* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit II Structures to ID
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
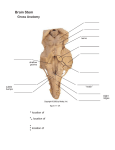
Structures to Identify: Head & Neck Practical Lab 1: Scalp, Interior of Skull, Dural Partitions and Sinuses, and Cranial Fossae Scalp: o 5 layers: Skin, Connective Tissue (dense), Aponeurosis, Loose Connective Tissue, Pericranium o Occipitofrontalis muscle o Temporalis muscle o Supraorbital nerve and vessels; if present, steps to find them: Pull anterior scalp flap inferiorly to see supraorbital margin Nerve and vessels exit supraorbital notch and enter deep surface of scalp Calvaria o Groove for superior sagittal sinus o Granular foveolae—caused by arachnoid granulations o Grooves for the branches of the middle meningeal artery Dural partitions o Cerebellar tentorium o Falx cerebri o Falx cerebelli Dural sinuses o Superior sagittal sinus—begins near crista galli and ends near cerebellar tentorium o Confluence of sinuses—at internal occipital protubernce o Inferior sagittal sinus—inferior margin of falx cerebri o Straight sinus—at junction of falx cerebri and tentorium cerebri o Great cerebral vein of Galen—at anterior end of straight sinus o Transverse sinus—will see groove on occipital bone o Sigmoid sinus—will see groove on occipital bone; ends at jugular foramen o Sphenoparietal sinus o Cavernous sinus o Superior pretrosal sinus o Inferior petrosal sinus o Basilar plexus Anterior Cranial Fossa: sphenoid, ehtmoid, frontal bones o Cribiform plate and [I] o Crista galli o Anterior clinoid process Middle Cranial Fossa: sphenoid and temporal bones o Foramen spinosum and Middle meningeal artery o Optic canal and [II] o Superior orbital fissure and [III], [IV], V1, [VI] o [V] and ganglion o Foramen rotundum and V2 o Foramen ovale and V3 o Carotid canal and internal carotid artery: carotid siphon in the cavernous sinus o Hypophyseal fossa, covered by diaphragm sellae o Anterior and posterior intercavernous sinuses: surrounds stalk of pituitary o Posterior clinoid process Posterior Cranial Fossa: temporal and occipital bones o Internal acoustic meatus and [VII] and [VIII] o Jugular foramen: [IX], [X], and [XI] o Foramen magnum: cervical root of [XI] enters fossa here o Groove for transverse sinus and groove for sigmoid sinus o Hypoglossal canal and [XII] Lab 2: Neck, Posterior Triangle Boundaries of Posterior Triangle: o Anterior: posterior border of SCM o Posterior: superior border of trapezius o Inferior: middle 1/3 of clavicle o Roof: investing layer of deep cervical fascia o Floor: muscles of the neck (scales, levator scapulae) and prevertebral fascia Platysma muscle—in superficial fascia, innervated by cervical branch of [VII] External jugular vein Branches of cervical plexus: o Lesser occipital nerve o Great auricular nerve o Transverse cervical nerve o Supraclavicular nerve—review referred diaphragmatic pain to shoulder (Grant’s pg. 208) [XI] Lab 3: Anterior Triangles (Muscular, Submandibular, and Submental) Bones and cartilage: Hyoid, thyrohiod membrane, laryngeal prominence of thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, first tracheal ring, isthmus of thyroid gland In superficial fascia: o Find retromandibular vein & posterior auricular vein uniting to form external jugular o Anterior jugular vein o Communicating vein (connects common facial vein w/ anterior jugular vein) Muscular Triangle o Bounderies: Superolateral: superior belly of omohyoid Inferolater: anterior border of SCM Medial: median plane of neck o Muscles: sternohyoid, superior belly of omohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid o Ansa cervicalis: innervates 3 of 4 infrahyoids o Nerve to thyrohyoid: from C1, via [XII] Submandibular Triangle o Boundaries: Superior: inferior border (base) of mandible Anteroinferior: anterior belly of the digastric Posteroinferior: posterior belly of the digastric Roof: investing layer of fascia Floor: mylohyoid and hyoglossus o On mandible: Digastric fossa Mylohyoid line Submandibular fossa Mylohyoid groove o Muscles: Anterior/posterior bellies of digastric; intermediate tendon Tendon of stylohyoid Mylohyoid muscle o [XII]: enters triangle deep to the posterior belly of digastric, then passes deep to mylohyoid Submental Triangle o Boundaries: Lateral: anterior bellies of right/left digrastric muscles Inferior: hyoid bone Roof: investing fascia Floor: mylohoid o Submental lymph and tributaries that form the anterior jugular vein Lab 4: Carotid Triangle, Thryoid and Parathyroid Boundaries of Carotid Triangle: o Anterior: superior belly of omohyoid o Posterior: anterior