The Digestive System
... Salivary glands Secretion of lubricating fluid containing enzymes that break down carbohydrates ...
... Salivary glands Secretion of lubricating fluid containing enzymes that break down carbohydrates ...
Chapter 45 ppt
... • A hormone can stimulate the release of a series of other hormones, the last of which activates a nonendocrine target cell; this is called a hormone cascade pathway • The release of thyroid hormone results from a hormone cascade pathway involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid ...
... • A hormone can stimulate the release of a series of other hormones, the last of which activates a nonendocrine target cell; this is called a hormone cascade pathway • The release of thyroid hormone results from a hormone cascade pathway involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid ...
Hormones
... • A hormone can stimulate the release of a series of other hormones, the last of which activates a nonendocrine target cell; this is called a hormone cascade pathway • The release of thyroid hormone results from a hormone cascade pathway involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid ...
... • A hormone can stimulate the release of a series of other hormones, the last of which activates a nonendocrine target cell; this is called a hormone cascade pathway • The release of thyroid hormone results from a hormone cascade pathway involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid ...
Digestive system notes
... Stomach (cont.) • Rugae - folds in lining allow for expansion • Pyloric sphincter - regulates food from stomach to intestine • Ulcers: not caused by stress – Bacterial infection of stomach ...
... Stomach (cont.) • Rugae - folds in lining allow for expansion • Pyloric sphincter - regulates food from stomach to intestine • Ulcers: not caused by stress – Bacterial infection of stomach ...
Ch 45 - Houston ISD
... • A hormone can stimulate the release of a series of other hormones, the last of which activates a nonendocrine target cell; this is called a hormone cascade pathway • The release of thyroid hormone results from a hormone cascade pathway involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid ...
... • A hormone can stimulate the release of a series of other hormones, the last of which activates a nonendocrine target cell; this is called a hormone cascade pathway • The release of thyroid hormone results from a hormone cascade pathway involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid ...
Disorders and Diseases of the Digestive System
... • one gram supplies 9 Calories • less than 25–35% of total calories from fat • minimize trans and saturated fat intake – Especially bad for cardiovascular health ...
... • one gram supplies 9 Calories • less than 25–35% of total calories from fat • minimize trans and saturated fat intake – Especially bad for cardiovascular health ...
Thyroid Hormones
... glucose in the liver – Stimulating the breakdown of fat and protein into glucose ...
... glucose in the liver – Stimulating the breakdown of fat and protein into glucose ...
• Physiological functions of the liver. • Describe the major functions
... Major route for loss of cholesterol from body Lubricating function due to mucus Alkaline helps in neutralizing acid chyme. ...
... Major route for loss of cholesterol from body Lubricating function due to mucus Alkaline helps in neutralizing acid chyme. ...
Proteins
... Major route for loss of cholesterol from body Lubricating function due to mucus Alkaline helps in neutralizing acid chyme. ...
... Major route for loss of cholesterol from body Lubricating function due to mucus Alkaline helps in neutralizing acid chyme. ...
Hormones
... body fluids in a normal individual for the conduction of various activities. 2. Permissive function. Not only does each endocrine gland affect a number of processes, but these glands also affect the functioning of one another. Thus certain hormones require the presence (or ‘permission’) of another h ...
... body fluids in a normal individual for the conduction of various activities. 2. Permissive function. Not only does each endocrine gland affect a number of processes, but these glands also affect the functioning of one another. Thus certain hormones require the presence (or ‘permission’) of another h ...
Digestive System
... – Largest organ and largest gland – Vital functions include: • Storage of glucose as glycogen, fat-soluble vitamins, and vitamin B12 • Making of plasma proteins • Excretion of bilirubin, cholesterol and drugs • Metabolism of carbohydrates, protein and fats • Making of bile salts • Detoxification of ...
... – Largest organ and largest gland – Vital functions include: • Storage of glucose as glycogen, fat-soluble vitamins, and vitamin B12 • Making of plasma proteins • Excretion of bilirubin, cholesterol and drugs • Metabolism of carbohydrates, protein and fats • Making of bile salts • Detoxification of ...
Blood Vessel Lab
... Interactive Anatomy Blood is collected from abdominal organs (especially digestive organs) and is passed to the liver, hence the “hepatic” part of the name. This system of veins is called portal because there are two groups of capillary beds along the route, one group in the abdominal organ and anot ...
