Ch. 25: GI System part A
... Total of 1 to 1.5 L of saliva per day Cells filter water from blood and add other substances Food stimulates receptors that signal salivatory nuclei in medulla and pons ...
... Total of 1 to 1.5 L of saliva per day Cells filter water from blood and add other substances Food stimulates receptors that signal salivatory nuclei in medulla and pons ...
NOTES: Introduction to Histology (Ch 5)
... -most are stored in the -can be incorporated into organic molecules (parts of enzymes, vitamins, etc.) -can be in the form of free ions (example: Ca2+ ions in muscle cells) ...
... -most are stored in the -can be incorporated into organic molecules (parts of enzymes, vitamins, etc.) -can be in the form of free ions (example: Ca2+ ions in muscle cells) ...
CHAPTER-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION The process of
... vessels. Meissner’s plexus is present between the muscular coat and mucosa that controls the secretion of intestinal juice. d) Mucosa- innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal that secretes mucus from goblet cells. It has irregular folding in stomach called rugae and villi in small i ...
... vessels. Meissner’s plexus is present between the muscular coat and mucosa that controls the secretion of intestinal juice. d) Mucosa- innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal that secretes mucus from goblet cells. It has irregular folding in stomach called rugae and villi in small i ...
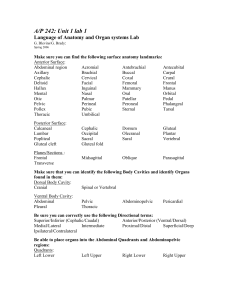
Language of Anatomy and Organ systems Lab
... Hypochondriac (L & R) Inguinal (L & R) Lumbar ( L & R) ...
... Hypochondriac (L & R) Inguinal (L & R) Lumbar ( L & R) ...
EMBRYOLOGY
... the ventral pancreas and common bile duct behind it into the dorsal mesentery. The ventral pancreas makes contact and fuses with the dorsal pancreas. After fusion of the two parts of the pancreas, the main duct of the ventral pancreas makes an anastomotic connection with the duct of the dorsal pancr ...
... the ventral pancreas and common bile duct behind it into the dorsal mesentery. The ventral pancreas makes contact and fuses with the dorsal pancreas. After fusion of the two parts of the pancreas, the main duct of the ventral pancreas makes an anastomotic connection with the duct of the dorsal pancr ...
Digestive system
... digestive tract is lined w/ mucous membranes to protect the epithelium of the digestive tract, and to help food move through Stratified in areas of high stress, like the mouth and simple in the small intestine where absorption takes ...
... digestive tract is lined w/ mucous membranes to protect the epithelium of the digestive tract, and to help food move through Stratified in areas of high stress, like the mouth and simple in the small intestine where absorption takes ...
Chapter 10
... you can deduce how it is affecting bodily functions. Pretty big deal, no? If a patient’s pancreatic islet cells stop making insulin, or if they can no longer act on their target cells, that patient has diabetes mellitus. Do you know someone with diabetes? ...
... you can deduce how it is affecting bodily functions. Pretty big deal, no? If a patient’s pancreatic islet cells stop making insulin, or if they can no longer act on their target cells, that patient has diabetes mellitus. Do you know someone with diabetes? ...
CH 45 Chemcial Signals2013
... blood flow for more O2 Growth factors ~ proteins for cell proliferation Prostaglandins~ immune, reproduction, blood clotting ...
... blood flow for more O2 Growth factors ~ proteins for cell proliferation Prostaglandins~ immune, reproduction, blood clotting ...
The Digestive System Chapter 16
... - comprised of three regions: Duodenum – 10” in length; receives chyme from stomach, secretions from liver, gallbladder & pancreas Jejunum – 8’ long; most digestion & absorption occurs here ...
... - comprised of three regions: Duodenum – 10” in length; receives chyme from stomach, secretions from liver, gallbladder & pancreas Jejunum – 8’ long; most digestion & absorption occurs here ...
Unit 3 F
... The digestive system works with the circulatory system to deliver nutrients to the body’s tissues. Saliva is mostly acid which helps to help break down food. The Esophagus lies anterior to the trachea and is the tube which carries food to the stomach. The Pancreas produces bile which helps in the di ...
... The digestive system works with the circulatory system to deliver nutrients to the body’s tissues. Saliva is mostly acid which helps to help break down food. The Esophagus lies anterior to the trachea and is the tube which carries food to the stomach. The Pancreas produces bile which helps in the di ...
Week 7 Digestion Lecture Study Guide
... 11. Name the 3 pairs of salivary glands. 12. What tissue type and muscle type do you find in the esophagus? How does affect function? 13. Where does the pancreas empty digestive enzymes? 14. Where does the gall bladder empty digestive enzymes? 15. In which part of the digestive system does food spen ...