border of SCM o Superior: posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid o Floor: posterior—inferior pharyngeal constrictor; anterior—thyrohyoid and hyoglossus o Roof: Investing fascia, cutaneous nerves, and platysma [XI]: look for it on deep surface of SCM Greater horn of hyoid bone [XII]: Superior to tip of greater horn of hyoid; crossed superiorly by occipital artery; passes medial to posterior belly of digastric, medial to stylohyoid, and deep to mylohyoid Ansa cervicalis o Superior root travels with [XII] o Inferior root passes lateral to carotid sheath Thyrohyoid membrane Superior laryngeal nerve o Internal branch: sensory to mucosa of larynx superior to vocal folds o External branch: motor to cricothyroid Cricothyroid muscle Carotid sheath: common carotid, internal carotid, internal jugular, and [X] o IJV tributaries: common facial vein, superior thyroid vein, middle thyroid vein External carotid artery and branches: o Superior thyroid: gives off superior laryngeal (runs with internal laryngeal nerve) o Lingual: passes deep to muscles of tongue o Facial: passes medial to posterior belly of digastric and deep to superficial submandibular gland o Occipital artery o Posterior auricular artery o Ascending pharyngeal artery Birfurcation of common carotid & carotid sinus and body [X]: posterior to the vessels Thyroid: @ C5-T1 o Right and left lobe, connected by isthmus o Look for pyramidal lobe: would extend superiorly from isthmus o Superior thyroid artery; enters superior end of lobe o Superior and middle thyroid veins o Right/Left inferior thyroid veins o Thyroid ima (rare): would enter thyroid gland inferiorly, near midline o Recurrent laryngeal nerve: posterior to lobe; in groove between trachea & esophagus Parathyroid: posterior aspect of thyroid (if you’ve dissected one of the lobes) Lab 5: Root of Neck Junction between thorax and neck; superior to superior thoracic aperture Inferior belly of omohyoid and intermediate tendon External jugular vein Subclavian vein o Joined by internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein Subclavian artery o Right: branch off brachiocephalic trunk o Left: branch off aortic arch o Branches (location where branches come off will vary): First part—from origin to medial border of anterior scalene Vertebral artery Internal thoracic artery Thyrocervical trunk o Transverse cervical artery o Suprascapular artery o Inferior thyroid artery Ascending cervical artery Second part—posterior to anterior scalene Costocervical trunk o Deep cervical artery o Supreme intercostal artery—gives rise to posterior intercostal arteries 1 & 2 Third part—between lateral border of anterior scalene & lateral border of rib 1 Dorsal scapular artery Thoracic duct: on left side; joins venous system near junction of right subclavian and IJV Lymphatic duct: right side; drains into junction of left subclavian and IJV [X]: passes posterior to root of lung Right recurrent laryngeal: comes off after [X] passes anterior to subclavian artery Left recurrent laryngeal: comes off after [X] passes on the left side of the aortic arch Phrenic nerve: crosses anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle Sympathetic trunk: cervical portion; inferior cervical sympathetic ganglion is low in neck Floor of posterior triangle: splenius capitis, levator scapulae, scales Interscalene triangle: first rib and adjacent borders of anterior and middle scalene muscles Roots of brachial plexus & subclavian artery: pass thru interscalene triangle between anterior and middle scalene muscles o Supraclavicular portion of brachial plexus: five roots, three trunks, six divisions Subclavian vein, transverse cervical artery, and suprascapular artery: cross anterior surface of anterior scalene muscle Phrenic nerve: descends vertically across anterior surface of anterior scalene muscle Lab 6: Head, Face, and Parotid Region Platysma: small part extends into face along inferior border of mandible Parotid gland and parotid duct: duct pierces buccinators muscle o Enclosed in parotid sheath (continuous with investing fascia) [VII]: forms parotid plexus within parotid gland o Branches: Posterior auricular Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Marginal mandibular Cervical Buccal fat pad: anterior to masseter muscle (may be different consistency than regular fat) o Buccal nerve of V3 emerges deep to masseter muscle Facial artery: crosses inferior border of mandible @ anterior border of masseter o Branches Inferior labial artery Superior labial artery Angular artery: continuation of facial artery @ lateral side of nose Facial vein: straighter, posterior