08 Vasculature of lower limb
... Formed by the union of venae comitantes around the anterior & posterior tibial arteries. lies posterior to popliteal artery. Femoral vein It enters the thigh by passing through the opening in the adductor magnus . It leaves the thigh in the intermediate compartment of the femoral sheath. ...
... Formed by the union of venae comitantes around the anterior & posterior tibial arteries. lies posterior to popliteal artery. Femoral vein It enters the thigh by passing through the opening in the adductor magnus . It leaves the thigh in the intermediate compartment of the femoral sheath. ...
chemically digested.
... digested down into the small soluble molecules, the body must separate them from the waste food that has not been digested. No food is 100% useful and so there will always be some waste that needs excreting. In order to understand how the body carry’s out this selection procedure, we need to take a ...
... digested down into the small soluble molecules, the body must separate them from the waste food that has not been digested. No food is 100% useful and so there will always be some waste that needs excreting. In order to understand how the body carry’s out this selection procedure, we need to take a ...
16.Digestive
... • Pancreatic amylase – Converts polysaccharides into the disaccharide amylase • Pancreatic lipase – Only enzyme secreted throughout entire digestive system that can digest fat Chapter 16 The Digestive System Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood ©2007 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning ...
... • Pancreatic amylase – Converts polysaccharides into the disaccharide amylase • Pancreatic lipase – Only enzyme secreted throughout entire digestive system that can digest fat Chapter 16 The Digestive System Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood ©2007 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning ...
File
... 2. Middle Cervical Ganglion: lies at level of cricoid Branches: Gray rami: (ant. rami of 5th & 6th cervical nerves) Thyroid branches: along inferior thyroid artery. Middle cardiac branch: ends in cardiac plexus. 3. Inferior Cervical Ganglion: fused with 1st thoracic ganglion to form stellate ganglio ...
... 2. Middle Cervical Ganglion: lies at level of cricoid Branches: Gray rami: (ant. rami of 5th & 6th cervical nerves) Thyroid branches: along inferior thyroid artery. Middle cardiac branch: ends in cardiac plexus. 3. Inferior Cervical Ganglion: fused with 1st thoracic ganglion to form stellate ganglio ...
Anatomy of the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid and adrenal glands
... posterior aspect of the middle/lower part of the gland. Additional branches may arise from pharyngeal and tracheal arteries, as well as the thyroidea ima artery. This latter vessel is variable in both its presence and origin and arises from either the aortic arch or the brachiocephalic artery. Arter ...
... posterior aspect of the middle/lower part of the gland. Additional branches may arise from pharyngeal and tracheal arteries, as well as the thyroidea ima artery. This latter vessel is variable in both its presence and origin and arises from either the aortic arch or the brachiocephalic artery. Arter ...
J Taste - CiteSeerX
... Digestive tract secretions aid digestion The digestive process is aided by substances that are secreted into the digestive tract from cells lining the digestive tract and from a number of accessory organs. One of these substances is mucus. It moistens, lubricates, and protects the digestive tract. E ...
... Digestive tract secretions aid digestion The digestive process is aided by substances that are secreted into the digestive tract from cells lining the digestive tract and from a number of accessory organs. One of these substances is mucus. It moistens, lubricates, and protects the digestive tract. E ...
Document
... mucus secretion from compound mucous glands called Brunner’s glands which are found in large no. in duodenal wall in area between pylorus and papilla of Vater. Brunner’s glands secretion (about 200 ml/day) is stimulated by: 1. Tactile or irritating stimuli on duodenal mucosa 2. Vagal stimulation 3. ...
... mucus secretion from compound mucous glands called Brunner’s glands which are found in large no. in duodenal wall in area between pylorus and papilla of Vater. Brunner’s glands secretion (about 200 ml/day) is stimulated by: 1. Tactile or irritating stimuli on duodenal mucosa 2. Vagal stimulation 3. ...
SECTION 2 Blood Supply Lymphatics Innervation
... During pregnancy, there is marked hypertrophy of the uterine vasculature, which is supplied principally from the uterine and ovarian arteries (see Fig. 2-9). The uterine artery, a main branch of the internal iliac artery—previously called the hypogastric artery—enters the base of the broad ligament ...
... During pregnancy, there is marked hypertrophy of the uterine vasculature, which is supplied principally from the uterine and ovarian arteries (see Fig. 2-9). The uterine artery, a main branch of the internal iliac artery—previously called the hypogastric artery—enters the base of the broad ligament ...
A Review. Fat Digestion in the Newborn: Role of Lingual
... Because high fatty acid uptake and esterification is directly related to high levels of free fatty acids (72) and monoglycerides (53) within the intestine, it is very difficult to reconcile the marked discrepancy between low intraluminal lipolysis (17,48,66,74) and increased mucosal reesterifying ca ...
