Bio 100 Guide 24
... – Thyroid hormones affect virtually all the tissues of vertebrates – Thyroid gland produces T4 (thyroxine) and T3 • Play crucial roles in development and maturation – In mammals, thyroid hormones maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, muscle tone, and digestive and reproductive functions ...
... – Thyroid hormones affect virtually all the tissues of vertebrates – Thyroid gland produces T4 (thyroxine) and T3 • Play crucial roles in development and maturation – In mammals, thyroid hormones maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, muscle tone, and digestive and reproductive functions ...
Diabetes Insipidus
... Central DI may occur as a congenital defect (rare and present at birth) or may arise following infections, inflammation, trauma, or tumors of the brain. Nephrogenic DI may also rarely occur as a congenital defect. More often, the nephrogenic form develops after an infection of the kidneys or uterus ...
... Central DI may occur as a congenital defect (rare and present at birth) or may arise following infections, inflammation, trauma, or tumors of the brain. Nephrogenic DI may also rarely occur as a congenital defect. More often, the nephrogenic form develops after an infection of the kidneys or uterus ...
Human Physiology Unit 3A: Endocrine System
... 1. Which part in the brain is known as the “master” gland? 2. True or False: the anterior pituitary is glandular tissue, but the posterior pituitary is neural (NOT glandular) tissue 3. Which part of the pituitary gland stores and releases hormones from the hypothalamus? 4. Which part of the pituitar ...
... 1. Which part in the brain is known as the “master” gland? 2. True or False: the anterior pituitary is glandular tissue, but the posterior pituitary is neural (NOT glandular) tissue 3. Which part of the pituitary gland stores and releases hormones from the hypothalamus? 4. Which part of the pituitar ...
The Endocrine System - Catherine Huff's Site
... • Each follicle consists of globule surrounding thyroid precursor called a colloid. • Only endocrine gland that stores large amounts of hormone precursor for use later. • Produces two hormones: • Thyroid hormone • Calcitonin ...
... • Each follicle consists of globule surrounding thyroid precursor called a colloid. • Only endocrine gland that stores large amounts of hormone precursor for use later. • Produces two hormones: • Thyroid hormone • Calcitonin ...
Chapter 10 Endocrine System
... Figure 19.3 Pituitary Hormones and Their Targets Hypothalamus Indirect Control through Release of Regulatory Hormones Regulatory hormones are released into the hypophyseal portal system for delivery to the enterior lobe of the pituitary ...
... Figure 19.3 Pituitary Hormones and Their Targets Hypothalamus Indirect Control through Release of Regulatory Hormones Regulatory hormones are released into the hypophyseal portal system for delivery to the enterior lobe of the pituitary ...
Animal By-Products
... adrenal gland function; treatment of psoriasis; allergies; mononucleosis and leukemia ...
... adrenal gland function; treatment of psoriasis; allergies; mononucleosis and leukemia ...
guide2409.ppt [Compatibility Mode]
... – Thyroid hormones affect virtually all the tissues of vertebrates – Thyroid gland produces T4 (thyroxine) and T3 • Play crucial roles in development and maturation – In mammals, thyroid hormones maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, muscle tone, and digestive and reproductive functions ...
... – Thyroid hormones affect virtually all the tissues of vertebrates – Thyroid gland produces T4 (thyroxine) and T3 • Play crucial roles in development and maturation – In mammals, thyroid hormones maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, muscle tone, and digestive and reproductive functions ...
For Examiner Only
... irregular tachycardia, fever, tender thyroid as clues. If not recognized and addressed early, patient continues to decompensate: 1) mental status gets worse and patient develops seizures 2) high output heart failure develops and cardiovascular collapse ensues. 2) Begin empiric treatment of thyrotoxi ...
... irregular tachycardia, fever, tender thyroid as clues. If not recognized and addressed early, patient continues to decompensate: 1) mental status gets worse and patient develops seizures 2) high output heart failure develops and cardiovascular collapse ensues. 2) Begin empiric treatment of thyrotoxi ...
Document
... Graves Disease: Immune System sends signals to the thyroid to make more hormone Nervousness Irritability Anxiety Muscle weakness fatigue Increased appetite, Weight loss despite normal eating Sweating, Shaking, heart pounding Hair loss or thinning ...
... Graves Disease: Immune System sends signals to the thyroid to make more hormone Nervousness Irritability Anxiety Muscle weakness fatigue Increased appetite, Weight loss despite normal eating Sweating, Shaking, heart pounding Hair loss or thinning ...
