23-1
... • Chromaffin cells receive direct innervation from sympathetic nervous system – develop from same tissue as postganglionic neurons ...
... • Chromaffin cells receive direct innervation from sympathetic nervous system – develop from same tissue as postganglionic neurons ...
Jason
... stomach. It has a pH of 1.5 to 3.5 and is composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl) (around 0.5%, or 5000 parts per million) as high as 0.1 N[1], and large quantities of potassium chloride (KCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl). The acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins, by activating digestive enzymes ...
... stomach. It has a pH of 1.5 to 3.5 and is composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl) (around 0.5%, or 5000 parts per million) as high as 0.1 N[1], and large quantities of potassium chloride (KCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl). The acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins, by activating digestive enzymes ...
Animal Histology- Endocrine System:
... Hormone: A substance, usually a peptide or steroid, produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another to effect physiological activity, such as growth or metabolism. A chemical produced in one part of the body and released into the blood to trigger or regulate particular functions of ...
... Hormone: A substance, usually a peptide or steroid, produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another to effect physiological activity, such as growth or metabolism. A chemical produced in one part of the body and released into the blood to trigger or regulate particular functions of ...
Clues
... 42. The gall bladder stores a secretion from the liver called ___. 43. The alveolar ridges around the tooth are covered by dense fibrous connective tissue & stratified squamous epithelium referred to as ___. 44. When the duodenum becomes filled with chyme it stretches the intestine causing an ___ re ...
... 42. The gall bladder stores a secretion from the liver called ___. 43. The alveolar ridges around the tooth are covered by dense fibrous connective tissue & stratified squamous epithelium referred to as ___. 44. When the duodenum becomes filled with chyme it stretches the intestine causing an ___ re ...
Biology 12 Digestive System The digestive process can be divided
... Villi - increase surface area for absorption. Fatty acids and glycerol diffuse into the lacteal, part of the lymphatic system which eventually empties into the blood stream. This prevents the tiny capillaries in the villi from becoming clogged. Glucose and amino acids (as well as vitamins and minera ...
... Villi - increase surface area for absorption. Fatty acids and glycerol diffuse into the lacteal, part of the lymphatic system which eventually empties into the blood stream. This prevents the tiny capillaries in the villi from becoming clogged. Glucose and amino acids (as well as vitamins and minera ...
Endocrine System
... contraction, increased breathing rate, elevated blood pressure, increased blood glucose, and decreased digestive activity Stimulated by sympathetic impulses fight or flight ...
... contraction, increased breathing rate, elevated blood pressure, increased blood glucose, and decreased digestive activity Stimulated by sympathetic impulses fight or flight ...
chapter 39 - section 2
... energy intense activities. The two hormones released by the adrenal medulla are epinephrine and norepinephrine. ...
... energy intense activities. The two hormones released by the adrenal medulla are epinephrine and norepinephrine. ...
DigestiveSystemQuiz
... 47. What part of the alimentary canal is being shown in the photomicrograph above? 48. What structure is being indicated by the black arrows? 49. What layer is being indicated by the red arrow? ...
... 47. What part of the alimentary canal is being shown in the photomicrograph above? 48. What structure is being indicated by the black arrows? 49. What layer is being indicated by the red arrow? ...
endocrine system
... replacement beta cells) • Type 2 Diabetes - non-insulin-dependent - insulin is produced but target cells fail to take up glucose from the blood so the levels remain high -genetic or if overweight ...
... replacement beta cells) • Type 2 Diabetes - non-insulin-dependent - insulin is produced but target cells fail to take up glucose from the blood so the levels remain high -genetic or if overweight ...
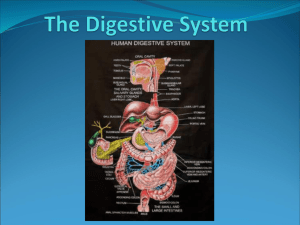
The Digestive System
... interior of the villi, and are transported through the body’s lymphatic system fat soluble vitamins will move with fats into lacteals for absorption in the body ...
... interior of the villi, and are transported through the body’s lymphatic system fat soluble vitamins will move with fats into lacteals for absorption in the body ...
Human Digestive System Anatomy
... tube about 3 meters long. The duodenum begins at the pylorus of the stomach, extends to the right side of the abdomen, then loops back to the left half of the body, passing close to the stomach and spleen. Accessory organs – these are not part of the alimentary canal, but are important organs for di ...
... tube about 3 meters long. The duodenum begins at the pylorus of the stomach, extends to the right side of the abdomen, then loops back to the left half of the body, passing close to the stomach and spleen. Accessory organs – these are not part of the alimentary canal, but are important organs for di ...
