pituitary tumor - American Academy of Ophthalmology
... common approach is to surgically remove the tumor. With certain types of pituitary tumors (depending on the type of hormone the tumor secretes), medication can be used to shrink tumor cells. This may improve both the visual problems as well as endocrine dysfunction. This type of medicine usually nee ...
... common approach is to surgically remove the tumor. With certain types of pituitary tumors (depending on the type of hormone the tumor secretes), medication can be used to shrink tumor cells. This may improve both the visual problems as well as endocrine dysfunction. This type of medicine usually nee ...
Exam
... a. esophagus b. stomach c. duodenum d. jejunum 34. What function is not associated with the large intestine? a. receives unabsorbed food b. absorbs water c. lubricates feces with mucus d. produces most digestive enzymes 35. What function is not associated with the skin? a. regulates body temperature ...
... a. esophagus b. stomach c. duodenum d. jejunum 34. What function is not associated with the large intestine? a. receives unabsorbed food b. absorbs water c. lubricates feces with mucus d. produces most digestive enzymes 35. What function is not associated with the skin? a. regulates body temperature ...
Endocrine System Study Questions with answers
... hormone? dwarfi sm, a condition caused by hyposecretion of growth hormone in which adult height reaches less than four feet; diabetes insipidus, caused by the hyposecretion of antidiuretic hormone when people experience excessive thirst called polydipsia. ...
... hormone? dwarfi sm, a condition caused by hyposecretion of growth hormone in which adult height reaches less than four feet; diabetes insipidus, caused by the hyposecretion of antidiuretic hormone when people experience excessive thirst called polydipsia. ...
Benign Brain Tumors - American Brain Tumor Association
... Acoustic Neuroma: Lesion Surveillance • For older patients and patients small tumors and limited hearing loss, often observation with serial imaging and audiometry is suggested • Patients should be monitored at least annually for evidence of tumor progression • Rapid tumor growth (>2.5 mm/year) rat ...
... Acoustic Neuroma: Lesion Surveillance • For older patients and patients small tumors and limited hearing loss, often observation with serial imaging and audiometry is suggested • Patients should be monitored at least annually for evidence of tumor progression • Rapid tumor growth (>2.5 mm/year) rat ...
A1981MC82000002
... Substance P and VIP affect smallgut motility and secretion; calcitonin itself increases jejunal water and salt secretion.4 Prostaglandins, calcitonin, serotonin, and substance P and VIP may therefore all play a role in the diarrhoea associated with medullary carcinoma. The fact that one tumour produ ...
... Substance P and VIP affect smallgut motility and secretion; calcitonin itself increases jejunal water and salt secretion.4 Prostaglandins, calcitonin, serotonin, and substance P and VIP may therefore all play a role in the diarrhoea associated with medullary carcinoma. The fact that one tumour produ ...
Lecture 9 th week
... Diseases of the thyroid Hyperthyroidism • Symptoms: 1) a high state of excitability, 2) Intolerance to heat, 3) increased sweating, 4) mild to extreme weight loss (sometimes as much as 100 pounds), 5) varying degrees of diarrhea 6) muscle weakness 7) nervousness or other psychic disorders 8) Extrem ...
... Diseases of the thyroid Hyperthyroidism • Symptoms: 1) a high state of excitability, 2) Intolerance to heat, 3) increased sweating, 4) mild to extreme weight loss (sometimes as much as 100 pounds), 5) varying degrees of diarrhea 6) muscle weakness 7) nervousness or other psychic disorders 8) Extrem ...
Module 09: General Medical Knowledge, Section 2: The
... larynx. This gland secretes thyroxine which controls the rate of metabolism. A lack of thyroxine during infancy can result in physical and mental impairment. Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s disease) is caused by an overactive thyroid gland. The increased level of thyroxine causes increased metabolism whi ...
