Thyroid hormones
... (hormones) into the blood (Figure 10-1) Hormones perform general functions of communication and control but a slower, longer-lasting type of control than that provided by nerve impulses Cells acted on by hormones are called target cells; organs containing target cells are target organs Slide 2 ...
... (hormones) into the blood (Figure 10-1) Hormones perform general functions of communication and control but a slower, longer-lasting type of control than that provided by nerve impulses Cells acted on by hormones are called target cells; organs containing target cells are target organs Slide 2 ...
Primary adrenal insufficiency “Addison`s disease”, causes, clinical
... - hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and a mild non– anion-gap metabolic acidosis due to the loss of the sodium-retaining and potassium and hydrogen ion-secreting action of aldosterone. - elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine due to the hypovolemia, a decreased glomerular filtration rate, and a ...
... - hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and a mild non– anion-gap metabolic acidosis due to the loss of the sodium-retaining and potassium and hydrogen ion-secreting action of aldosterone. - elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine due to the hypovolemia, a decreased glomerular filtration rate, and a ...
PPT slides handout as PDF 08
... Anterior Pituitary Hormones A. Structure 1. glycoproteins or proteins B. Hormones ...
... Anterior Pituitary Hormones A. Structure 1. glycoproteins or proteins B. Hormones ...
You have completed this lesson regarding the Endocrine System of
... organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. ...
... organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. ...
File
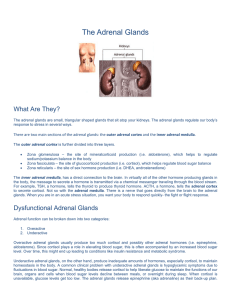
... • There are two parts, each of which makes hormones and has a different function. • The outer part, or the Adrenal Cortex, makes hormones (corticosteroids) that control the salt and water balance in the body, responses to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. • The ...
... • There are two parts, each of which makes hormones and has a different function. • The outer part, or the Adrenal Cortex, makes hormones (corticosteroids) that control the salt and water balance in the body, responses to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. • The ...
Animal Hormones
... • hormone secretion is under multi-level control – hypothalamus collects external information – pituitary responds to hypothalamus – pituitary controls many functions directly or through other endocrine glands – many endocrine functions are controlled by feedback mechanisms – many effectors are cont ...
... • hormone secretion is under multi-level control – hypothalamus collects external information – pituitary responds to hypothalamus – pituitary controls many functions directly or through other endocrine glands – many endocrine functions are controlled by feedback mechanisms – many effectors are cont ...
NewSChapter18
... ▪The gonads- produce various hormones in both males and females. ▫Males- interstitial cells of the testes produce androgens, testosterone is the most important. Nurse cells in the testes secrete inhibin ▫Females- cells surrounding the developing oocyte produce estrogens, the principle estrogen is es ...
... ▪The gonads- produce various hormones in both males and females. ▫Males- interstitial cells of the testes produce androgens, testosterone is the most important. Nurse cells in the testes secrete inhibin ▫Females- cells surrounding the developing oocyte produce estrogens, the principle estrogen is es ...
Thyroid replacement hormone (levothyroxine sodium)
... production of the hormone which is called negative feedback. ...
... production of the hormone which is called negative feedback. ...
Scholars Bulletin Multicystic ovaries in uncontrolled congenital
... management. The association of cystic ovaries enlargement with the primary hypothyroidism is not widely recognized in the medical literature [2-4]. The pathophysiology of this entity is unclear. Various mechanisms have been proposed as to the cause, these include altered estrogen metabolism, hypotha ...
... management. The association of cystic ovaries enlargement with the primary hypothyroidism is not widely recognized in the medical literature [2-4]. The pathophysiology of this entity is unclear. Various mechanisms have been proposed as to the cause, these include altered estrogen metabolism, hypotha ...
Nelson`s syndrome - Dynamic Health
... hormone/endocrine function. Because of this (primary) hypogonadism, individuals will often have a low serum testosterone level but high serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels. Despite this misunderstanding of the term, however, it is true that XXY men also have ...
... hormone/endocrine function. Because of this (primary) hypogonadism, individuals will often have a low serum testosterone level but high serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels. Despite this misunderstanding of the term, however, it is true that XXY men also have ...
The Adrenal Glands
... Overactive adrenal glands usually produce too much cortisol and possibly other adrenal hormones (i.e. epinephrine, aldosterone). Since cortisol plays a role in elevating blood sugar, this is often accompanied by an increased blood sugar level. Over time, this might end up leading to conditions like ...
... Overactive adrenal glands usually produce too much cortisol and possibly other adrenal hormones (i.e. epinephrine, aldosterone). Since cortisol plays a role in elevating blood sugar, this is often accompanied by an increased blood sugar level. Over time, this might end up leading to conditions like ...
Endocrine
... • Usually occurs after age 40 – risk increases with age. • Accounts for over 90% of diabetes cases. ...
... • Usually occurs after age 40 – risk increases with age. • Accounts for over 90% of diabetes cases. ...
Endocrine Dysfunction
... If symptoms occur: Jitteriness Poor feeding Lethargy Seizures Apnea Hypotonia High-pitched cry Bradycardia cyanosis ...
... If symptoms occur: Jitteriness Poor feeding Lethargy Seizures Apnea Hypotonia High-pitched cry Bradycardia cyanosis ...
45-Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Hormone~ chemical signal secreted into body fluids (blood) communicating regulatory messages Target cells~ body cells that respond to hormones Endocrine system/glands~ hormone secreting system/glands (ductless); exocrine glands secrete chemicals (sweat, mucus, enzymes) through ducts Neurosecretory c ...
