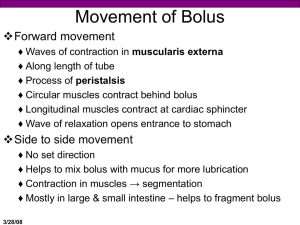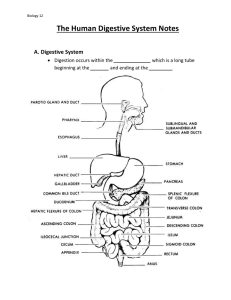
chapter-9-digestive-system-student-notes
... digestion→ the thought of food caused the nervous system to stimulate secretion of digestive juices __________ also cause secretion of digestive juices For example: a) In response to protein, stomach produces _________ hormone → ...
... digestion→ the thought of food caused the nervous system to stimulate secretion of digestive juices __________ also cause secretion of digestive juices For example: a) In response to protein, stomach produces _________ hormone → ...
Introduction to Gastrointestinal tract
... Largest gland of human body Largest internal organ Weighs 1.4 – 1.6 kg Rests on diaphragm on the right side of abdomen. ...
... Largest gland of human body Largest internal organ Weighs 1.4 – 1.6 kg Rests on diaphragm on the right side of abdomen. ...
The Digestive System
... sphincter (LES) closes to prevent reentry. If rejected by the stomach, the esophageal sphincter, reopen, by contractions, and force the food back into the mouth, as vomit. ...
... sphincter (LES) closes to prevent reentry. If rejected by the stomach, the esophageal sphincter, reopen, by contractions, and force the food back into the mouth, as vomit. ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... oestrogen and testosterone These hormones maintain the reproductive system and develop sexual characteristics ...
... oestrogen and testosterone These hormones maintain the reproductive system and develop sexual characteristics ...
Digestion!!!!!! Chpt 45, topic 5
... The Pathway of food--• Mouth—pharynx—larynx—esophagus—stomach—small intestine—large intestine—anus Layers of the GI tract— • Inner—closest to food— o Mucosa—epithelial and collective tissue—lots of folds for surface area • Submucosa—collective tissue—contains the capillaries (where nutrients are abs ...
... The Pathway of food--• Mouth—pharynx—larynx—esophagus—stomach—small intestine—large intestine—anus Layers of the GI tract— • Inner—closest to food— o Mucosa—epithelial and collective tissue—lots of folds for surface area • Submucosa—collective tissue—contains the capillaries (where nutrients are abs ...
Unit 10 Chapter 35 The Digestive and Endocrine Systems
... secrete hormones into the bloodstream ...
... secrete hormones into the bloodstream ...
The GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM Module (SYS 328) Credit Hours
... the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. The layers of muscles and associated nerves that surround the lumen propel food and waste through the system for eventual elimination. The pancreas secretes enzymes into the small intestine to help break down proteins, fat, and carbohydrates. The ...
... the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. The layers of muscles and associated nerves that surround the lumen propel food and waste through the system for eventual elimination. The pancreas secretes enzymes into the small intestine to help break down proteins, fat, and carbohydrates. The ...
Document
... -2- gastric: after ingestion. Protein most stimulatory. -3- intestinal: results from duodenal response. Inhibitory. IV. Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas All connect to small intestine. (A) Liver – largest gland. Most functions not digestive. -1- gross anatomy: four lobes, surface ligaments. -2- microsco ...
... -2- gastric: after ingestion. Protein most stimulatory. -3- intestinal: results from duodenal response. Inhibitory. IV. Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas All connect to small intestine. (A) Liver – largest gland. Most functions not digestive. -1- gross anatomy: four lobes, surface ligaments. -2- microsco ...
Introduction to Health Science
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. • The response of hormones is slower and longer-lasting than those of nerve impulses. • The effects may last up to several hours or ...
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. • The response of hormones is slower and longer-lasting than those of nerve impulses. • The effects may last up to several hours or ...
Layers of the digestive tube - Chicagoland Jewish High School
... Wall of the GI Tract Mucous Membrane Epithelium (varies) Lamina propria (Connective tissue) Muscularis Mucosa (smooth muscle) ...
... Wall of the GI Tract Mucous Membrane Epithelium (varies) Lamina propria (Connective tissue) Muscularis Mucosa (smooth muscle) ...
Digestion in intestine and colon
... monoglycerides; cholesterol esterase, which causes hydrolysis of cholesterol esters; and phospholipase, which splits fatty acids from phospholipids. • Lipolytic enzymes ejected in active (pancreatic lipase, muntinase) and inactive conditions (prophospholipase A). ...
... monoglycerides; cholesterol esterase, which causes hydrolysis of cholesterol esters; and phospholipase, which splits fatty acids from phospholipids. • Lipolytic enzymes ejected in active (pancreatic lipase, muntinase) and inactive conditions (prophospholipase A). ...
EnzymesandChemDig
... Main Function of Enzymes • 'Digestive enzymes' are enzymes (biological catalysts) that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. • Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tract of animals (including humans) wher ...