... larynx. This gland secretes thyroxine which controls the rate of metabolism. A lack of thyroxine during infancy can result in physical and mental impairment. Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s disease) is caused by an overactive thyroid gland. The increased level of thyroxine causes increased metabolism whi ...
Screening for Thyroid Dysfunction: U.S. Preventive Services Task
... methimazole) or nonreversible thyroid ablation therapy (e.g., radioactive iodine or surgery). Treatment is generally recommended for patients with a TSH level that is undetectable or <0.1 mlU/L, particularly those with overt Graves disease or nodular thyroid disease. ...
... methimazole) or nonreversible thyroid ablation therapy (e.g., radioactive iodine or surgery). Treatment is generally recommended for patients with a TSH level that is undetectable or <0.1 mlU/L, particularly those with overt Graves disease or nodular thyroid disease. ...
Hormone
... • The endocrine system assists the nervous system with communication and control of the body • Endocrine glands • They are ductless • They secrete hormones into bloodstream • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Exocrine glands • They have du ...
... • The endocrine system assists the nervous system with communication and control of the body • Endocrine glands • They are ductless • They secrete hormones into bloodstream • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Exocrine glands • They have du ...
Endocrine Physiology
... • Each of the releasing hormones is the first in a three-hormone sequence 1. Hypothalamus releasing hormone 2. Anterior pituitary stimulating hormone 3. Endocrine gland hormone ...
... • Each of the releasing hormones is the first in a three-hormone sequence 1. Hypothalamus releasing hormone 2. Anterior pituitary stimulating hormone 3. Endocrine gland hormone ...
9/13/12 Practice Exam 1
... exam. Use key words and topic sentences to make an outline of a potential essay. Make sure to draw any diagrams required. Note: Most of these questions can most easily be answered with a schematic representation accompanied by brief descriptions of the drawn elements. In other words: if it helps – D ...
... exam. Use key words and topic sentences to make an outline of a potential essay. Make sure to draw any diagrams required. Note: Most of these questions can most easily be answered with a schematic representation accompanied by brief descriptions of the drawn elements. In other words: if it helps – D ...
- ScienceCentral
... hoarseness, and paresthesia. The typical clinical features include a puffy face with edematous eyelids. However, adult patients with isolated TSH deficiency are generally presented with absent or mild symptoms of hypothyroidism [9]. In out patient’s case, she was diagnosed incidentally with hypot ...
... hoarseness, and paresthesia. The typical clinical features include a puffy face with edematous eyelids. However, adult patients with isolated TSH deficiency are generally presented with absent or mild symptoms of hypothyroidism [9]. In out patient’s case, she was diagnosed incidentally with hypot ...
Key Endocrine Glands
... Hypersecretion of T3 and T4– causes Grave's disease: thyroid enlargement (goitre), exopthalmos, increased heat production, heat intolerance, increased sweating, and weight loss despite healthy appetite, tremor and nervousness. ...
... Hypersecretion of T3 and T4– causes Grave's disease: thyroid enlargement (goitre), exopthalmos, increased heat production, heat intolerance, increased sweating, and weight loss despite healthy appetite, tremor and nervousness. ...
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia TYPE 2 Background
... routinely treat patients with a beta-blocker, while others selectively treat patients based on blood pressure control and tachycardia. ...
... routinely treat patients with a beta-blocker, while others selectively treat patients based on blood pressure control and tachycardia. ...
CHAPTER 40 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
... than total T4 and T3. The levels of T4 and T3 are decreased in hypothyroidism, and they are increased in hyperthyroidism. Free T4 and TSH are the most common useful tests in paediatric thyroid disorders, but test results must be interpreted in conjunction with the child’s overall clinical condition. ...
... than total T4 and T3. The levels of T4 and T3 are decreased in hypothyroidism, and they are increased in hyperthyroidism. Free T4 and TSH are the most common useful tests in paediatric thyroid disorders, but test results must be interpreted in conjunction with the child’s overall clinical condition. ...
