C H A P T E R T W E N T Y
... activity and inhibiting osteoclast activity. New bone matrix is formed, with simultaneous deposition of calcium salts onto this matrix, and resorption of bone matrix decreases. 7. PTH secretion occurs when the calcium ion concentration in the body decreases. Calcium ions are needed for many body fu ...
... activity and inhibiting osteoclast activity. New bone matrix is formed, with simultaneous deposition of calcium salts onto this matrix, and resorption of bone matrix decreases. 7. PTH secretion occurs when the calcium ion concentration in the body decreases. Calcium ions are needed for many body fu ...
Congenital and Acquired Hypothyroidism
... Hypothyroidism refers to a state of decreased production and release of thyroid hormone from the thyroid gland. It is one of the most common endocrine abnormalities seen by primary care physicians and pediatric endocrinologists alike. Hypothyroidism in childhood may be congenital (present at birth) ...
... Hypothyroidism refers to a state of decreased production and release of thyroid hormone from the thyroid gland. It is one of the most common endocrine abnormalities seen by primary care physicians and pediatric endocrinologists alike. Hypothyroidism in childhood may be congenital (present at birth) ...
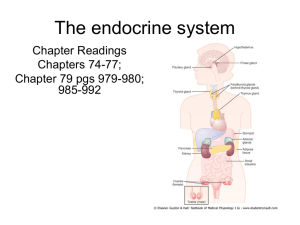
Unit P: Endocrine System
... 2. In preadolescence – overgrowth of long bones leads to excessive tallness B. Dwarfism 1. Hypofunction of pituitary in childhood 2. Small size, but body proportions and intellect normal 3. Rx – early diagnosis, injection of growth hormone C. Hyperthyroidism 1. Overactive thyroid gland 2. Too much t ...
... 2. In preadolescence – overgrowth of long bones leads to excessive tallness B. Dwarfism 1. Hypofunction of pituitary in childhood 2. Small size, but body proportions and intellect normal 3. Rx – early diagnosis, injection of growth hormone C. Hyperthyroidism 1. Overactive thyroid gland 2. Too much t ...
Endocrine System - Mr. Ford`s Class
... • Some glands respond to the changes caused by hormone secretions of other glands ...
... • Some glands respond to the changes caused by hormone secretions of other glands ...
The Endocrine System
... Some hormones are hydrophilic and mix freely with water, so they are easily transported with blood Steroid hormones and thyroid hormones are hydrophobic They must bind to a transport protein in the blood plasma to be carried to their target cells o Transport proteins also protect hormones from ...
... Some hormones are hydrophilic and mix freely with water, so they are easily transported with blood Steroid hormones and thyroid hormones are hydrophobic They must bind to a transport protein in the blood plasma to be carried to their target cells o Transport proteins also protect hormones from ...
Document
... A hormone is a chemical that is secreted into extracellular fluid and carried by the blood -Can therefore act at a distance from source -Only targets with receptor can respond Paracrine regulators do not travel in blood -Allow cells of organ to regulate each other Pheromones are chemicals released i ...
... A hormone is a chemical that is secreted into extracellular fluid and carried by the blood -Can therefore act at a distance from source -Only targets with receptor can respond Paracrine regulators do not travel in blood -Allow cells of organ to regulate each other Pheromones are chemicals released i ...
02 Hypothyroidism
... disease The American Academy of Family Physicians: screening asymptomatic patients older than 60 years The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists: recommends TSH measurements in all women of childbearing age before pregnancy or during the first trimester The US Preventive Task Force ...
... disease The American Academy of Family Physicians: screening asymptomatic patients older than 60 years The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists: recommends TSH measurements in all women of childbearing age before pregnancy or during the first trimester The US Preventive Task Force ...
Subclinical hypothyroidism
... reached by compensatory increasing of TSH secretion and that’s why synthesis and secretion of such level of thyroid hormone that will be enough for organism. It is an asymptomatic state in which serum T4 and free T4 are normal, but serum TSH is elevated. The therapy may provide the patient with more ...