to facial artery o Angular vein anastomoses with ophthalmic veins in orbit (might see in prosection) Muscles: Buccinator muscle, masseter muscle, orbicularis oculi (orbital and palpebral part), levator labii superioris, zygomaticus major/minor, orbicularis oris, buccinators, depressor anguli oris Supraorbital nerve Infraorbital nerve: covered by levator labii superioris o Infraorbital artery and vein related to nerve Mental nerve o Mental artery and vein related to nerve Auriculotemporal nerve: often loops middle meningeal artery Retromandibular vein: find where it is formed by joining of maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein Superficial temporal vein Maxillary artery and superficial temporal arteries Lab 7: Temporal and Infratemporal fossae Skeletal structures to identify for this region: o Temporal fossa—formed by parts of four cranial bones Parietal, frontal, squamous temporal, and greater wing of sphenoid o Superior and inferior temporal lines—on parietal bone o Zygomatic arch—formed by zygomatic process of temporal bone and temporal process of zygomatic bone o Mandibular fossa and articular tubercle—on temporal bone o On Mandible: Head (condyle), neck, mandibular notch, coronoid process, ramus, and angle Lingula: attachment for sphenomandibular ligament Mandibular foramen: for inferior alveolar nerves and vessels Mylohyoid groove: for nerve to mylohyoid and mylohyoid vessels o Pterygomaxillary fissure—between lateral pterygoid plate and maxilla o Pterygopalatine fossa—at superior end of PT fissure o Sphenopalatine foramen—passage from PT fossa to nasal cavity o Inferior orbital fissure—between greater wing of sphenoid and maxilla o Infratemporal surface of the maxilla o Greater wing of the sphenoid—contains foramen ovale and formaen spinosum o Lateral pterygoid plate of pterygoid process—on sphenoid Temporal fossa: o Boundaries: Superior and posterior: superior temporal line Anterior: forntal and zygomatic bones Inferior: zygomatic arch (superficially) and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone (deeply) Deep: Parts of the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones o Temporalis muscle: sup. attachment is temporal fascia and surface of fossa; inf. attachment is coronoid process of mandible; ant. fibers elevate mandible, post. fibers retract mandible Infratemporal fossa: o Boundaries: Superior: zygomatic arch (superficially), infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone (deeply) Anterior: infratemporal surface of maxilla Lateral: ramus of mandible Medial: lateral plate of the pterygoid process o Masseter muscle: sup. attachment is inf. border of zyg. arc; inf. attachment is lateral surface of ramus and mandible Masseteric vessels and nerve: cross superior to mandibular notch to enter deep surface of muscle o Mandibular nerve (V3) and branches: Inferior alveolar: enters mandibular foramen and passes anteriorly to mandibular canal and provides sensory innervation the mandibular teeth Mental: passes through the mental foramen to innervate chin and lower lip Lingual Buccal Auriculotemporal Deep temporal Mylohyoid o Chorda Tympani: joins posterior side of lingual nerve high in IT fossa o Maxillary artery and branches: Middle meningeal Deep temporal (anterior and posterior) Masseteric Inferior alveolar Buccal Posterior superior alveolar artery: enters infratemporal surface of the maxilla o Medial and lateral pterygoid muscles Temporomandibular joint o Joint capsule: loose, reinforced laterally by lateral ligament o Lateral ligament o Articular disc and superior/inferior synovial cavities Hinge motion: inferior cavity between head of mandible and articular disc Gliding motion: superior cavity between articular disc and mandibular fossa o Tendon of lateral pterygoid muscle: attaches to neck of mandible and articular disc Lab 8: Disarticulation of the head, pharynx, and bisection of head Disarticulation ID the following on occipital bone/posterior cranial fossa: o Hypoglossal canal, occipital condyle, basilar part, pharyngeal tubercle, foramen magnum, external occipital protuberance; grooves for sigmoid and transverse sinuses, and superior border of petrous portion of temporal bone Retropharyngeal space: boundaries? o Structures passing through foramen magnum: Brainstem, vertebral arteries, cervical roots of [XI] o [XII] passing through hypoglossal canal o Structures entering the jugular foramen: [IX], [X], [XI], and sigmoid sinus/jugular vein Prevertebral and lateral vertebral regions: o Sympathetic trunk Superior, middle and inferior cervical ganglia Gray rami communicantes Cervicothoracic (stellate) ganglion