Thyroid hormones
... triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – iodine is needed to synthesize these hormones - calcitonin decrease blood calcium ...
... triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – iodine is needed to synthesize these hormones - calcitonin decrease blood calcium ...
Dr. Dodd`s Take on Heartworm Meds
... after an animal has had 2-5 doses. Occasionally, animals that have been taking monthly preventives for a relatively long time will develop subsequent product intolerance. This usually indicates that some underlying disease process has emerged to explain the problem. Based on cumulative data, it is m ...
... after an animal has had 2-5 doses. Occasionally, animals that have been taking monthly preventives for a relatively long time will develop subsequent product intolerance. This usually indicates that some underlying disease process has emerged to explain the problem. Based on cumulative data, it is m ...
Chalazion - Virginia Eye Center
... About 25 percent of chalazia have no symptoms and will disappear without any treatment. Sometimes, however, a chalazion may become red, swollen and tender. A larger chalazion may also cause blurred vision by distorting the shape of the eye. Occasionally, a chalazion can cause the entire eyelid to sw ...
... About 25 percent of chalazia have no symptoms and will disappear without any treatment. Sometimes, however, a chalazion may become red, swollen and tender. A larger chalazion may also cause blurred vision by distorting the shape of the eye. Occasionally, a chalazion can cause the entire eyelid to sw ...
Lesson 19 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands: Secretion and
... 13. Regulation of calcium and phosphate metabolism. Forms of Ca2+ in blood. Overall calcium homeostasis. Parathyroid hormone. Calcitonin. Vitamin D. Homework ...
... 13. Regulation of calcium and phosphate metabolism. Forms of Ca2+ in blood. Overall calcium homeostasis. Parathyroid hormone. Calcitonin. Vitamin D. Homework ...
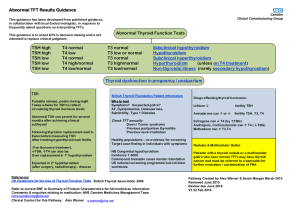
Thyroid Function Test Pathway PDF, 77.29 KB
... + consider initiating Carbimazole after discussion with endocrinology (Warn re rash, agranulocytosis) ...
... + consider initiating Carbimazole after discussion with endocrinology (Warn re rash, agranulocytosis) ...
Endocrine system review Know WHAT THEY DO and WHERE THEY
... 3. ADH(antidiuretic hormone)- Posterior Pituitary- promotes water reabsorption in kidneys 4. Oxytocin- posterior pituitary- involved in milk production and uterine contractions 5. PTH(parathyroid hormone)- Parathyroid- raises blood calcium levels 6. Calcitonin- Thyroid-reduces blood calcium levels 7 ...
... 3. ADH(antidiuretic hormone)- Posterior Pituitary- promotes water reabsorption in kidneys 4. Oxytocin- posterior pituitary- involved in milk production and uterine contractions 5. PTH(parathyroid hormone)- Parathyroid- raises blood calcium levels 6. Calcitonin- Thyroid-reduces blood calcium levels 7 ...
chalazion - Oregon Eye Specialists
... About 25 percent of chalazia have no symptoms and will disappear without any treatment. Sometimes, however, a chalazion may become red, swollen and tender. A larger chalazion may also cause blurred vision by distorting the shape of the eye. Occasionally, a chalazion can cause the entire eyelid to sw ...
... About 25 percent of chalazia have no symptoms and will disappear without any treatment. Sometimes, however, a chalazion may become red, swollen and tender. A larger chalazion may also cause blurred vision by distorting the shape of the eye. Occasionally, a chalazion can cause the entire eyelid to sw ...
2.3 Chemical Communication by Hisrich
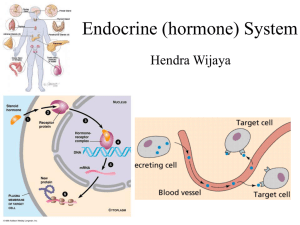
... name for an organ that secretes something) that signals a system to do something. Some hormones are short-term (like adrenalin speeding up heart rate) and some are long term (like growth hormone) The same hormone can be secreted by multiple organs (for example, the ovaries and adrenal glands bot ...
... name for an organ that secretes something) that signals a system to do something. Some hormones are short-term (like adrenalin speeding up heart rate) and some are long term (like growth hormone) The same hormone can be secreted by multiple organs (for example, the ovaries and adrenal glands bot ...