The Endocrine System
... • --Controls other glands --ACTHadrenal cortex --PRLmammary glands --FSHovaries --LHovaries • --GH is the only hormone with wider effects—causes growth of bone and muscle ...
... • --Controls other glands --ACTHadrenal cortex --PRLmammary glands --FSHovaries --LHovaries • --GH is the only hormone with wider effects—causes growth of bone and muscle ...
The Endocrine System
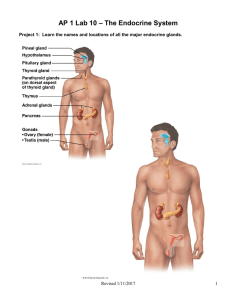
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
Thyroid Hormone Dependent Regulation of Target Genes
... reaction (Q-RT-PCR) was applied. The protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide was used to determine whether the regulation was direct or indirect. A promoter assay further showed that T3 regulation was largely at the level of transcription. Although those genes were isolated from a human tumor cel ...
... reaction (Q-RT-PCR) was applied. The protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide was used to determine whether the regulation was direct or indirect. A promoter assay further showed that T3 regulation was largely at the level of transcription. Although those genes were isolated from a human tumor cel ...
The effect of resistance training on thyroid hormones
... case of disagreement, the differences in the study population, should not be overlooked. Also, based on the findings of the present study, serum TSH concentrations, followed by a work session before the start of training, no significant change. Many researchers, a significant decrease in serum TSH, ...
... case of disagreement, the differences in the study population, should not be overlooked. Also, based on the findings of the present study, serum TSH concentrations, followed by a work session before the start of training, no significant change. Many researchers, a significant decrease in serum TSH, ...
Evaluation of maternal thyroid function during pregnancy
... Background: Maternal thyroid dysfunction has been associated with a variety of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Laboratory measurement of thyroid function plays an important role in the assessment of maternal thyroid health. However, occult thyroid disease and physiologic changes associated with pregnanc ...
... Background: Maternal thyroid dysfunction has been associated with a variety of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Laboratory measurement of thyroid function plays an important role in the assessment of maternal thyroid health. However, occult thyroid disease and physiologic changes associated with pregnanc ...
Evaluation of Autoimmune Thyroid Disease in Patients with Mitral
... Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is common in young adults; thus, the evaluation of its pathogenesis requires attention. A close relationship between the thyroid and heart and the migration of both organs together during ontogenic development may explain the cardiovascular alterations in thyroid diseases ...
... Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is common in young adults; thus, the evaluation of its pathogenesis requires attention. A close relationship between the thyroid and heart and the migration of both organs together during ontogenic development may explain the cardiovascular alterations in thyroid diseases ...
endocrinology
... (4) PTU & methimazole can give rash, arthralgias, agranulocytosis and hepatitis. Methimazole and I121 contraind. in pregnancy. Give I131 if severe hyperthyroidism, goiter 4X normal size, or T3/T4 > 20. For methimazole therapy, get CBC baseline; instruct patient to call if T ^ or ST. Monitor thyroid ...
... (4) PTU & methimazole can give rash, arthralgias, agranulocytosis and hepatitis. Methimazole and I121 contraind. in pregnancy. Give I131 if severe hyperthyroidism, goiter 4X normal size, or T3/T4 > 20. For methimazole therapy, get CBC baseline; instruct patient to call if T ^ or ST. Monitor thyroid ...
AP 1 Lab 10 – The Endocrine System
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
What to eat and how to exercise for your body type
... Thyroid body types need smaller amounts of protein – between 8 and 12 grams per main meal. This is because of their lowered metabolism. It’s important to consume a protein breakfast to establish stable blood sugars all day long. If you consume a grain breakfast, you will notice major cravings later ...
... Thyroid body types need smaller amounts of protein – between 8 and 12 grams per main meal. This is because of their lowered metabolism. It’s important to consume a protein breakfast to establish stable blood sugars all day long. If you consume a grain breakfast, you will notice major cravings later ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.