o Internal carotid nerve o Anterior scalene muscle Pharynx Pharyngeal wall layers o Buccopharyngeal fascia o Muscular layer o Mucous membrane Muscles: o Inferior pharyngeal constrictor: pharyngeal raphe o Middle pharyngeal constrictor: pharyngeal raphe o Superior pharyngeal constrictor: pterygomandibular raphe (ant. att.); pharyngeal tubercle (post. att.) Pharyngobasilar fascia o Stylopharyngeus muscle [IX] relationship to stylopharyngeus Pharyngeal plexus of nerves Contents of carotid sheath o Relationship to sympathetic trunk and superior cervical sympathetic ganglion? [IX], [X], and [XI] at jugular foramen o Superior laryngeal nerve and pharyngeal branch of [X] [XII] from submandibular triangle to base of skull Internal carotid nerve Bisection ID bisected structures: nasal bone, frontal bone, cribiform plate, body of sphenoid, hard palate, basilar part of occipital bone as far as the foramen magnum Parts of the pharynx: o Nasopharynx: Boundaries? Posterior nasal aperture (choana) Opening of the pharyngotympanic tube (aka auditory tube aka eustachian tube) Torus tubarius Salpingopharyngeal fold Pharyngeal recess Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid) o Oropharynx: Boundaries? Palatoglossal fold Fauces: transitional region between oral cavity and oropharynx Palatopharygneal fold Palatine tonsil o Laryngopharynx: Boundaries? Epiglottis Aditus of the larynx Piriform recess: borders? (Medial=larynx; lateral=thyroid cartilage; post.=inf. constrictor) Lab 9: Nose, Nasal Cavity, and Hard/Soft Palate Skeleton of nasal cavity: find these from anterior view of skull o Nasal Bone o Lacrimal bone o Maxila Frontal process Anterior nasal aperture Anterior nasal spine o Nasal septum—bony part o Middle nasal concha o Inferior nasal concha Skeleton of lateral nasal wall: o Ethmoid bone Cribiform plate Superior nasal concha Middle nasal concha o Lacrimal bone o Inferior nasal concha o Maxilla Palatine process Incisive canal o Sphenoid bone Opening of the sphenoidal sinus Sphenoidal sinus Body Medial/Lateral plates of the pterygoid process o Palatine bone Perpendicular plate Horizontal plate o Sphenopalatine foramen External nose Septal cartilage o Lateral nasal cartilage Alar cartilage Boundaries of nasal cavity Nasal septum Perpendicular plate of ehtmoid bone Vomer Septal Cartilage (ID it stripped of mucosa) Nasopalatine nerve: runs from sphenopalatine foramen to the incisive canal Sphenopalatine artery: same course as nasopalatine n.; Grant’s says this artery going thru incisive canal… Olfactory area: mucosa near cribiform plate Lateral wall of nasal cavity Sphenoethmoidal recess o Opening of the sphenoidal sinus Sphenoidal sinus—directly inferior to hypophyseal fossa and pituitary gland Superior/middle/inferior concha Superior/middle/inferior meatus Vestibule Atrium Nasolacrimal duct: opening in inferior meatus Semilunar hiatus: in middle concha o Opening of the maxillary sinus o Opening of the frontal sinus/anterior ethmoidal cells (in infundibulum) Ethmoidal bulla: in middle concha o Opening of the middle ethmoidal cells Opening of the posterior ethmoidal cells in the superior meatus Ethmoidal cells: located between nasal cavity and orbit Maxillary sinus: o Roof is the floor of orbit; infraorbital nerve innervates sinus mucosa o Floor is alveolar process of maxilla; roots of teeth project into sinus Hard and Soft Palates Skeleton of the palate: o Maxilla: Incisive foramen Alveolar process Palatine process o Palatine bone: Horizontal plate Greater palatine foramen Lesser palatine foramina Posterior nasal spine o Sphenoid bone: Hamulus of the medial plate of the pterygoid process Medial/lateral plate of pterygoid process Scaphoid fossa Pterygoid canal o Inferior orbital fissure o Sphenopalatine foramen o Pterygopalatine fossa o Pterygomaxillary fissure Soft Palate Torus tubarius Opening of the pharyngotympanic tube Salpingopalatine fold Torus levatorius Salpingopharyngeal fold Palatoglossal fold Palatopharyngeal fold Palatine tonsil Muscles: Innervated by pharyngeal plexus of [X] or V3 o Palatoglossus: sup. att.=palatine aponeurosis; inf. att.=lateral side of tongue o Palatopharyngeus: sup. att.=hard palate & aponeurosis; inf. att.=thyroid cartilage & pharyngeal wall o Salpingopharyngeus: sup. att.=cartilage of auditory tube; inf. att.=same as palatopharyngeus Blends with palatopharyngeus; both are inner longitudinal muscles of pharynx o Stylopharyngeus: anterior and parallel to palatopharyngeus and salpingopharyngeus Those three muscles blend near inferior end Stylopharyngeus enters pharynx between superior and middle pharyngeal constrictors o Pharyngobasilar fascia: closes gap between superior constrictor and base of skull Auditory tube and levator veli palatini pass through this gap o Levator veli palatini: sup. att.