Endocrine
... Follicles are the srucutueal and functional units of thyroid gland , the cells that surrounded the follicles , the follicular cells .in addition to follicular cells , the thyroid gland also contains larger , pale – staining parafollicular cells these cells are found either peripherally in the follic ...
... Follicles are the srucutueal and functional units of thyroid gland , the cells that surrounded the follicles , the follicular cells .in addition to follicular cells , the thyroid gland also contains larger , pale – staining parafollicular cells these cells are found either peripherally in the follic ...
MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA (MEN)
... lips, buccal mucosa). Also seen on eyelids, conjunctivae, cornea and gastrointestinal tract. 2)The oral lesions occur very early in life, often within the first decade or even at birth. 3)The lesions consist of hypertrophied nerve fibers. ...
... lips, buccal mucosa). Also seen on eyelids, conjunctivae, cornea and gastrointestinal tract. 2)The oral lesions occur very early in life, often within the first decade or even at birth. 3)The lesions consist of hypertrophied nerve fibers. ...
Ready for Review - Paramedic EMS Zone
... is impaired. It is characterised by the passage of large quantities of urine containing glucose, significant thirst, and deterioration of body function. In type 1 diabetes, most patients do not produce insulin at all. They require daily injections of supplemental synthetic insulin throughout their l ...
... is impaired. It is characterised by the passage of large quantities of urine containing glucose, significant thirst, and deterioration of body function. In type 1 diabetes, most patients do not produce insulin at all. They require daily injections of supplemental synthetic insulin throughout their l ...
ALS (Lou Gehrig`s Disease)
... the patient experiences atrophy, sometimes leading to the loss of all motor functions, excluding the eyes. Usually, cognitive activity remains functional. The initial symptoms for ALS are usually muscle weakness leading to twitching, cramping, and stiffness. Later on the patient experiences slurred ...
... the patient experiences atrophy, sometimes leading to the loss of all motor functions, excluding the eyes. Usually, cognitive activity remains functional. The initial symptoms for ALS are usually muscle weakness leading to twitching, cramping, and stiffness. Later on the patient experiences slurred ...
Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Anatomy
... - The thyroid gland is situated in the neck right below the thyroid cartilage, at the lower part of the larynx and upper part of the trachea. To the naked eye, it has left and right lobes connected by the isthmus. There may be a pyramidal lobe extending superiorly. - It is supplied by the superior ...
... - The thyroid gland is situated in the neck right below the thyroid cartilage, at the lower part of the larynx and upper part of the trachea. To the naked eye, it has left and right lobes connected by the isthmus. There may be a pyramidal lobe extending superiorly. - It is supplied by the superior ...
PPT #3 Human Body Endocrine System
... • Location: lies deep within the center of the brain • The master control gland !!! • Primary Hormones: No one specific hormone; called the “gate-keeper” regulating the release and inhibition of hormones • Functions: “gate-keeper” role; regulates pituitary ...
... • Location: lies deep within the center of the brain • The master control gland !!! • Primary Hormones: No one specific hormone; called the “gate-keeper” regulating the release and inhibition of hormones • Functions: “gate-keeper” role; regulates pituitary ...
Graves' disease

Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter and Flajani-Basedow-Graves disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in hyperthyroidism and an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, and weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye problems such as bulging, a condition known as Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25% to 80% of people develop eye problems.The exact cause is unclear; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A person is more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one twin is affected there is a 30% chance the other twin will also have the disease. The onset of disease may be triggered by stress, infection, or giving birth. Those with other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to be affected. Smoking increases the risk of disease and may make the eye problems worse. The disorder results from an antibody, called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI), that has a similar effect to thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). These antibodies cause the thyroid gland to produce excess thyroid hormone. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms with blood tests and radioiodine uptake used to confirm the disease. Typically blood tests show a raised T3 and T4, low TSH, increased radioiodine uptake in all areas of the thyroid, and TSI antibodies.There are three treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. Eye problems may require additional treatments.Graves' disease occurs in about 0.5% of people. It occurs about 7.5 times more often in women than men. Often it starts between the ages of forty and sixty. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States (about 50% to 80% of cases). The condition is named after Robert Graves who described it in 1835. A number of prior descriptions also exist.






![guide2409.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001502774_1-62a347145ddf836c3494bd6f5c6ae337-300x300.png)