Endocrine (regulatory) System
... Name the nine major endocrine glands found in the body. Which one ins called the “master gland”? Name three major local regulators that act on nearby target cells. (pgs. 947-948) Name three key molecules that play a role in the signal transduction pathway (typical reactions in the endocrine system). ...
... Name the nine major endocrine glands found in the body. Which one ins called the “master gland”? Name three major local regulators that act on nearby target cells. (pgs. 947-948) Name three key molecules that play a role in the signal transduction pathway (typical reactions in the endocrine system). ...
LAB 14 Practical Histology Digestive system Components: Digestive
... 3. Muscularis externa of inner circular and outer longitudinal layers 4. Serosa covers all of small intestine except for the beginning of the duodenum, which is retroperitoneal and possesses an adventitia. 5. The intestinal lining bears a series of transverse folds called plicae, or plicae circulare ...
... 3. Muscularis externa of inner circular and outer longitudinal layers 4. Serosa covers all of small intestine except for the beginning of the duodenum, which is retroperitoneal and possesses an adventitia. 5. The intestinal lining bears a series of transverse folds called plicae, or plicae circulare ...
Digestion
... Name 3 other molecules which the body needs in a balanced diet. Vitamins, minerals and water. Where in the alimentary canal are these 3 absorbed? The large intestine. ...
... Name 3 other molecules which the body needs in a balanced diet. Vitamins, minerals and water. Where in the alimentary canal are these 3 absorbed? The large intestine. ...
BIOL 103 Homework (Ch. 3)
... Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. 2. Name the four “assisting” organs that are not part of the GI tract but are needed for proper digestion. What are their roles in digestion? - The salivary glands produce saliva that moistens food, lubricating it for easy swal ...
... Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. 2. Name the four “assisting” organs that are not part of the GI tract but are needed for proper digestion. What are their roles in digestion? - The salivary glands produce saliva that moistens food, lubricating it for easy swal ...
Practical Histology Digestive system Components: Digestive Tract
... c) Muscularis mucosae of smooth muscle is usually present. 2. Submucosa. Denser connective tissue than the lamina propria. The submucosa possesses glands in the esophagus and duodenum. 3. Muscularis externa of smooth muscle is usually arranged into inner circular and outer longitudinal layers. 4. Se ...
... c) Muscularis mucosae of smooth muscle is usually present. 2. Submucosa. Denser connective tissue than the lamina propria. The submucosa possesses glands in the esophagus and duodenum. 3. Muscularis externa of smooth muscle is usually arranged into inner circular and outer longitudinal layers. 4. Se ...
Chapter 18: Digestive and Excretory System
... b) Villi produce a large surface, where nutrients are absorbed by diffusion and active transport into the blood and lymph ...
... b) Villi produce a large surface, where nutrients are absorbed by diffusion and active transport into the blood and lymph ...
Module 2 / Endocrine System
... The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that stimulate the production of special lymphocytes (white blood cells) called T-cells, which play an important role in the immune system by attacking foreign or abnormal cells. The adrenal glands produce steroid hormones that regulate ...
... The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that stimulate the production of special lymphocytes (white blood cells) called T-cells, which play an important role in the immune system by attacking foreign or abnormal cells. The adrenal glands produce steroid hormones that regulate ...
The Digestive System
... • Phagocytosis of worn out RBCs and foreign substances • Removes toxins such as alcohol and certain drugs from the blood ...
... • Phagocytosis of worn out RBCs and foreign substances • Removes toxins such as alcohol and certain drugs from the blood ...
Gastroenterology - Cardinal Health
... Gastroenterology is the study of the digestive track and its disorders. The digestive tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus, including all other organs that help the body break down and absorb food. The digestive tract organs consist of the mou ...
... Gastroenterology is the study of the digestive track and its disorders. The digestive tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus, including all other organs that help the body break down and absorb food. The digestive tract organs consist of the mou ...
Digestive System - Fall River Public Schools
... the surface area of the small intestine – Digested carbs and proteins are absorbed into the capillaries of the villi – Undigested fat and fatty acids are absorbed by lymph vessels ...
... the surface area of the small intestine – Digested carbs and proteins are absorbed into the capillaries of the villi – Undigested fat and fatty acids are absorbed by lymph vessels ...
The Digestive System
... counteract the acidic gastric fluid that has entered it. These ions change the pH from 2.5 to about 9.0. This change in pH inactivates pepsin so the small intestine is not being degraded. ...
... counteract the acidic gastric fluid that has entered it. These ions change the pH from 2.5 to about 9.0. This change in pH inactivates pepsin so the small intestine is not being degraded. ...
Digestion - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... amino acids, fatty acids & glycerol which are soluble in water and can easily be absorbed into blood stream Once absorbed, monomers are used to build essential ...
... amino acids, fatty acids & glycerol which are soluble in water and can easily be absorbed into blood stream Once absorbed, monomers are used to build essential ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.