ECE 4362: Modern Optics for Engineers Credit / Contact hours: Course coordinator:
... Catalog description: Modern concepts in optics related to engineering applications. Geometrical optics, matrix methods in optics; Polarization, interference, coherence, and lasers; Fourier optics, Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction. Pre-requisite(s) or co-requisite: ECE 3323, ECE 3342 Designation: E ...
... Catalog description: Modern concepts in optics related to engineering applications. Geometrical optics, matrix methods in optics; Polarization, interference, coherence, and lasers; Fourier optics, Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction. Pre-requisite(s) or co-requisite: ECE 3323, ECE 3342 Designation: E ...
Negative Refraction Makes a Perfect Lens
... retains its positive sign so that, when both ´ 苷 21 and m 苷 21, the medium is a perfect match to free space and the interfaces show no reflection. At the far boundary there is again an impedance match and the light is perfectly ...
... retains its positive sign so that, when both ´ 苷 21 and m 苷 21, the medium is a perfect match to free space and the interfaces show no reflection. At the far boundary there is again an impedance match and the light is perfectly ...
Negative Refraction Makes a Perfect Lens
... retains its positive sign so that, when both ´ 苷 21 and m 苷 21, the medium is a perfect match to free space and the interfaces show no reflection. At the far boundary there is again an impedance match and the light is perfectly ...
... retains its positive sign so that, when both ´ 苷 21 and m 苷 21, the medium is a perfect match to free space and the interfaces show no reflection. At the far boundary there is again an impedance match and the light is perfectly ...
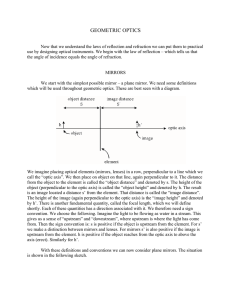
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... Summarizing we say that plane mirrors produce virtual images the same distance behind the mirror that the object is in front. We note also that the image is the same size as the object and erect. ...
... Summarizing we say that plane mirrors produce virtual images the same distance behind the mirror that the object is in front. We note also that the image is the same size as the object and erect. ...
9-26 Geometrical Optics
... Thus a mirror is like a lens with a focal length of f=R/ 2. The sign convention is as follows R>0 if the center of curvature comes before the surface (i.e. if the mirror is concave as seen by the source) so>0 and si>0 if they are on the same side of the mirror ...
... Thus a mirror is like a lens with a focal length of f=R/ 2. The sign convention is as follows R>0 if the center of curvature comes before the surface (i.e. if the mirror is concave as seen by the source) so>0 and si>0 if they are on the same side of the mirror ...
09Optics
... – White light: bright white at central max (m=0) • THEN DISPERSION; SPECTROSCOPIC APPLICATIONS ...
... – White light: bright white at central max (m=0) • THEN DISPERSION; SPECTROSCOPIC APPLICATIONS ...
op_bessel1 - School of Physics
... Irradiance I is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area (radiative flux) incident on a surface and its S.I. unit is watts per square meter [W.m-2]. A more general term for irradiance that you can use is the term intensity. The irradiance I0 of a monochromatic light plane-wave in matter ...
... Irradiance I is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area (radiative flux) incident on a surface and its S.I. unit is watts per square meter [W.m-2]. A more general term for irradiance that you can use is the term intensity. The irradiance I0 of a monochromatic light plane-wave in matter ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction from a circular aperture
... Irradiance I is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area (radiative flux) incident on a surface and its S.I. unit is watts per square meter [W.m-2]. A more general term for irradiance that you can use is the term intensity. The irradiance I0 of a monochromatic light plane-wave in matter ...
... Irradiance I is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area (radiative flux) incident on a surface and its S.I. unit is watts per square meter [W.m-2]. A more general term for irradiance that you can use is the term intensity. The irradiance I0 of a monochromatic light plane-wave in matter ...
PDF
... and the waveguide can be written as µ = −4 j ω ∆ε Ẽ?r · Ẽwg dv, where ∆ε is the difference in the electric permittivities between the antenna metal and the surrounding dielectric, Ẽwg is the three-dimensional electric field mode in the waveguide, and Ẽr is the radiated electric field. Since meta ...
