Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... • A compound is a distinct substance that is composed of atoms of two or more elements. • Compounds are identified by the number and type of each atom in the simplest unit of the compound. – Molecules or ions ...
... • A compound is a distinct substance that is composed of atoms of two or more elements. • Compounds are identified by the number and type of each atom in the simplest unit of the compound. – Molecules or ions ...
Name Objective 1: Matter and Energy C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... • Cations: ions that have a positive charge – Form when an atom loses electrons ...
... • Cations: ions that have a positive charge – Form when an atom loses electrons ...
Chapter 12
... Often two or more oxoacids have the same cetral atom but a different number of O atoms. Starting with the oxoacids whose names end with “-ic” we use these rules to name these compounds. 1- Adding of one O atom to the _-ic_ acid: The acid is called 菟er..-ic) acid. Adding an O atom to HClO3 changes c ...
... Often two or more oxoacids have the same cetral atom but a different number of O atoms. Starting with the oxoacids whose names end with “-ic” we use these rules to name these compounds. 1- Adding of one O atom to the _-ic_ acid: The acid is called 菟er..-ic) acid. Adding an O atom to HClO3 changes c ...
Element Symbol
... (,,,, and) and the names and symbols for the elements listed in the elements Sodium (Na), Chlorine (Cl), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Carbon (C), and Nitrogen (N). For example, students see the formula H2O, Common names when formulas they should table salt be able to recognize that this is water. simpl ...
... (,,,, and) and the names and symbols for the elements listed in the elements Sodium (Na), Chlorine (Cl), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Carbon (C), and Nitrogen (N). For example, students see the formula H2O, Common names when formulas they should table salt be able to recognize that this is water. simpl ...
Chapter 2 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry This chapter deals with
... ternary acids: acids that contain H, two nonmetal atoms, one of which is usually an O atom (oxoacids)... the H atoms are attached to the O-atoms and not to the nonmetal atom. See Table 2.5 (p. 58) for common ternary acids and their salts that you should know! Note that HCl and H2 S are the only bina ...
... ternary acids: acids that contain H, two nonmetal atoms, one of which is usually an O atom (oxoacids)... the H atoms are attached to the O-atoms and not to the nonmetal atom. See Table 2.5 (p. 58) for common ternary acids and their salts that you should know! Note that HCl and H2 S are the only bina ...
Matter
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
The Nature of Matter
... • General definition: molecules are the smallest part of a compound. • Formed by combining 2 or more of the SAME atom or DIFFERENT atoms • Note: molecules are covalently bonded • Ex: H2, O2, N2 ,H20, C6H12O6 ...
... • General definition: molecules are the smallest part of a compound. • Formed by combining 2 or more of the SAME atom or DIFFERENT atoms • Note: molecules are covalently bonded • Ex: H2, O2, N2 ,H20, C6H12O6 ...
Test #1 Study Guide
... root of the nonmetal, ic to the end of the root name of the nonmetal, and follow that with acid. This only works if the acids are aqueous and not if they are in a gaseous state. If they are in the gaseous state, name them as a molecular compound Oxyacids are acids that contain a hydrogen and an oxya ...
... root of the nonmetal, ic to the end of the root name of the nonmetal, and follow that with acid. This only works if the acids are aqueous and not if they are in a gaseous state. If they are in the gaseous state, name them as a molecular compound Oxyacids are acids that contain a hydrogen and an oxya ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... • When two elements form several compounds, Greek prefixes are used to specify the number of atoms of each element – e.g.; CO : carbon monoxide CO2 : carbon dioxide NO2 : nitrogen dioxide N2O4 : dinitrogen tetroxide • Many covalent compounds containing hydrogen are referred to by their common name – ...
... • When two elements form several compounds, Greek prefixes are used to specify the number of atoms of each element – e.g.; CO : carbon monoxide CO2 : carbon dioxide NO2 : nitrogen dioxide N2O4 : dinitrogen tetroxide • Many covalent compounds containing hydrogen are referred to by their common name – ...
