Dissection of the Superior Thyroid Pole
... "tips out" facilitates avoidance of inadvertent injury to the external laryngeal nerve as it crosses in this plane. Taking such precautions to prevent injury to the nerve, referred to as the "Amelita Gala Curci nerve" is mandatory to avoid loss of highpitched sounds After creation of the space, the ...
... "tips out" facilitates avoidance of inadvertent injury to the external laryngeal nerve as it crosses in this plane. Taking such precautions to prevent injury to the nerve, referred to as the "Amelita Gala Curci nerve" is mandatory to avoid loss of highpitched sounds After creation of the space, the ...
13. ch 12(244-260) THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... kept within a specific range. Negative feedback, described in Chapter 1, is the method most commonly used to regulate these levels. In negative feedback, the hormone itself (or the result of its action) controls further hormone secretion. Each endocrine gland tends to oversecrete its hormone, exerti ...
... kept within a specific range. Negative feedback, described in Chapter 1, is the method most commonly used to regulate these levels. In negative feedback, the hormone itself (or the result of its action) controls further hormone secretion. Each endocrine gland tends to oversecrete its hormone, exerti ...
endocrine system
... Steroid hormones are lipids and thus are not very soluble in blood plasma, which is mostly water. Instead of traveling in the plasma as free molecules, they attach to soluble plasma proteins. As you can see in Figure 16-7, a steroid hormone molecule dissociates from its carrier before approaching th ...
... Steroid hormones are lipids and thus are not very soluble in blood plasma, which is mostly water. Instead of traveling in the plasma as free molecules, they attach to soluble plasma proteins. As you can see in Figure 16-7, a steroid hormone molecule dissociates from its carrier before approaching th ...
A rare variation of the inferior alveolar artery with potential clinical
... The inferior alveolar nerve is the largest branch of the mandibular nerve and descends with the inferior alveolar artery. Blocks of the inferior alveolar nerve are one of the most common injections performed during dental procedures to achieve mandibular anaesthesia [4]. A potential hazard of this p ...
... The inferior alveolar nerve is the largest branch of the mandibular nerve and descends with the inferior alveolar artery. Blocks of the inferior alveolar nerve are one of the most common injections performed during dental procedures to achieve mandibular anaesthesia [4]. A potential hazard of this p ...
HusainResidentlectur.. - Ob/Gyn Residents` Resources
... for 40%. • Jejunum and ileum differ in that the jejunum is thicker, has thicker mucosal folds, the mesenteric fat extends onto the wall of the ileum but not the jejunum, the vasa recta are shorter in the ileum ...
... for 40%. • Jejunum and ileum differ in that the jejunum is thicker, has thicker mucosal folds, the mesenteric fat extends onto the wall of the ileum but not the jejunum, the vasa recta are shorter in the ileum ...
Variations of the superior thyroid artery and Internal jugular vein
... similarity in origin) ran in the anterior triangle of neck to drain into the internal jugular vein on left side. The knowledge of such variations is important for any invasive or surgical procedure in the neck. region. Key words : superior thyroid artery, common carotid and external carotid arteries ...
... similarity in origin) ran in the anterior triangle of neck to drain into the internal jugular vein on left side. The knowledge of such variations is important for any invasive or surgical procedure in the neck. region. Key words : superior thyroid artery, common carotid and external carotid arteries ...
Gross 8/27/99 - GEOCITIES.ws
... 2. Daughter cells are identical-no genetic recombination. Size of zygote stays same—divided cells shrink with each divisionincrease ratio of DNA chromosomes (nuclear) to cytoplasm(more DNA than cytoplasm) D. Morula-32 cell stage-reaches uterus at this time (about day 5) 1. upon reaching uterus—zona ...
... 2. Daughter cells are identical-no genetic recombination. Size of zygote stays same—divided cells shrink with each divisionincrease ratio of DNA chromosomes (nuclear) to cytoplasm(more DNA than cytoplasm) D. Morula-32 cell stage-reaches uterus at this time (about day 5) 1. upon reaching uterus—zona ...
11-2014-15 Vascular anatomy of the upper limb)
... pairs, and are situated one on either side of the corresponding artery, and connected at intervals by short transverse branches. The superficial and deep palmar arterial arches are each accompanied by a pair of venæ comitantes which constitute the superficial and deep palmar venous arches, and rec ...