=cartilage/temporal bone of auditory tube; inf. att.=aponeurosis o Tensor veli palatini: sup. att.=scaphoid fossa; belly btwn. medial/lateral pterygoid plates tendon turns medially around hamulus of medial plate and forms palatine aponeurosis Pharyngotympanic tube: 2/3 cartilaginous (pharynx side); 1/3 temporal bone (middle ear side) Greater palatine nerve and artery: emerge from greater palatine foramen Nasopalatine nerve and distal end of sphenopalatine artery Lesser palatine nerve and artery Tonsillar bed: houses palatine tonsil o Boundaries? [IX]: enters tonsillar bed between superior and middle constrictors Sphenopalatine foramen and PT fossa Sphenopalatine artery branches (not dissected): posterior lateral nasal arteries and posterior septal branch Sphenopalatine foramen Greater palatine canal contents: greater palatine nerve, lesser palatine nerve, and descending palatine artery o Descending palatine artery gives rise to greater/lesser palatine arteries Pterygopalatine ganglion Nerve to pterygoid canal Deep to IT fossa: o Maxillary artery Sphenopalatine artery Descending palatine artery Infraorbital artery: through inferior orbital fissure to enter infraorbital canal, emerges on face at infraorbital foramen o V2 Lab 10: Oral region and larynx Surface anatomy of oral vestibule Maxilla: alveolar process and anterior surface Mandible: alveolar process and coronoid process (with tendon of temporalis muscle) Masseter muscle Communication between oral vestibule and oral cavity proper: posterior to third molar tooth Frenulum Opening of the parotid duct (lateral to second maxillary molar) Surface anatomy of oral cavity proper: Boundaries? Tongue: body, apex, median sulcus Sublingual area: frenulum, sublingual folds, opening of submand. duct on caruncle, & deep lingual veins Tongue Root (pharyngeal tongue): lies more vertically o Median/Lateral glossoepiglottic fold o Epiglottic vallecula Body (oral tongue): lies more horizontally Apex Dorsum o Sulcus terminalis o Lingula tonsil o Foramen cecum o Median sulcus o Lingual papillae: four types Bisection of tongue and mandible: Find mylohyoid, geniohyoid, and genioglossus msucles Sublingual region Sublingual gland: rests on mylohyoid muscle Submandibular duct: opens on the sublingual caruncle Deep part of the submandibular gland: on deep side of mylohyoid Lingual nerve: passes lateral, inferior, and then medial to submandibular duct Submandibular ganglion: near third mandibular molar tooth [XII]: passes btwn. deep part of submandibular gland and the hyoglossus; btwn. hyoglossus and mylohhyoid o it’s course is inferior to course of lingual nerve Hyoglossus: inf. att.=body and greater horn of hyoid; sup. att.=lateral side of tongue Styloglossus: inf. att.=lateral side of tongue; sup. att.=styloid process Intrinsic muscles of tongue: vertical, transverse, superior/inferior longitudinal groups of fibers Lingual artery: passes medial to hyoglossus muscle o Gives off sublingual artery, and after that name changes to deep lingual artery Larynx Skeleton of the larynx: o Epiglottic cartilage Stalk: attached to inner surface of the angle formed by the thyroid laminae o Thyrohyoid membrane o Thyroid cartilage: formed by two laminae joined in ant. midline Laryngeal prominence Superior horn Inferior horn—articulates w/ cricoid cartilage through cricothyroid joint o Cricoid cartilage: lamina is posterior, arch is anterio o Arytenoid cartilages Muscular and vocal processes o Vocal ligaments Intrinsic muscles of the larynx Cricothyroid muscle Lamina of the cricoid cartilage Piriform recess Internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve Inferior laryngeal nerve Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle Arytenoid muscle o Transverse and oblique fibers Cricothyroid joint o Recurrent laryngeal passes posteriorly and name changes to inferior laryngeal nerve Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle Thyroarytenoid muscle o Vocalis muscle (not seen in dissection): formed by medial fibers; attached to vocal ligament Vocal folds: rima glottidis and glottis Interior of the larynx Laryngeal cavity: Vestibule, ventricle (may extend into a recess called the saccule), and infraglottic cavity Epiglottis Vestibular fold—false vocal fold Vocal fold—true vocal fold o Vocal ligament Internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve External branch of superior laryngeal nerve Inferior laryngeal branch of the recurrent laryngeal nerve