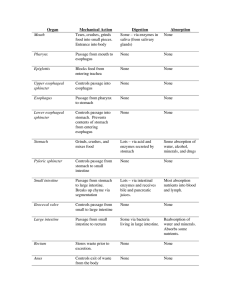
How do hormones that are controlled by a negative feedback system
... Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is involved in mineral regulation. This hormone is produced by the parathyroid glands. Parathyroid glands are attached to the thyroid gland. The release of PTH leads to an increase in the rate that minerals are absorbed in the intestine. The three minerals affected are calc ...
... Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is involved in mineral regulation. This hormone is produced by the parathyroid glands. Parathyroid glands are attached to the thyroid gland. The release of PTH leads to an increase in the rate that minerals are absorbed in the intestine. The three minerals affected are calc ...
the_digestive_system
... food after you eat • The acid (ph 2) and churning helps to break food into smaller pieces so your body can use it for energy and nutrition • Just under the edge of the left side of your rib cage ...
... food after you eat • The acid (ph 2) and churning helps to break food into smaller pieces so your body can use it for energy and nutrition • Just under the edge of the left side of your rib cage ...
oesophagus and stomach - Curriculum for Excellence Science
... enzyme lipase • Lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol ...
... enzyme lipase • Lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol ...
I-Mention Only
... ( )Failure of the pituitary to stop producing growth hormone after body growth is completed results in _________. - giantism ...
... ( )Failure of the pituitary to stop producing growth hormone after body growth is completed results in _________. - giantism ...
Slide 1
... villus ensure the distance is small? Think about how the absorbed products of digestion are taken away from the gut. What is it in a villus that allows this? ...
... villus ensure the distance is small? Think about how the absorbed products of digestion are taken away from the gut. What is it in a villus that allows this? ...
Fundamentals of Human Digestion www.AssignmentPoint.com The
... dry food. There is either saliva or mucus present all along the digestive tract. This keeps food soft and moist. ...
... dry food. There is either saliva or mucus present all along the digestive tract. This keeps food soft and moist. ...
lecture 15
... – ruminant periodically regurgitates and re-chews parts of the bolus (called “the cud) in its mouth to continue physically breaking down the grass » because cattle don’t spend much time actually chewing the first time – chemical digestion of cellulose continues in reticulum ...
... – ruminant periodically regurgitates and re-chews parts of the bolus (called “the cud) in its mouth to continue physically breaking down the grass » because cattle don’t spend much time actually chewing the first time – chemical digestion of cellulose continues in reticulum ...
Organogenesis Of The Gastrointestinal Tract.
... Pharyngeal and Foregut region (i).Pharynx and oesophagus. •The short rostral tip of the pharyngeal region form the pharynx •The caudal part of pharyngeal region and rostral foregut forms the oesophagus. •Oesophagus elongates to match growth of Cr. cervical,and thoracic and abdominal regions. •Failu ...
... Pharyngeal and Foregut region (i).Pharynx and oesophagus. •The short rostral tip of the pharyngeal region form the pharynx •The caudal part of pharyngeal region and rostral foregut forms the oesophagus. •Oesophagus elongates to match growth of Cr. cervical,and thoracic and abdominal regions. •Failu ...
PMHS
... Two major categories of glands in the body • Exocrine – Exocrine glands have ________________that carry their secretory product to a surface • Endocrine – The endocrine glands do ______________________________ to carry their product to a surface Endocrine Glands • The endocrine glands do not have du ...
... Two major categories of glands in the body • Exocrine – Exocrine glands have ________________that carry their secretory product to a surface • Endocrine – The endocrine glands do ______________________________ to carry their product to a surface Endocrine Glands • The endocrine glands do not have du ...
Digestive System
... j. Choledocho = root for common bile duct 3. Pancreas: accessory organ; behind the stomach; head attached to duodenum, tail reaching to spleen a. Exocrine functions: acini cells secrete digestive juices and bicarbonate ions (to adjust pH and) b. Endocrine functions: for CHO (carbohydrate) metabolism ...
... j. Choledocho = root for common bile duct 3. Pancreas: accessory organ; behind the stomach; head attached to duodenum, tail reaching to spleen a. Exocrine functions: acini cells secrete digestive juices and bicarbonate ions (to adjust pH and) b. Endocrine functions: for CHO (carbohydrate) metabolism ...
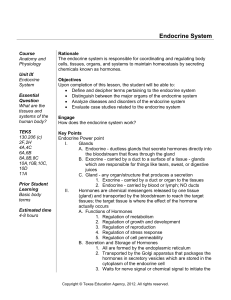
The Encorine System and Homeostasis
... The Endocrine System The hormones of the endocrine system regulate the physiologic and metabolic activities and growth of target cells in the body. Comparison of Control by the Nervous and Endocrine Systems The nervous and endocrine systems act together to coordinate functions of all body systems. N ...
... The Endocrine System The hormones of the endocrine system regulate the physiologic and metabolic activities and growth of target cells in the body. Comparison of Control by the Nervous and Endocrine Systems The nervous and endocrine systems act together to coordinate functions of all body systems. N ...