... pairs, and are situated one on either side of the corresponding artery, and connected at intervals by short transverse branches. The superficial and deep palmar arterial arches are each accompanied by a pair of venæ comitantes which constitute the superficial and deep palmar venous arches, and rec ...
15 Vascular anatomy of the upper limb2010
... pairs, and are situated one on either side of the corresponding artery, and connected at intervals by short transverse branches. The superficial and deep palmar arterial arches are each accompanied by a pair of venæ comitantes which constitute the superficial and deep palmar venous arches, and rec ...
... pairs, and are situated one on either side of the corresponding artery, and connected at intervals by short transverse branches. The superficial and deep palmar arterial arches are each accompanied by a pair of venæ comitantes which constitute the superficial and deep palmar venous arches, and rec ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... What is up-regulation, and what conditions lead to this phenomenon? What is down-regulation, and what conditions lead to this phenomenon? What does “permissive” mean in the context of endocrinology? In general, how do peptide and catecholamine hormones affect their target cells? In general, how do t ...
... What is up-regulation, and what conditions lead to this phenomenon? What is down-regulation, and what conditions lead to this phenomenon? What does “permissive” mean in the context of endocrinology? In general, how do peptide and catecholamine hormones affect their target cells? In general, how do t ...
Vertebral Column, Sinuses that Collect Venous Blood, Dorsal View
... outside the dura matter, extends from the sacral levels to the foramen magnum. Blood goes in different directions because there are no valves which exist in veins of other parts of body, such as those leading to the heart from the legs. That is a problem with the transmission of cancerous cells thro ...
... outside the dura matter, extends from the sacral levels to the foramen magnum. Blood goes in different directions because there are no valves which exist in veins of other parts of body, such as those leading to the heart from the legs. That is a problem with the transmission of cancerous cells thro ...
RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES
... due to unligated upper or lower pole renal artery may be avoided if variations are well known to the operating surgeon. In arriving at a cause for varicocele, which may be due to obstruction of testicular venous outflow by an aberrant renal artery. Hence there is a need for study of variations of re ...
... due to unligated upper or lower pole renal artery may be avoided if variations are well known to the operating surgeon. In arriving at a cause for varicocele, which may be due to obstruction of testicular venous outflow by an aberrant renal artery. Hence there is a need for study of variations of re ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine
... The posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) stores and secretes two hormones that are made by certain neurosecretory cells located in the hypothalamus. Posterior Pituitary Hormones: The two hormones released from the posterior pituitary act directly on nonendocrine tissues o Oxytocin - induces uteri ...
... The posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) stores and secretes two hormones that are made by certain neurosecretory cells located in the hypothalamus. Posterior Pituitary Hormones: The two hormones released from the posterior pituitary act directly on nonendocrine tissues o Oxytocin - induces uteri ...
Anatomy of thyroid gland Introduction • Brownish
... Brownish-‐red and soft during life Usually weighs about 25-‐ 30g (larger in women) Surrounded by a thin, fibrous capsule of connective tissue External to this is a “false capsule” formed by pretrache ...
... Brownish-‐red and soft during life Usually weighs about 25-‐ 30g (larger in women) Surrounded by a thin, fibrous capsule of connective tissue External to this is a “false capsule” formed by pretrache ...
Gastrin-Like Peptide
... satiety in mammals (16). At this point, Janssen and co-workers (1), however, do not discount hyperphagia as the underlying cause for increased fat content in NLP-12 and CKR-2 mutant worms and don’t dismiss a role for CK signaling in the regulation of satiety in nematodes. In humans, where a parallel ...
... satiety in mammals (16). At this point, Janssen and co-workers (1), however, do not discount hyperphagia as the underlying cause for increased fat content in NLP-12 and CKR-2 mutant worms and don’t dismiss a role for CK signaling in the regulation of satiety in nematodes. In humans, where a parallel ...
Sialography - El Camino College
... salivary glands – Only __________________done at a time – CT and MRI have largely replaced this exam for Salivary stone or lesion is suspected ...
... salivary glands – Only __________________done at a time – CT and MRI have largely replaced this exam for Salivary stone or lesion is suspected ...
