress quickly. Fight or flight response. ...
The Endocrine System - Destiny High School
... The pituitary gland is the vice president. The other glands serve as managers. As the president, the hypothalamus directs the activities of the pituitary gland (VP). The pituitary gland then releases its many hormones to direct the “managers”. – The hormones from the “managers” have an end goal to s ...
... The pituitary gland is the vice president. The other glands serve as managers. As the president, the hypothalamus directs the activities of the pituitary gland (VP). The pituitary gland then releases its many hormones to direct the “managers”. – The hormones from the “managers” have an end goal to s ...
6. Glucose Homeostasis 2nd edition
... Glucose is diffused into cells through hexose transporters such as GLUT4 GLUT4 is present in cytoplasmic vesicles Insulin binding to its receptor causes vesicles to diffuse into plasma membrane GLUT4 is inserted into the membrane Allowing glucose transport into the cell Brain and liver h ...
... Glucose is diffused into cells through hexose transporters such as GLUT4 GLUT4 is present in cytoplasmic vesicles Insulin binding to its receptor causes vesicles to diffuse into plasma membrane GLUT4 is inserted into the membrane Allowing glucose transport into the cell Brain and liver h ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.