... Interactive Anatomy Blood is collected from abdominal organs (especially digestive organs) and is passed to the liver, hence the “hepatic” part of the name. This system of veins is called portal because there are two groups of capillary beds along the route, one group in the abdominal organ and anot ...
ON THE INTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE FAMILIES OF OPISTHOMI.
... The precaval vein is well developed. Fig. Sa.-Heart and ventral aorta The anterior cardinal vein persists only of M. armatus, X 2. v. ven· on the left side. An internal jugular vein tricle; a. auricle; acv. anterior is present on both the sides. The posterior cardinal vein. cardinal veins and hepati ...
... The precaval vein is well developed. Fig. Sa.-Heart and ventral aorta The anterior cardinal vein persists only of M. armatus, X 2. v. ven· on the left side. An internal jugular vein tricle; a. auricle; acv. anterior is present on both the sides. The posterior cardinal vein. cardinal veins and hepati ...
Cerebrovascular Anatomy 2016
... A lumbar drain system was not utilized during surgery and the operative course is complicated by hemorrhage and recurrent hypotension. Post-operatively, the patient is noted to have BLE weakness and a sensory level with loss of pain and temperature sensation below. Hypoperfusion through the Artery o ...
... A lumbar drain system was not utilized during surgery and the operative course is complicated by hemorrhage and recurrent hypotension. Post-operatively, the patient is noted to have BLE weakness and a sensory level with loss of pain and temperature sensation below. Hypoperfusion through the Artery o ...
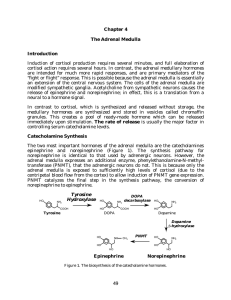
Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction - Rose
... The biosynthesis pathway begins with the amino acid tyrosine. The first step in the pathway is the committed step for catecholamine synthesis. Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step for the production of epinephrine and norepinephrine, the conversion of tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalan ...
... The biosynthesis pathway begins with the amino acid tyrosine. The first step in the pathway is the committed step for catecholamine synthesis. Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step for the production of epinephrine and norepinephrine, the conversion of tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalan ...
Digestive System - Network Learning Institute
... • Large Intestine (large bowel) – Cecum (appendix attached) – Colon ...
... • Large Intestine (large bowel) – Cecum (appendix attached) – Colon ...
SURFACE ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEY I
... below this (about three quarters) of the surface adjoins the renal impression of the right lobe of the liver, while a narrow medial area is related to the descending duodenum. Inferiorly, the anterior surface is related laterally to the right colic flexure, and medially to the small intestine. The a ...
... below this (about three quarters) of the surface adjoins the renal impression of the right lobe of the liver, while a narrow medial area is related to the descending duodenum. Inferiorly, the anterior surface is related laterally to the right colic flexure, and medially to the small intestine. The a ...
Introduction to Human Anatomy
... sandwitched between two densely stained protein layers. Phospholipid molecules have two parts. They are1)Head (Phosphate)& 2) Tail (Fatty acid) outer surface of cell wall contains pinocytotic vesicles. Inner surface is continuous with endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Functions of cell wall are1) Transpor ...
... sandwitched between two densely stained protein layers. Phospholipid molecules have two parts. They are1)Head (Phosphate)& 2) Tail (Fatty acid) outer surface of cell wall contains pinocytotic vesicles. Inner surface is continuous with endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Functions of cell wall are1) Transpor ...
21 Endocrine 10a
... for months afterwards. Then start on artificial thyroxin, need to figure out what their set point is for normal. • The other way (not so good) is to have the thyroid gland surgically removed. However, the parathyroid glands are often damaged or removed during this surgery. They often intentionally l ...
... for months afterwards. Then start on artificial thyroxin, need to figure out what their set point is for normal. • The other way (not so good) is to have the thyroid gland surgically removed. However, the parathyroid glands are often damaged or removed during this surgery. They often intentionally l ...
Common Carotid Artery
... The right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic artery behind the right sternoclavicular joint The left artery arises from the arch of aorta in the superior mediastenum Runs upward through the neck Divides into external and internal carotid arteries ...
... The right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic artery behind the right sternoclavicular joint The left artery arises from the arch of aorta in the superior mediastenum Runs upward through the neck Divides into external and internal carotid arteries ...
hormones
... Stimulus: Action potentials in preganglionic sympathetic fibers to adrenal medulla. Response: Adrenal medulla cells secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Stimulus: Action potentials in preganglionic sympathetic fibers to adrenal medulla. Response: Adrenal medulla cells secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.