... 11. Name the 3 pairs of salivary glands. 12. What tissue type and muscle type do you find in the esophagus? How does affect function? 13. Where does the pancreas empty digestive enzymes? 14. Where does the gall bladder empty digestive enzymes? 15. In which part of the digestive system does food spen ...
Mouth Digestive System Mind Map
... break food into usable nutrient molecules molecules are absorbed into the blood eliminates waste ...
... break food into usable nutrient molecules molecules are absorbed into the blood eliminates waste ...
No Slide Title
... – bile acid (salts) emulsify fats & aid in their digestion • enterohepatic circulation is recycling of bile salts from ileum ...
... – bile acid (salts) emulsify fats & aid in their digestion • enterohepatic circulation is recycling of bile salts from ileum ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... acromegaly: no height increase due to bones ossifying; but diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary ...
... acromegaly: no height increase due to bones ossifying; but diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary ...
1. What sex is your pig?
... 6. The small intestine is held together by mesentery. Here, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. ...
... 6. The small intestine is held together by mesentery. Here, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. ...
Digestion
... like a detergent to break large fats into smaller ones that the lipase can chemically break down – Bile is stored in gallbladder until needed ...
... like a detergent to break large fats into smaller ones that the lipase can chemically break down – Bile is stored in gallbladder until needed ...
Process of Digestion: There are four components of the digestive
... The circulatory system then takes the glucose to the body cells for the ...
... The circulatory system then takes the glucose to the body cells for the ...
Digestivesystem
... the juices into tiny ducts that flow into the pancreatic duct The pancreatic duct connects with the duodenum where the bile duct form the liver connects in = hepatopancreatic sphincter Pancreatic amylase - splits carbohydrates Pancreatic lipase - breaks down triglycerides (fats) Nucleases - break do ...
... the juices into tiny ducts that flow into the pancreatic duct The pancreatic duct connects with the duodenum where the bile duct form the liver connects in = hepatopancreatic sphincter Pancreatic amylase - splits carbohydrates Pancreatic lipase - breaks down triglycerides (fats) Nucleases - break do ...
Ch 8 Digestive System
... – Pear shaped sac located inferior the liver – Stores and concentrates bile for later use • Pancreas – Feather shaped organ located posterior to the stomach – Has digestive and endocrine functions. We will discuss the endocrine function in a different chapter. – Synthesizes and secretes pancreatic j ...
... – Pear shaped sac located inferior the liver – Stores and concentrates bile for later use • Pancreas – Feather shaped organ located posterior to the stomach – Has digestive and endocrine functions. We will discuss the endocrine function in a different chapter. – Synthesizes and secretes pancreatic j ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... turn dehydrates them – leaves the cells vulnerable to infection and poisons. • Type I – born with it – Controlled by insulin injections ...
... turn dehydrates them – leaves the cells vulnerable to infection and poisons. • Type I – born with it – Controlled by insulin injections ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... turn dehydrates them – leaves the cells vulnerable to infection and poisons. • Type I – born with it – Controlled by insulin injections ...
... turn dehydrates them – leaves the cells vulnerable to infection and poisons. • Type I – born with it – Controlled by insulin injections ...
Study Guide Answer Keys - I
... d. Insulin: Produced by the beta cells of the pancreas; helps cells use CHO for energy e. Glucagon: Produced by alpha cells of the pancreas; regulates blood glucose levels 2. An exocrine gland secretes substances through a duct system outward (e.g., sweat glands). An endocrine gland produces chemica ...
... d. Insulin: Produced by the beta cells of the pancreas; helps cells use CHO for energy e. Glucagon: Produced by alpha cells of the pancreas; regulates blood glucose levels 2. An exocrine gland secretes substances through a duct system outward (e.g., sweat glands). An endocrine gland produces chemica ...
Nutrition and Metabolism I NUTR 451
... Pancreatic secretions contains enzymes for digesting all three major food types Stimuli for secretion include acetylcholine, cholecystokinen, secretin Pancreatic secretions – Proteolytic enzymes: trypsin, chymotrypsin – Pancreatic amylase – Pancreatic lipase, cholesterol esterase, phospholipase – Bi ...
... Pancreatic secretions contains enzymes for digesting all three major food types Stimuli for secretion include acetylcholine, cholecystokinen, secretin Pancreatic secretions – Proteolytic enzymes: trypsin, chymotrypsin – Pancreatic amylase – Pancreatic lipase, cholesterol esterase, phospholipase – Bi ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.