... reached by compensatory increasing of TSH secretion and that’s why synthesis and secretion of such level of thyroid hormone that will be enough for organism. It is an asymptomatic state in which serum T4 and free T4 are normal, but serum TSH is elevated. The therapy may provide the patient with more ...
endocrinology - Endo, GIT, Urology, Cardio - misiek
... Normal Findings: AM: <80 pg/ml or <18 pmol/L (SI units) PM: <50 pg/ml or <11 pmol/L (SI units) Indications: The serum ACTH study is a test of that affords to differentiate the causes of either Cushing's syndrome (overproduction of cortisol) or Addison's disease (underproduction of cortisol). Cortico ...
... Normal Findings: AM: <80 pg/ml or <18 pmol/L (SI units) PM: <50 pg/ml or <11 pmol/L (SI units) Indications: The serum ACTH study is a test of that affords to differentiate the causes of either Cushing's syndrome (overproduction of cortisol) or Addison's disease (underproduction of cortisol). Cortico ...
QA56_7_Armour_thyroid_March_2016_FINAL
... Hypothyroidism is underactivity of the thyroid gland. The aim of treatment is to render the patient ‘euthyroid’, or with a normal thyroid state.(1) The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) recommend that, due to overwhelming evidence supporting its use, levothyroxine (tetra-iodothyronine, or T4) alone ...
... Hypothyroidism is underactivity of the thyroid gland. The aim of treatment is to render the patient ‘euthyroid’, or with a normal thyroid state.(1) The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) recommend that, due to overwhelming evidence supporting its use, levothyroxine (tetra-iodothyronine, or T4) alone ...
The Colorado Thyroid Disease Prevalence Study
... was used to determine which symptoms were independent predictors of a disease state, while controlling for other symptoms. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) areas were calculated using the ROC Curve Analyzer, version 6 (R. Centor and J. Keightley, University of Alabama, Birmingham). The sympto ...
... was used to determine which symptoms were independent predictors of a disease state, while controlling for other symptoms. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) areas were calculated using the ROC Curve Analyzer, version 6 (R. Centor and J. Keightley, University of Alabama, Birmingham). The sympto ...
Ch 17 PowerPoint - Damien Rutkoski
... PTH levels remain fairly constant with age, and lack of estrogen in women make them more vulnerable to bone-demineralizing effects of PTH ...
... PTH levels remain fairly constant with age, and lack of estrogen in women make them more vulnerable to bone-demineralizing effects of PTH ...
Hyperechoic Nodules In Hashimoto`s Thyroiditis
... olgularda saptanan hiperekojen nodüllerin histopatolojik inceleme bulguları eşliğinde radyolojik evaluasyonunu ve bu nodüllerden biopsi gerekliliğini araştırmayı amaçladık. ...
... olgularda saptanan hiperekojen nodüllerin histopatolojik inceleme bulguları eşliğinde radyolojik evaluasyonunu ve bu nodüllerden biopsi gerekliliğini araştırmayı amaçladık. ...
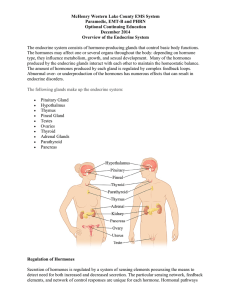
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT
... For example, for the hormones that are regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sent from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland in the form of a “releasing hormone.” This causes the pituitary to secrete a “stimulating hormone” into the circulation. The stimulating hormone then signals the tar ...
... For example, for the hormones that are regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sent from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland in the form of a “releasing hormone.” This causes the pituitary to secrete a “stimulating hormone” into the circulation. The stimulating hormone then signals the tar ...
Print-friendly PDF
... may be required to achieve optimal testosterone levels. There are also alternative options that some naturopathic doctors recommend for boosting testosterone in women. Some naturopaths may suggest the use of chasteberry; however, researchers are not certain how ingredients in this herb work. Also, c ...
... may be required to achieve optimal testosterone levels. There are also alternative options that some naturopathic doctors recommend for boosting testosterone in women. Some naturopaths may suggest the use of chasteberry; however, researchers are not certain how ingredients in this herb work. Also, c ...
64 cases of hyperthyroidism in patients with hepatic dysfunction
... 64 patients with hyperthyroidism with patients with impaired liver function were in the use of antithyroid drugs prior to liver function (detected by automatic biochemical analyzer, in which 18 patients with elevated ALT (accounting for 25.0%, AST increased in 12 cases (accounting for 18.7%, ALP inc ...