Name: ______ Aim 36: Elements, atoms, compounds and miztures
... New properties are formed. Only metals retain their original properties. New elements are formed. ...
... New properties are formed. Only metals retain their original properties. New elements are formed. ...
form revision a
... Elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together. Elements can be categorised as metals and non-metals. Compounds are substances formed when atoms of two or more elements join together. The name of a comp ...
... Elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together. Elements can be categorised as metals and non-metals. Compounds are substances formed when atoms of two or more elements join together. The name of a comp ...
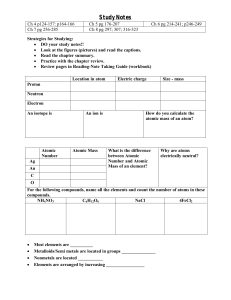
Study Notes
... • DO your study notes!! • Look at the figures (pictures) and read the captions. • Read the chapter summary. • Practice with the chapter review. • Review pages in Reading-Note Taking Guide (workbook) Location in atom ...
... • DO your study notes!! • Look at the figures (pictures) and read the captions. • Read the chapter summary. • Practice with the chapter review. • Review pages in Reading-Note Taking Guide (workbook) Location in atom ...
Document
... 10. How many Chlorine atoms are present in the compound Ca(ClO3)2? 11. How many hydrogen atoms are present in one molecule of ammonium acetate, NH4C2H3O2? 12. What is the name of the compound with the formula NaCl? 13. Why do the noble gases NOT form compounds readily? 14. In a chemical formula, the ...
... 10. How many Chlorine atoms are present in the compound Ca(ClO3)2? 11. How many hydrogen atoms are present in one molecule of ammonium acetate, NH4C2H3O2? 12. What is the name of the compound with the formula NaCl? 13. Why do the noble gases NOT form compounds readily? 14. In a chemical formula, the ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductors? G 7. Which elements are considered poor conductors? F, B, A,H 8. Which element is considered met ...
... H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductors? G 7. Which elements are considered poor conductors? F, B, A,H 8. Which element is considered met ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... Naming Covalent Compounds CO CO2 CO32C2O42 Rules for naming covalent compounds: 1) Write the less electronegative element first. 2) Write the root of the more electronegative element with the -ide ending second. 3) Add prefixes to both indicating the number of atoms of each element ...
... Naming Covalent Compounds CO CO2 CO32C2O42 Rules for naming covalent compounds: 1) Write the less electronegative element first. 2) Write the root of the more electronegative element with the -ide ending second. 3) Add prefixes to both indicating the number of atoms of each element ...
Activity 17 Follow-up
... •An element can have a different number of neutrons, but always has the same number of protons •The atomic weight is the average weight of all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
... •An element can have a different number of neutrons, but always has the same number of protons •The atomic weight is the average weight of all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound ...
... elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound ...
Chemical Reactions
... base and the negative ion of an acid – When an acid and a base are combined, they produce a salt and water • HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O Acid ...
... base and the negative ion of an acid – When an acid and a base are combined, they produce a salt and water • HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O Acid ...
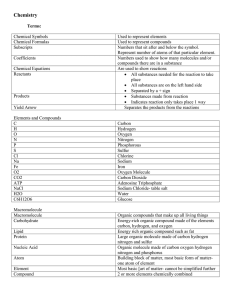
4 Chemistry
... Used to represent elements Used to represent compounds Numbers that sit after and below the symbol. Represent number of atoms of that particular element. Numbers used to show how many molecules and/or compounds there are in a substance Are used to show reactions All substances needed for the react ...
... Used to represent elements Used to represent compounds Numbers that sit after and below the symbol. Represent number of atoms of that particular element. Numbers used to show how many molecules and/or compounds there are in a substance Are used to show reactions All substances needed for the react ...