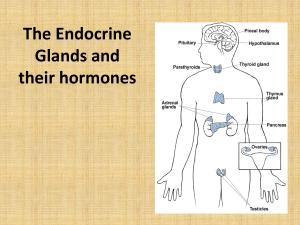
endocrine system
... behaviour. • If oxytocin is given to healthy individuals it seems that brain circuits involved in fear regulation are affected, and there is an increase in trust and generosity. • Kosfiled et al (2005) carried out a clinical trial with 194 male participants and found that those who received a intran ...
... behaviour. • If oxytocin is given to healthy individuals it seems that brain circuits involved in fear regulation are affected, and there is an increase in trust and generosity. • Kosfiled et al (2005) carried out a clinical trial with 194 male participants and found that those who received a intran ...
Endocrine ppt 2014
... C. Unlike exocrine glands that release their products at the body’s surface or into body cavities through ducts, the endocrine glands do not secrete substances into ducts instead their hormones are secreted directly into the surrounding extracellular space & then diffuse into nearby capillaries & a ...
... C. Unlike exocrine glands that release their products at the body’s surface or into body cavities through ducts, the endocrine glands do not secrete substances into ducts instead their hormones are secreted directly into the surrounding extracellular space & then diffuse into nearby capillaries & a ...
The Endocrine System
... Produced by the corpus luteum Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus ...
... Produced by the corpus luteum Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus ...
Chapter 18 Endocrine system
... 1. most endocrine glands are made of glandular epithelium 2. a few glands in the brain are made of modified neurons these are called neurosecretory tissue or neuroendocrine tissue the major endocrine glands include; 1. pituitary 2. thyroid 3. parathyroid 4. adrenal 5. pineal 6. thymus other organs w ...
... 1. most endocrine glands are made of glandular epithelium 2. a few glands in the brain are made of modified neurons these are called neurosecretory tissue or neuroendocrine tissue the major endocrine glands include; 1. pituitary 2. thyroid 3. parathyroid 4. adrenal 5. pineal 6. thymus other organs w ...
ENDOCRINE - Wikispaces
... coordinates & integrates cellular functions at a distance. Maintains homeostasis (internal environment) ...
... coordinates & integrates cellular functions at a distance. Maintains homeostasis (internal environment) ...
The Endocrine System
... Mostly ______________________ (male sex hormones) are made but some __________________ (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
... Mostly ______________________ (male sex hormones) are made but some __________________ (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
The Endocrine System
... With progesterone, estrogens also Promote breast development Regulate menstrual cycle Progesterone Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Helps prepare breasts for lactation ...
... With progesterone, estrogens also Promote breast development Regulate menstrual cycle Progesterone Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Helps prepare breasts for lactation ...
H1 Hormones - TASIS IB Biology
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
Endocrine Glands
... • Function: Increase blood calcium • Function: decrease blood levels by releasing the calcium calcium levels and blood from bones and re-absorbing it phosphate levels (by from the kidneys and intestines. helping them get deposited in bone, and by stimulating excretion of Calcium by kidneys) • Contro ...
... • Function: Increase blood calcium • Function: decrease blood levels by releasing the calcium calcium levels and blood from bones and re-absorbing it phosphate levels (by from the kidneys and intestines. helping them get deposited in bone, and by stimulating excretion of Calcium by kidneys) • Contro ...
Topic: Ecological Issues Aim : How do we take part in solving
... ways that the body can respond. In negative feedback, the body responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Because this tends to keep things constant, it allows us to maintain homeostasis. On the other hand, positive feedback is also possible. This means that if a change occurs in ...
... ways that the body can respond. In negative feedback, the body responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Because this tends to keep things constant, it allows us to maintain homeostasis. On the other hand, positive feedback is also possible. This means that if a change occurs in ...
doc Lecture 5-8
... Type I: Mineracorticoid. High affinity for steroid hormones, stimulates further hormone release, predominantly in the limbic system and HC. Type II: Glucocorticoid. Low affinity, inhibits further hormone release, distributed throughout the brain. Thyroid hormone receptors Located throughout the brai ...
... Type I: Mineracorticoid. High affinity for steroid hormones, stimulates further hormone release, predominantly in the limbic system and HC. Type II: Glucocorticoid. Low affinity, inhibits further hormone release, distributed throughout the brain. Thyroid hormone receptors Located throughout the brai ...
Hormones
... prescribed a synthetic estrogen called diethylstilbestrol (DES) • Daughters of women treated with DES are at higher risk for reproductive abnormalities, including miscarriage, structural changes, and cervical and vaginal cancers • DES is an endocrine disruptor, a molecule that interrupts the normal ...
... prescribed a synthetic estrogen called diethylstilbestrol (DES) • Daughters of women treated with DES are at higher risk for reproductive abnormalities, including miscarriage, structural changes, and cervical and vaginal cancers • DES is an endocrine disruptor, a molecule that interrupts the normal ...
File
... • The process by which our body maintains an internal balance of all body systems. • Usually it is regulated by one of two major systems ...
... • The process by which our body maintains an internal balance of all body systems. • Usually it is regulated by one of two major systems ...
Endocrine Glands and Hormones Hormone
... Placenta – made from fetal and maternal tissue; the chorion produces HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) which causes the anterior pituitary to continue producing LH, which keeps the corpus luteum alive. Pregnancy test. ...
... Placenta – made from fetal and maternal tissue; the chorion produces HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) which causes the anterior pituitary to continue producing LH, which keeps the corpus luteum alive. Pregnancy test. ...
1) - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 18) Kidneys are often difficult to see without dissection because they are surrounded by a layer of fat. What is the significance of this fat? A) It expands for storage of additional urine once the bladder is full; it acts as a sponge. B) It provides cushioning or padding for protection from sudden ...
... 18) Kidneys are often difficult to see without dissection because they are surrounded by a layer of fat. What is the significance of this fat? A) It expands for storage of additional urine once the bladder is full; it acts as a sponge. B) It provides cushioning or padding for protection from sudden ...
Module 6: The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
... The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs Monitors the autonomic functions Controls breathing, blood pressure, and digestive processes Sub-divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems ...
... The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs Monitors the autonomic functions Controls breathing, blood pressure, and digestive processes Sub-divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems ...
File
... • These are chemicals that circulate throughout the blood and exert some measure of control over most every organ and tissue in the body. Types of Hormones Hormones are either Steroidal or Non-steroidal 1. Steroid Hormones- hormones manufactured from fatty substances called cholesterol. 2. These sub ...
... • These are chemicals that circulate throughout the blood and exert some measure of control over most every organ and tissue in the body. Types of Hormones Hormones are either Steroidal or Non-steroidal 1. Steroid Hormones- hormones manufactured from fatty substances called cholesterol. 2. These sub ...
Hormones - Castle High School
... After a stressful stimulus, blood cortisol rises. Cells not critical for action decrease their use of blood glucose—immune system reactions are also blocked. ...
... After a stressful stimulus, blood cortisol rises. Cells not critical for action decrease their use of blood glucose—immune system reactions are also blocked. ...
Hormones - Humble ISD
... After a stressful stimulus, blood cortisol rises. Cells not critical for action decrease their use of blood glucose—immune system reactions are also blocked. ...
... After a stressful stimulus, blood cortisol rises. Cells not critical for action decrease their use of blood glucose—immune system reactions are also blocked. ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.