... Hormone~ chemical signal secreted into body fluids (blood) communicating regulatory messages Target cells~ body cells that respond to hormones Endocrine system/glands~ hormone secreting system/glands (ductless); exocrine glands secrete chemicals (sweat, mucus, enzymes) through ducts Neurosecretory c ...
9 - Mr-Js-Science
... • Results from hyposecretion of all adrenal cortex hormones • Bronze skin tone, muscles are weak, burnout, susceptibility to infection • Hyperaldosteronism • May result from an ACTH-releasing tumor • Excess water and sodium are retained leading to high blood pressure and edema ...
... • Results from hyposecretion of all adrenal cortex hormones • Bronze skin tone, muscles are weak, burnout, susceptibility to infection • Hyperaldosteronism • May result from an ACTH-releasing tumor • Excess water and sodium are retained leading to high blood pressure and edema ...
Endocrine and Reproductive System Web Quest Vanessa Cooper
... hypothalamus is located in the brain and is the main connection between the endocrine and nervous system It controls the pituitary gland by telling it when to make more or to stop producing hormones. • The pituitary gland is very important because it makes hormones that controls other endocrine glan ...
... hypothalamus is located in the brain and is the main connection between the endocrine and nervous system It controls the pituitary gland by telling it when to make more or to stop producing hormones. • The pituitary gland is very important because it makes hormones that controls other endocrine glan ...
Common Endocrine Disorders
... Testosterone Terminology • Testosterone • Total = Free + SHBG-bound + Albumin-Associated • In contrast to cortisol and T4, Free Testosterone is not the best indicator • Rather, “Bioavailable Testosterone” =Total – SHBG-bound = Albumin-Associated + Free ~ Albumin-Associated >> Free) ...
... Testosterone Terminology • Testosterone • Total = Free + SHBG-bound + Albumin-Associated • In contrast to cortisol and T4, Free Testosterone is not the best indicator • Rather, “Bioavailable Testosterone” =Total – SHBG-bound = Albumin-Associated + Free ~ Albumin-Associated >> Free) ...
Year 12 ATAR Human Biology Unit 3 – Endocrine System
... Hormone A chemical secreted by an endocrine gland that affects the funbctioning of a cell or organ. Target Cells A cell whose activity is affected by a particular hormone. Target Organs An organ whose activity is affected by a particular hormone Paracrines Any chemical that is secreted from a cell t ...
... Hormone A chemical secreted by an endocrine gland that affects the funbctioning of a cell or organ. Target Cells A cell whose activity is affected by a particular hormone. Target Organs An organ whose activity is affected by a particular hormone Paracrines Any chemical that is secreted from a cell t ...
Chapter 45 Objective Questions
... 15. Distinguish between alpha and beta cells in the pancreas and explain how their antagonistic hormones (insulin and glucagon) regulate carbohydrate metabolism. 16. Distinguish between type I diabetes mellitus and type II diabetes mellitus. 17. Describe the development of the adrenal medulla. List ...
... 15. Distinguish between alpha and beta cells in the pancreas and explain how their antagonistic hormones (insulin and glucagon) regulate carbohydrate metabolism. 16. Distinguish between type I diabetes mellitus and type II diabetes mellitus. 17. Describe the development of the adrenal medulla. List ...
Notes Chapter 51 Endocrine System
... (2) Hypothyroidism - under activity. Symptoms include lethargy, weight gain, and low heart rate and body temperature, cretinism (form of mental retardation), and goiter (a swelling of the thyroid gland because of lack of iodine). ...
... (2) Hypothyroidism - under activity. Symptoms include lethargy, weight gain, and low heart rate and body temperature, cretinism (form of mental retardation), and goiter (a swelling of the thyroid gland because of lack of iodine). ...
Chapter 13
... gland. (p. 498) The anterior lobe is composed of layers of epithelial tissues grouped around many blood vessels. The epithelial tissues contain five types of secretory cells responsible for hormone production: mammatropes, somatotropes, thyrotropes, corticotropes, and gonadotropes. The posterior pit ...
... gland. (p. 498) The anterior lobe is composed of layers of epithelial tissues grouped around many blood vessels. The epithelial tissues contain five types of secretory cells responsible for hormone production: mammatropes, somatotropes, thyrotropes, corticotropes, and gonadotropes. The posterior pit ...
Adrenal_and_Pituitary_Incidentaloma
... prolactinoma during infertility work up. She wishes to conceive soon. The best next step is A. Start bromocriptine 2.5 mg daily ...
... prolactinoma during infertility work up. She wishes to conceive soon. The best next step is A. Start bromocriptine 2.5 mg daily ...
chapter 16-the endocrine system
... a. Glucagon-an amino acid hormone produced in the alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans. This hormone stimulates the liver to convert glycogen into glucose (Glycogenolysis). b. Insulin-a protein hormone produced in the beta cells of the Islets of Langerhans. This hormone causes a decrease in blood ...
... a. Glucagon-an amino acid hormone produced in the alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans. This hormone stimulates the liver to convert glycogen into glucose (Glycogenolysis). b. Insulin-a protein hormone produced in the beta cells of the Islets of Langerhans. This hormone causes a decrease in blood ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Control of trophic hormone secretion from the adenohypophysis by hypothalamic-releasing hormones (RH) and release-inhibiting hormones (RIH). The releasing and release-inhibiting hormones are synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus, transported by axonal processes, and released into capillary plex ...
... Control of trophic hormone secretion from the adenohypophysis by hypothalamic-releasing hormones (RH) and release-inhibiting hormones (RIH). The releasing and release-inhibiting hormones are synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus, transported by axonal processes, and released into capillary plex ...