nutri ch 3 quiz
... Chapter 3- The Basics of Digestion Take-Home Quiz True or False. 1. The digestive system breaks food down into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution the body cells; indigestible foodstuffs are eliminated as feces. 2. The small intestine is at least 20 feet long (possibly up to 30 fe ...
... Chapter 3- The Basics of Digestion Take-Home Quiz True or False. 1. The digestive system breaks food down into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution the body cells; indigestible foodstuffs are eliminated as feces. 2. The small intestine is at least 20 feet long (possibly up to 30 fe ...
Osvaldo
... with pointers to where related material can be found in a document Specifically, a text added to the end of a book or an article, containing information that is important to, but is not the main idea of, the main text ...
... with pointers to where related material can be found in a document Specifically, a text added to the end of a book or an article, containing information that is important to, but is not the main idea of, the main text ...
Gastrointestinal hormones - Teacherschoice
... Gastrointestinal hormones Enteroendocrine system regulates the digestive process through the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones. The lower part of the alimentary canal contains endocrine cells called Paracrine cells or Histocrine cells. These cells secrete Gut polypeptides or GI hormones. The GI ...
... Gastrointestinal hormones Enteroendocrine system regulates the digestive process through the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones. The lower part of the alimentary canal contains endocrine cells called Paracrine cells or Histocrine cells. These cells secrete Gut polypeptides or GI hormones. The GI ...
Chapter 20
... • May cause exophthalmos (bulging eyes) • Caused by enlargement of tissues around eyes ...
... • May cause exophthalmos (bulging eyes) • Caused by enlargement of tissues around eyes ...
Review-Unit3-Dig Sys
... 8. List and explain the function of each enzyme found in pancreatic juice. (enzymes from the pancreas) 9. List and explain the function of each enzyme secreted by the small intestine. 10. Describe what is absorbed in the small intestine. 11. What does the large intestine absorb? 12. What does the la ...
... 8. List and explain the function of each enzyme found in pancreatic juice. (enzymes from the pancreas) 9. List and explain the function of each enzyme secreted by the small intestine. 10. Describe what is absorbed in the small intestine. 11. What does the large intestine absorb? 12. What does the la ...
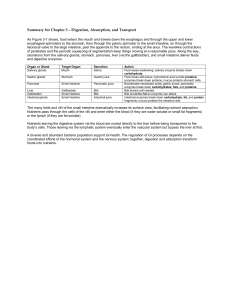
Summary for Chapter 3 – Digestion, Absorption, and
... Bicarbonate neutralizes acidic gastric juices; pancreatic enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Bile stored until needed. Bile emulsifies fat so enzymes can attack. Intestinal enzymes break down carbohydrate, fat, and protein fragments; mucus protects the intestinal wall. ...
... Bicarbonate neutralizes acidic gastric juices; pancreatic enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Bile stored until needed. Bile emulsifies fat so enzymes can attack. Intestinal enzymes break down carbohydrate, fat, and protein fragments; mucus protects the intestinal wall. ...
Fetal Pig Structure Function Practice
... o larger tubular structure that receives the liquid waste products of digestion, reabsorbs water and minerals, and forms and stores feces for defecation. o middle portion of the small intestine extending from the duodenum to the ileum; primarily responsible for nutrient absorption. o muscular passa ...
... o larger tubular structure that receives the liquid waste products of digestion, reabsorbs water and minerals, and forms and stores feces for defecation. o middle portion of the small intestine extending from the duodenum to the ileum; primarily responsible for nutrient absorption. o muscular passa ...
Study Notes - Northern Highlands
... - Absorption is limited to water and electrolytes - Intestinal Flora – breakdown some cellulose and help produce vitamins such as K, B12, thiamine, and riboflavin - Feces – water, electrolytes, mucus, and bacteria. Bile gives its color ...
... - Absorption is limited to water and electrolytes - Intestinal Flora – breakdown some cellulose and help produce vitamins such as K, B12, thiamine, and riboflavin - Feces – water, electrolytes, mucus, and bacteria. Bile gives its color ...
Digestion Unit Test
... found in the intestines that catch and absorb nutrients. 12. ___________________ is the accessory organ that has no known function and can be removed when an infection called an __________________________ occurs. 13. __________________________ is an accessory organ of the digestive system which stor ...
... found in the intestines that catch and absorb nutrients. 12. ___________________ is the accessory organ that has no known function and can be removed when an infection called an __________________________ occurs. 13. __________________________ is an accessory organ of the digestive system which stor ...
File - Sheffield Peer Teaching Society
... when there is excess iron (because there’s no way of excreting it) Kuppfer cells are very important for the portal vein circulation- what about when you strain to poo!? ...