... Because high fatty acid uptake and esterification is directly related to high levels of free fatty acids (72) and monoglycerides (53) within the intestine, it is very difficult to reconcile the marked discrepancy between low intraluminal lipolysis (17,48,66,74) and increased mucosal reesterifying ca ...
The Endocrine System
... Catecholamines enhance and prolong the effect of the (fight or flight) (Sympathetic nerve system) response to short term stress HYPERSECRETION leads to symptoms of excessive sympathetic nerve system activity ...
... Catecholamines enhance and prolong the effect of the (fight or flight) (Sympathetic nerve system) response to short term stress HYPERSECRETION leads to symptoms of excessive sympathetic nerve system activity ...
VEINS - ANTERIOR REGION
... The systemic veins below the heart empty into the po~terior vena cava. The upper portion of this enlarged blood vessel was observed when we studied the thoracic veins. It passes through the diaphragm and lies along the mid-dorsal body wall of the thorax. It then enters the right atrium of the heart ...
... The systemic veins below the heart empty into the po~terior vena cava. The upper portion of this enlarged blood vessel was observed when we studied the thoracic veins. It passes through the diaphragm and lies along the mid-dorsal body wall of the thorax. It then enters the right atrium of the heart ...
Major Vessels of the Head & Neck
... terminal branches, the common carotid artery gives off no branches. ...
... terminal branches, the common carotid artery gives off no branches. ...
kidney and ureter
... the mesonephric duct close to the entrance of the duct at the cloaca • The ureteric bud is responsible for the development of the collecting system ...
... the mesonephric duct close to the entrance of the duct at the cloaca • The ureteric bud is responsible for the development of the collecting system ...
The Endocrine System
... organs, called endocrine glands (EN duh krin). An endocrine gland produces and releases chemical substances that signal changes in other parts of the body. Some of your body’s glands, such as sweat glands, release their chemicals into tiny tubes called ducts. The ducts carry the chemicals to the pla ...
... organs, called endocrine glands (EN duh krin). An endocrine gland produces and releases chemical substances that signal changes in other parts of the body. Some of your body’s glands, such as sweat glands, release their chemicals into tiny tubes called ducts. The ducts carry the chemicals to the pla ...
Animal or Plant Hormone Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH
... bone. T3- active form- increases cellular respiration. T4- inactive formmovement in the blood to the cells & raises blood Ca levels by causing bone cells to break down bone ...
... bone. T3- active form- increases cellular respiration. T4- inactive formmovement in the blood to the cells & raises blood Ca levels by causing bone cells to break down bone ...
Clues
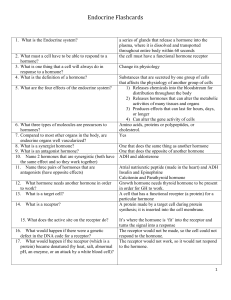
... 25. A hromone acts as a ____ messenger, which carries a signal to the cell membrane. 27. Hormones produced by sex glands and the adrenal cortex are mainly the ____type in chemical composition. 28. The ____gland lies behind the peritoneum between the greater curvature of the stomach and the duodenum. ...
... 25. A hromone acts as a ____ messenger, which carries a signal to the cell membrane. 27. Hormones produced by sex glands and the adrenal cortex are mainly the ____type in chemical composition. 28. The ____gland lies behind the peritoneum between the greater curvature of the stomach and the duodenum. ...
hormones
... • Describe the location, structure, and general functions of the adrenal glands, identify the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla, and list the effects of each hormone. ...
... • Describe the location, structure, and general functions of the adrenal glands, identify the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla, and list the effects of each hormone. ...
VASCULARIZATION OF THE HEAD AND NECK
... ---------- these two anastomose in antero/inferior part of septum Internal Carotid: blood supply to the interior of the skull: after branching from the external carotid, it rises vertically, before entering the carotid canal in the petrous part of the temporal bone. It then enters the middle cranial ...
... ---------- these two anastomose in antero/inferior part of septum Internal Carotid: blood supply to the interior of the skull: after branching from the external carotid, it rises vertically, before entering the carotid canal in the petrous part of the temporal bone. It then enters the middle cranial ...
The Umbilical Cord and Body- stalk. The umbilical cord (Fig. 28
... tissues and open into the maternal blood vessels, with the result that the spaces in the trophoblastic network are filled with maternal blood; these spaces communicate freely with one another and become greatly distended and form the intervillous space. ...
... tissues and open into the maternal blood vessels, with the result that the spaces in the trophoblastic network are filled with maternal blood; these spaces communicate freely with one another and become greatly distended and form the intervillous space. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.