1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... The endocrine system is responsible for coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained and work for longer periods of time. The endocri ...
... The endocrine system is responsible for coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained and work for longer periods of time. The endocri ...
Unit IV: Regulation Endocrine System
... • pores in cell membrane allow signaling chemicals to move from cell to cell – neurotransmitters • released from neurons to travel across gap to 2nd cell – paracrine (local) hormones • secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells – hormones • chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream ...
... • pores in cell membrane allow signaling chemicals to move from cell to cell – neurotransmitters • released from neurons to travel across gap to 2nd cell – paracrine (local) hormones • secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells – hormones • chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream ...
Endocrine system
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). ...
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). ...
File
... helps prepare the body for “fight or flight” by triggering sympathetic impulses to various organs stimulates epinephrine release, intensifying the sympathetic responses secretes corticotropin-releasing hormones, which sets into motion more lasting responses to stress ...
... helps prepare the body for “fight or flight” by triggering sympathetic impulses to various organs stimulates epinephrine release, intensifying the sympathetic responses secretes corticotropin-releasing hormones, which sets into motion more lasting responses to stress ...
endocrine & nervous systems
... Which substances are found on cell surfaces and respond to nerve and hormone signals? starches and simple sugars subunits of DNA vitamins and minerals receptor molecules ...
... Which substances are found on cell surfaces and respond to nerve and hormone signals? starches and simple sugars subunits of DNA vitamins and minerals receptor molecules ...
The Structure of the Nervous System
... controls the muscles and glands of the internal organs monitors the automatic functions ...
... controls the muscles and glands of the internal organs monitors the automatic functions ...
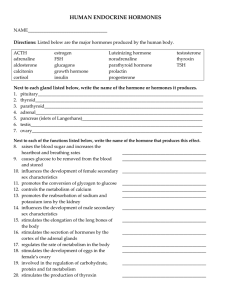
human endocrine hormones
... Next to each gland listed below, write the name of the hormone or hormones it produces. 1. pituitary_________________________________________________________________________ 2. thyroid__________________________________________________________________________ 3. parathyroid___________________________ ...
... Next to each gland listed below, write the name of the hormone or hormones it produces. 1. pituitary_________________________________________________________________________ 2. thyroid__________________________________________________________________________ 3. parathyroid___________________________ ...
Endocrine System
... Reacts to stress, but responds to endocrine rather than nervous system Hypothalamus secretes anterior pituitary releases ACTH adrenal cortex secretes corticosteroids (glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, & mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone) ...
... Reacts to stress, but responds to endocrine rather than nervous system Hypothalamus secretes anterior pituitary releases ACTH adrenal cortex secretes corticosteroids (glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, & mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone) ...
Chemical Mixtures: Parabens and Triclosan
... endocrine system. Further studies need to be conducted in order to determine chemical exposure safety. However, the novelty of the chemicals and their constant use has created an experimental generation for our current society. Taking a preventative approach to these chemicals is recommended as stud ...
... endocrine system. Further studies need to be conducted in order to determine chemical exposure safety. However, the novelty of the chemicals and their constant use has created an experimental generation for our current society. Taking a preventative approach to these chemicals is recommended as stud ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... – An increase in blood sugar level triggers the release of the hormone insulin by the pancreas – the hormone insulin lowers blood sugar level restoring the body to its original blood glucose level in two major ways: • it increases the ability of body cells to take in glucose from the blood • it conv ...
... – An increase in blood sugar level triggers the release of the hormone insulin by the pancreas – the hormone insulin lowers blood sugar level restoring the body to its original blood glucose level in two major ways: • it increases the ability of body cells to take in glucose from the blood • it conv ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... – An increase in blood sugar level triggers the release of the hormone insulin by the pancreas – the hormone insulin lowers blood sugar level restoring the body to its original blood glucose level in two major ways: • it increases the ability of body cells to take in glucose from the blood • it conv ...
... – An increase in blood sugar level triggers the release of the hormone insulin by the pancreas – the hormone insulin lowers blood sugar level restoring the body to its original blood glucose level in two major ways: • it increases the ability of body cells to take in glucose from the blood • it conv ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system control activities of the body?
... Cells must have a RECEPTOR with the matching shape to receive the message. ...
... Cells must have a RECEPTOR with the matching shape to receive the message. ...
A. Nervous Multiple Choice 1. Lipofuscin A. Increases in
... _____ 1. The hypodermis has endocrine functions _____ 2. The posterior lobe does not synthesize oxytocin _____ 3. Thyrotropin promotes secretion of pentaiodothyronine _____ 4. The pituitary gland produces mostly growth hormone _____ 5. Humans use melanocyte-stimulating hormone to darken skin color ...
... _____ 1. The hypodermis has endocrine functions _____ 2. The posterior lobe does not synthesize oxytocin _____ 3. Thyrotropin promotes secretion of pentaiodothyronine _____ 4. The pituitary gland produces mostly growth hormone _____ 5. Humans use melanocyte-stimulating hormone to darken skin color ...
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
Endocrine System
... before the typical adolescent growth spurt • In addition, people who inject AAS run the added risk of contracting or transmitting HIV/AIDS or hepatitis. ...
... before the typical adolescent growth spurt • In addition, people who inject AAS run the added risk of contracting or transmitting HIV/AIDS or hepatitis. ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 4. Hormones are a. chemical signals, b. produced by endocrine glands, c. usually carried in the blood, and d. responsible for specific changes in target cells. 5. Hormones may also be released from specialized nerve cells called neurosecretory cells. B. 26.2 Hormones affect target cells using two ma ...
... 4. Hormones are a. chemical signals, b. produced by endocrine glands, c. usually carried in the blood, and d. responsible for specific changes in target cells. 5. Hormones may also be released from specialized nerve cells called neurosecretory cells. B. 26.2 Hormones affect target cells using two ma ...
File ap notes chapter 45
... Chapter 45: Hormones & the Endocrine System Regulatory systems Nervous system High ...
... Chapter 45: Hormones & the Endocrine System Regulatory systems Nervous system High ...
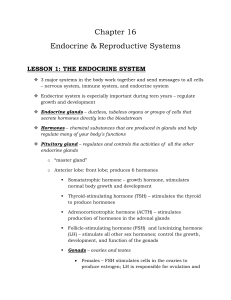
Chapter 16 Notes
... Endocrine & Reproductive Systems LESSON 1: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 3 major systems in the body work together and send messages to all cells – nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system Endocrine system is especially important during teen years – regulate growth and development Endocrine ...
... Endocrine & Reproductive Systems LESSON 1: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 3 major systems in the body work together and send messages to all cells – nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system Endocrine system is especially important during teen years – regulate growth and development Endocrine ...
The Endocrine System
... – Is involved in the regulation of calcium levels in animals by stopping the loss of calcium from bone to the blood ...
... – Is involved in the regulation of calcium levels in animals by stopping the loss of calcium from bone to the blood ...
The Endocrine System
... growth and development, sexual reproduction and mood among other things. Its main function is to establish and keep homeostasis (equilibrium) within the body. ...
... growth and development, sexual reproduction and mood among other things. Its main function is to establish and keep homeostasis (equilibrium) within the body. ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.