Tissues, organs and systems (Student Support)
... ■ epithelial tissue, which covers some parts of the body. c) Organs are made of tissues. One organ may contain several tissues. The stomach is an organ that contains: ■ muscular tissue, to churn the contents ■ glandular tissue, to produce digestive juices ■ epithelial tissue, to cover the outside an ...
... ■ epithelial tissue, which covers some parts of the body. c) Organs are made of tissues. One organ may contain several tissues. The stomach is an organ that contains: ■ muscular tissue, to churn the contents ■ glandular tissue, to produce digestive juices ■ epithelial tissue, to cover the outside an ...
Endocrine Glands
... concentrations of sodium ions, blood volume, or blood pressure, or by an increase in blood potassium levels. The three main glucocorticoids are cortisol, corticosterone, and cortisone. The glucocorticoids stimulate the synthesis of glucose and gluconeogenesis (converting a non-carbohydrate to glucos ...
... concentrations of sodium ions, blood volume, or blood pressure, or by an increase in blood potassium levels. The three main glucocorticoids are cortisol, corticosterone, and cortisone. The glucocorticoids stimulate the synthesis of glucose and gluconeogenesis (converting a non-carbohydrate to glucos ...
The Digestive System
... •Secretes a yellowish-brown to greenish substance called bile which is stored in the gall bladder •Stores glucose in the form of glycogen •Secretes bilirubin, a bile pigment that is combined with bile and excreted into the duodenum ...
... •Secretes a yellowish-brown to greenish substance called bile which is stored in the gall bladder •Stores glucose in the form of glycogen •Secretes bilirubin, a bile pigment that is combined with bile and excreted into the duodenum ...
The Digestive System - Northwest Technology Center
... •Secretes a yellowish-brown to greenish substance called bile which is stored in the gall bladder •Stores glucose in the form of glycogen •Secretes bilirubin, a bile pigment that is combined with bile and excreted into the duodenum ...
... •Secretes a yellowish-brown to greenish substance called bile which is stored in the gall bladder •Stores glucose in the form of glycogen •Secretes bilirubin, a bile pigment that is combined with bile and excreted into the duodenum ...
ACTH
... • The endocrine secretions were first identified at the turn of the 20th century. The first to speak about internal secretions, that is, secretions released into the blood circulations, was the French physiologist CE Brown-Sequard (1817-1894). ...
... • The endocrine secretions were first identified at the turn of the 20th century. The first to speak about internal secretions, that is, secretions released into the blood circulations, was the French physiologist CE Brown-Sequard (1817-1894). ...
Endocrine System
... stomach and peritoneal membranes. It is a pink organ with a nodular appearance. It contains both exocrine cells which produce digestive enzymes, and endocrine cells which produce hormones. 1. Glucagon - produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas, glucagon functions to increase blood glucose (sugar) ...
... stomach and peritoneal membranes. It is a pink organ with a nodular appearance. It contains both exocrine cells which produce digestive enzymes, and endocrine cells which produce hormones. 1. Glucagon - produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas, glucagon functions to increase blood glucose (sugar) ...
85KB - NZQA
... down lipids. These are located in similar places with similar optimum pH’s: amylase – mouth and small intestine pH = 7, pepsin in stomach pH = 1-2, and lipase (and trypsin) in small intestine pH = 7-8. • Because enzymes need a specific optimum pH each part of the digestive system has difference in p ...
... down lipids. These are located in similar places with similar optimum pH’s: amylase – mouth and small intestine pH = 7, pepsin in stomach pH = 1-2, and lipase (and trypsin) in small intestine pH = 7-8. • Because enzymes need a specific optimum pH each part of the digestive system has difference in p ...
106KB - NZQA
... down lipids. These are located in similar places with similar optimum pH’s: amylase – mouth and small intestine pH = 7, pepsin in stomach pH = 1-2, and lipase (and trypsin) in small intestine pH = 7-8. • Because enzymes need a specific optimum pH each part of the digestive system has difference in ...
... down lipids. These are located in similar places with similar optimum pH’s: amylase – mouth and small intestine pH = 7, pepsin in stomach pH = 1-2, and lipase (and trypsin) in small intestine pH = 7-8. • Because enzymes need a specific optimum pH each part of the digestive system has difference in ...
01 - ALCA
... - INSERT picture of the placement of the endocrine glands & get two different map/marker colors. - The first color represents the ‘true’ endocrine glands, which means this is the only job…to be an endocrine gland. - The second color represents glands that have other functions, but also have endocrin ...
... - INSERT picture of the placement of the endocrine glands & get two different map/marker colors. - The first color represents the ‘true’ endocrine glands, which means this is the only job…to be an endocrine gland. - The second color represents glands that have other functions, but also have endocrin ...
01 Digestion in oral cavity and stomach
... (by mean of central nerves system) and local – peripheral reflexes, which are closed in stomach walls. Duration of these phase is longer and quantity of juice is much. It has humoral mechanisms too (production of gastrin and histamin. ...
... (by mean of central nerves system) and local – peripheral reflexes, which are closed in stomach walls. Duration of these phase is longer and quantity of juice is much. It has humoral mechanisms too (production of gastrin and histamin. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.