... 64 patients with hyperthyroidism with patients with impaired liver function were in the use of antithyroid drugs prior to liver function (detected by automatic biochemical analyzer, in which 18 patients with elevated ALT (accounting for 25.0%, AST increased in 12 cases (accounting for 18.7%, ALP inc ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... Post-1970s: Treat TSH test using T4 only! Doctors often lowered doses by 30-50%! TSH-normalizing T4 dose oftenlower free T3 levels weight gain, persistence of symptoms Thyroid optimization helps most patients with ...
... Post-1970s: Treat TSH test using T4 only! Doctors often lowered doses by 30-50%! TSH-normalizing T4 dose oftenlower free T3 levels weight gain, persistence of symptoms Thyroid optimization helps most patients with ...
3-endocrine
... hormone is released, some of it will bind to receptors in the hypothalamus, and the hypothalamus will stop releasing TSH-RH. Until the receptors in the hypothalamus are bound with the resulting thyroid hormone, the hypothalamus is not satisfied that there is enough thyroid hormone present. The pitui ...
... hormone is released, some of it will bind to receptors in the hypothalamus, and the hypothalamus will stop releasing TSH-RH. Until the receptors in the hypothalamus are bound with the resulting thyroid hormone, the hypothalamus is not satisfied that there is enough thyroid hormone present. The pitui ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... stimulates production of milk after childbirth • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-stimulates growth and secretion of thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-stimulates growth and secretion of adrenal cortex • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)-production of estrogen in females; production of s ...
... stimulates production of milk after childbirth • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-stimulates growth and secretion of thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-stimulates growth and secretion of adrenal cortex • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)-production of estrogen in females; production of s ...
I can File
... hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, and describe how they maintain homeostasis through feedback ...
... hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, and describe how they maintain homeostasis through feedback ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... dwarfism & mental retardation; b. prevention = newborn testing; c. treatment = oral thyroid therapy. ...
... dwarfism & mental retardation; b. prevention = newborn testing; c. treatment = oral thyroid therapy. ...
Dear Sir
... failure of the mitochondria, 53 or Euthyroid hypometabolism.4,5 Ideally, when such tests are undertaken, there is only one cause left, and that cause is treated. If there are none, the list of potential causes should be checked for completeness. Failure to address these issues is a failure to meet t ...
... failure of the mitochondria, 53 or Euthyroid hypometabolism.4,5 Ideally, when such tests are undertaken, there is only one cause left, and that cause is treated. If there are none, the list of potential causes should be checked for completeness. Failure to address these issues is a failure to meet t ...
THYROID HORMONES – An Overview
... Thyroid hormone, the TSH level will be very high in an attempt to stimulate the Thyroid gland to secrete more Thyroid hormone; • Non-Thyroidal illness (NTI): a number of hormones and other agents inhibit the release of TSH; • These include the following: ...
... Thyroid hormone, the TSH level will be very high in an attempt to stimulate the Thyroid gland to secrete more Thyroid hormone; • Non-Thyroidal illness (NTI): a number of hormones and other agents inhibit the release of TSH; • These include the following: ...
Lecture 18, The Endocrine System - Websupport1
... • Glucagon raises blood glucose by increasing the rates of glycogen breakdown and glucose manufacture by the liver • Beta cells secrete insulin • Insulin lowers blood glucose by increasing the rate of glucose uptake and utilization • Delta cells secrete GH-IH • F cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide ...
... • Glucagon raises blood glucose by increasing the rates of glycogen breakdown and glucose manufacture by the liver • Beta cells secrete insulin • Insulin lowers blood glucose by increasing the rate of glucose uptake and utilization • Delta cells secrete GH-IH • F cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide ...
Common Variation in the DIO2 Gene Predicts Baseline
... proportions by 2 test. Initial analysis of the relationship between psychological well-being and genotype at baseline was performed by linear regression, with total GHQ Likert score as the dependent variable and genotype as the independent variable, with each allele considered additive. Logistic re ...
... proportions by 2 test. Initial analysis of the relationship between psychological well-being and genotype at baseline was performed by linear regression, with total GHQ Likert score as the dependent variable and genotype as the independent variable, with each allele considered additive. Logistic re ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.