... when there is excess iron (because there’s no way of excreting it) Kuppfer cells are very important for the portal vein circulation- what about when you strain to poo!? ...
Chapter 24
... • Bile production – Salts emulsify fats, neutralizes stomach acid – Stored in gall bladder – Gallstones can form as precipitate of cholesterol ...
... • Bile production – Salts emulsify fats, neutralizes stomach acid – Stored in gall bladder – Gallstones can form as precipitate of cholesterol ...
B. Pancreatic digestive Enzymes
... most other carbohydrates (except cellulose ) to form mostly disaccharides and a few disaccharides. b. The main enzymes for fat digestion are (1) pancreatic lipase, which is capable of hydrolyzing neutral fat into fatty acids and monoglycerides; (2) cholesterol esterase, which causes hydrolysis of ch ...
... most other carbohydrates (except cellulose ) to form mostly disaccharides and a few disaccharides. b. The main enzymes for fat digestion are (1) pancreatic lipase, which is capable of hydrolyzing neutral fat into fatty acids and monoglycerides; (2) cholesterol esterase, which causes hydrolysis of ch ...
a. digestive enzymes for carbohydrates
... most other carbohydrates (except cellulose ) to form mostly disaccharides and a few disaccharides. b. The main enzymes for fat digestion are (1) pancreatic lipase, which is capable of hydrolyzing neutral fat into fatty acids and monoglycerides; (2) cholesterol esterase, which causes hydrolysis of ch ...
... most other carbohydrates (except cellulose ) to form mostly disaccharides and a few disaccharides. b. The main enzymes for fat digestion are (1) pancreatic lipase, which is capable of hydrolyzing neutral fat into fatty acids and monoglycerides; (2) cholesterol esterase, which causes hydrolysis of ch ...
Digestive System
... Endocrine function of Pancreas (See diagram on pg. 404) Usually the pancreas is shown as a long cream coloured organ that lies transversely underneath and behind the stomach. It is beside the duodenum of the small intestine. Recall: alpha cells produce pancreatic juice for the pancreas exocrine ...
... Endocrine function of Pancreas (See diagram on pg. 404) Usually the pancreas is shown as a long cream coloured organ that lies transversely underneath and behind the stomach. It is beside the duodenum of the small intestine. Recall: alpha cells produce pancreatic juice for the pancreas exocrine ...
The Endocrine System
... Regulation through feedback Done by hormones (chemical messengers) Thermostat Example: -Too hot, shuts down -Too cold, starts furnace ...
... Regulation through feedback Done by hormones (chemical messengers) Thermostat Example: -Too hot, shuts down -Too cold, starts furnace ...
Digestive System Review #2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... invasion and creates an optimal pH for the activation of Pepsin. It also acts to convert Pepsinogen into the active enzyme called Pepsin. ...
... invasion and creates an optimal pH for the activation of Pepsin. It also acts to convert Pepsinogen into the active enzyme called Pepsin. ...
Biology 12 - Digestion
... Answer the following Short Answers for 4 marks each. Answer clearly and with at least 3 ...
... Answer the following Short Answers for 4 marks each. Answer clearly and with at least 3 ...
Pituitary gland
... Basic Endocrine Anatomy Some important endocrine glands 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, ...
... Basic Endocrine Anatomy Some important endocrine glands 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, ...
Study Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Tiny fingerlike projections of the mucosa. Cytoplasmic extensions from cells on the surface of villi. Lymphatic capillaries found in villi. Junction between the ileum and large intestine. Ring of smooth muscle surrounding the ileocecal junction. One-way valve at the junction between the ileum and sm ...
... Tiny fingerlike projections of the mucosa. Cytoplasmic extensions from cells on the surface of villi. Lymphatic capillaries found in villi. Junction between the ileum and large intestine. Ring of smooth muscle surrounding the ileocecal junction. One-way valve at the junction between the ileum and sm ...
Accessory Organs of the Digestive System
... partly digested food expelled by the stomach into the duodenum. ...
... partly digested food expelled by the stomach into the duodenum. ...
Digestive System PowerPoint
... • Bicarbonate rich p.j. neutralizes HCl in the duodenum (Stimulated by secretin when HCl enters the duodenum) • Enzyme rich p.j. stimulated by CCK when fatty or protein rich foods enter the duodenum Note • Hormones released in inactive form so they don’t digest the pancreas ...
... • Bicarbonate rich p.j. neutralizes HCl in the duodenum (Stimulated by secretin when HCl enters the duodenum) • Enzyme rich p.j. stimulated by CCK when fatty or protein rich foods enter the duodenum Note • Hormones released in inactive form so they don’t digest the pancreas ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.