... Main Function of Enzymes • 'Digestive enzymes' are enzymes (biological catalysts) that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. • Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tract of animals (including humans) wher ...
A & P of the Gastrointestinal Tract
... •15oo mL of blood are delivered to the liver every minute via the portal vein & hepatic artery •Bile –Yellow-brown or greenbrown color –Necessary for metabolism of fats •500-1,000 mL/daily ...
... •15oo mL of blood are delivered to the liver every minute via the portal vein & hepatic artery •Bile –Yellow-brown or greenbrown color –Necessary for metabolism of fats •500-1,000 mL/daily ...
Gastrointestinal hormones
... myenteric plexus and nerves of the pancreas. It stimulates ravenous appetite, inhibits insulin and SMS secretion. At the same time it stimulates the release of glucagon. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) is produced by endocrine K cells of the duodenum and jejunum. The original term (GIP) which r ...
... myenteric plexus and nerves of the pancreas. It stimulates ravenous appetite, inhibits insulin and SMS secretion. At the same time it stimulates the release of glucagon. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) is produced by endocrine K cells of the duodenum and jejunum. The original term (GIP) which r ...
06 General anatomy of the digestive system
... Same 4 basic layers When the stomach is empty, the mucosa lies in large folds Rugae Pyloric sphincter separates stomach from small intestine ...
... Same 4 basic layers When the stomach is empty, the mucosa lies in large folds Rugae Pyloric sphincter separates stomach from small intestine ...
Biology 12 – Review Sheet
... A 26. People who have their gall bladder removed have the most difficulty digesting A. butter. B. apples. C. vitamins. D. egg whites. A 27. The gall bladder functions to A. store bile. B. digest fats. C. store urine. D. release sodium bicarbonate. A 28. Removal of the gall bladder would affect a per ...
... A 26. People who have their gall bladder removed have the most difficulty digesting A. butter. B. apples. C. vitamins. D. egg whites. A 27. The gall bladder functions to A. store bile. B. digest fats. C. store urine. D. release sodium bicarbonate. A 28. Removal of the gall bladder would affect a per ...
Digestive System, Day 3 (Professor Powerpoint)
... Acidic environment – pH drops (pepsinogen → pepsin at low pH) Secretions stop when pH reaches 2.0 Digestion Proteins in food →pepsin →amino acids Milk proteins →gastric lipase → amino acids & renin ...
... Acidic environment – pH drops (pepsinogen → pepsin at low pH) Secretions stop when pH reaches 2.0 Digestion Proteins in food →pepsin →amino acids Milk proteins →gastric lipase → amino acids & renin ...
Digestive System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 3 segments Duodenum: first and shortest Jejunum ...
... 3 segments Duodenum: first and shortest Jejunum ...
Slides on Digestion 1
... as such its cellular morphology reflects this dual function. Acinar cells or an acinus, these secrete pancreatic enzymes + bicarbonate islets of Langerhans containing beta cells. These cells are hormonal and secrete into the blood stream hormones such as Insulin, Glucagon and somatostatin. ...
... as such its cellular morphology reflects this dual function. Acinar cells or an acinus, these secrete pancreatic enzymes + bicarbonate islets of Langerhans containing beta cells. These cells are hormonal and secrete into the blood stream hormones such as Insulin, Glucagon and somatostatin. ...
BIO242 Lab 27 Endocrine
... A. Draw and clearly label the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and posterior pituitary. State the types of cell found in each region (are they neuronal, or endocrine)? B. Clearly list ALL of the hormones released by EACH region of the pituitary. Thyroid A. Draw and clearly label a portion of the thyr ...
... A. Draw and clearly label the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and posterior pituitary. State the types of cell found in each region (are they neuronal, or endocrine)? B. Clearly list ALL of the hormones released by EACH region of the pituitary. Thyroid A. Draw and clearly label a portion of the thyr ...
NewYork-Presbyterian Digestive Disease Services
... image processing and enhanced optics. It is improving the outcomes of GI surgical patients and speeding their recovery from conditions such as GERD, gallbladder disease, and benign and malignant colon and rectal disease. • Our surgeons also perform endoscopic sewing (endocinch) and radiofrequency tr ...
... image processing and enhanced optics. It is improving the outcomes of GI surgical patients and speeding their recovery from conditions such as GERD, gallbladder disease, and benign and malignant colon and rectal disease. • Our surgeons also perform endoscopic sewing (endocinch) and radiofrequency tr ...
File - singhscience
... The stomach continues to mix the food with digestive enzymes. Amylase continues to digest carbohydrates Proteins are digested in the stomach and small intestine. Protease enzymes break down proteins into amino acids. Digestion of proteins in the stomach is helped by stomach acid, which is strong hyd ...
... The stomach continues to mix the food with digestive enzymes. Amylase continues to digest carbohydrates Proteins are digested in the stomach and small intestine. Protease enzymes break down proteins into amino acids. Digestion of proteins in the stomach is helped by stomach acid, which is strong hyd ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.