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1
... Comprises area within superior thoracic aperture and transverse thoracic plane -Transverse thoracic plane – arbitrary line from the sternal angle anteriorly to the IV disk or T4 and T5 posteriorly Inferior mediastinum Extends from transverse thoracic plane to diaphragm; 3 subdivisions Anterior media ...
... Comprises area within superior thoracic aperture and transverse thoracic plane -Transverse thoracic plane – arbitrary line from the sternal angle anteriorly to the IV disk or T4 and T5 posteriorly Inferior mediastinum Extends from transverse thoracic plane to diaphragm; 3 subdivisions Anterior media ...
Ch 22 Summary: Lymphatic System 2014
... 2. have a slightly larger diameter than blood capillaries and have "one way' valves for fluid to enter the lymphatic capillary. 3. Anchoring filaments attach endothelial cells to surrounding tissue. 4. The lymphatic capillary in the villus of the small intestine is the lacteal. Its function is to tr ...
... 2. have a slightly larger diameter than blood capillaries and have "one way' valves for fluid to enter the lymphatic capillary. 3. Anchoring filaments attach endothelial cells to surrounding tissue. 4. The lymphatic capillary in the villus of the small intestine is the lacteal. Its function is to tr ...
File
... • Divides into medial & lateral plantar aa • Latter forms plantar arch & anastomosis with dorsalis pedis a ...
... • Divides into medial & lateral plantar aa • Latter forms plantar arch & anastomosis with dorsalis pedis a ...
Posteriorly
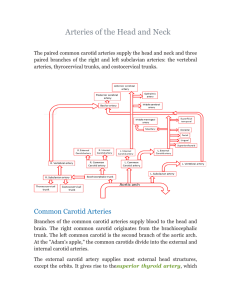
... • The external carotid artery is one of the terminal branches of the common carotid artery. It supplies structures in the neck, face, and scalp; it also supplies the tongue and the maxilla. The artery begins at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage and terminates in the substance of ...
... • The external carotid artery is one of the terminal branches of the common carotid artery. It supplies structures in the neck, face, and scalp; it also supplies the tongue and the maxilla. The artery begins at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage and terminates in the substance of ...
Anomalous origin of the radial recurrent artery
... The brachial artery begins at the distal border of teres major and ends about a centimetre below to the elbow joint at the level of the neck of the radius by dividing into the radial and the ulnar arteries. But in the present case an unusual variation in the branching pattern of the right brachial a ...
... The brachial artery begins at the distal border of teres major and ends about a centimetre below to the elbow joint at the level of the neck of the radius by dividing into the radial and the ulnar arteries. But in the present case an unusual variation in the branching pattern of the right brachial a ...
Unit II Structures to ID
... o Supreme intercostal artery—gives rise to posterior intercostal arteries 1 & 2 Third part—between lateral border of anterior scalene & lateral border of rib 1 Dorsal scapular artery Thoracic duct: on left side; joins venous system near junction of right subclavian and IJV Lymphatic duct: right ...
... o Supreme intercostal artery—gives rise to posterior intercostal arteries 1 & 2 Third part—between lateral border of anterior scalene & lateral border of rib 1 Dorsal scapular artery Thoracic duct: on left side; joins venous system near junction of right subclavian and IJV Lymphatic duct: right ...
Anomalous origin of left coronary artery in an adult
... dilated and tortuous with presence of multiple dilated collateral branches (Figs 1B and 2). The patient was advised catheter coronary angiogram and surgery, however, the patient refused and she is currently on medical management. ALCAPA is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 300,00 ...
... dilated and tortuous with presence of multiple dilated collateral branches (Figs 1B and 2). The patient was advised catheter coronary angiogram and surgery, however, the patient refused and she is currently on medical management. ALCAPA is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 300,00 ...
Arteries of the Head and Neck
... The arterial circle, also called the circle of Willis, is an arrangement of arteries surrounding the pituitary gland and optic chiasm. It creates redundancies to ensure blood supply to the brain if one artery feeding the circle—or a part of the circle—is damaged. The arterial circle is fed anteriorl ...
... The arterial circle, also called the circle of Willis, is an arrangement of arteries surrounding the pituitary gland and optic chiasm. It creates redundancies to ensure blood supply to the brain if one artery feeding the circle—or a part of the circle—is damaged. The arterial circle is fed anteriorl ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.