... and the waveguide can be written as µ = −4 j ω ∆ε Ẽ?r · Ẽwg dv, where ∆ε is the difference in the electric permittivities between the antenna metal and the surrounding dielectric, Ẽwg is the three-dimensional electric field mode in the waveguide, and Ẽr is the radiated electric field. Since meta ...
Near-perfect hologram reconstruction with a spatial light modulator
... the two-dimensional Fourier transform of the desired holographic image (optionally superposed with a parabolic phase term to control the imaging distance) onto an incoming wave. However, in practice the “imprinting process” is difficult. One reason for this is that the twodimensional Fourier transfo ...
... the two-dimensional Fourier transform of the desired holographic image (optionally superposed with a parabolic phase term to control the imaging distance) onto an incoming wave. However, in practice the “imprinting process” is difficult. One reason for this is that the twodimensional Fourier transfo ...
2 Modeling and Design of Lens Systems
... Note: If D=0 an other arrangement of the above sequence of four operations is useful propagation to the exact focus point. 3) Transformation of a spherical wave: Consider the illumination of the system with a spherical wave with radius of curvature R1 ...
... Note: If D=0 an other arrangement of the above sequence of four operations is useful propagation to the exact focus point. 3) Transformation of a spherical wave: Consider the illumination of the system with a spherical wave with radius of curvature R1 ...
Magneto Optical Kerr Effect (MOKE)
... drives the electromagnet (by means of a Digital-to-Analog Converter: DAC), records the magnetic field intensity measured by an Hall probe, detects the signals coming from the lock-in amplifier (by an Analog-to-Digital Converter: ADC) and finally displays the hysteresis loop directly on the computer ...
... drives the electromagnet (by means of a Digital-to-Analog Converter: DAC), records the magnetic field intensity measured by an Hall probe, detects the signals coming from the lock-in amplifier (by an Analog-to-Digital Converter: ADC) and finally displays the hysteresis loop directly on the computer ...
speckling in diffraction patterns and optical images formed with the
... and the amplitude of the wave scattered by any lens-element will be determined by the area and curvature of the element. For two facets of the same area, the one of greater curvature will scatter a wave of greater angular aperture, and consequently the energy will be distributed through a larger sol ...
... and the amplitude of the wave scattered by any lens-element will be determined by the area and curvature of the element. For two facets of the same area, the one of greater curvature will scatter a wave of greater angular aperture, and consequently the energy will be distributed through a larger sol ...
Measurement of the 4Pi-confocal point spread function proves 75
... Cambridge, England). The bead was scanned 1.5 pm along the optical axis and 0.8 pm in lateral direction. The smallest resolvable step of the stage was 10 nm, thus providing a high-precision measurement of the PSF. The confocal resolution was determined by using the 4Pi-confocal arrangement with the ...
... Cambridge, England). The bead was scanned 1.5 pm along the optical axis and 0.8 pm in lateral direction. The smallest resolvable step of the stage was 10 nm, thus providing a high-precision measurement of the PSF. The confocal resolution was determined by using the 4Pi-confocal arrangement with the ...
Unit 7 Study Guide
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
CHAPTER 10
... Using partial differential equations, the one-dimensional wave equation can be written as, ...
... Using partial differential equations, the one-dimensional wave equation can be written as, ...
Spectra of Underwater Light-Field Fluctuations in the Photic Zone
... normalizing and displaying the data to maximize its usefulness to the experimental marine biologist. The normalization method we have chosen is very closely tied to a simple experimental arrangement now in use in biological studies at the University of Miami. In this arrangement one focuses the fila ...
... normalizing and displaying the data to maximize its usefulness to the experimental marine biologist. The normalization method we have chosen is very closely tied to a simple experimental arrangement now in use in biological studies at the University of Miami. In this arrangement one focuses the fila ...
The Fractional Fourier Transform. with Applications in Optics and Signal
... covering both theory and applications. As a generalisation of the Fourier transform, the fractional Fourier transform is richer in theory and more flexible in applications but not more costly in implementation. This text consolidates knowledge on the transform and illustrates its application in dive ...
... covering both theory and applications. As a generalisation of the Fourier transform, the fractional Fourier transform is richer in theory and more flexible in applications but not more costly in implementation. This text consolidates knowledge on the transform and illustrates its application in dive ...